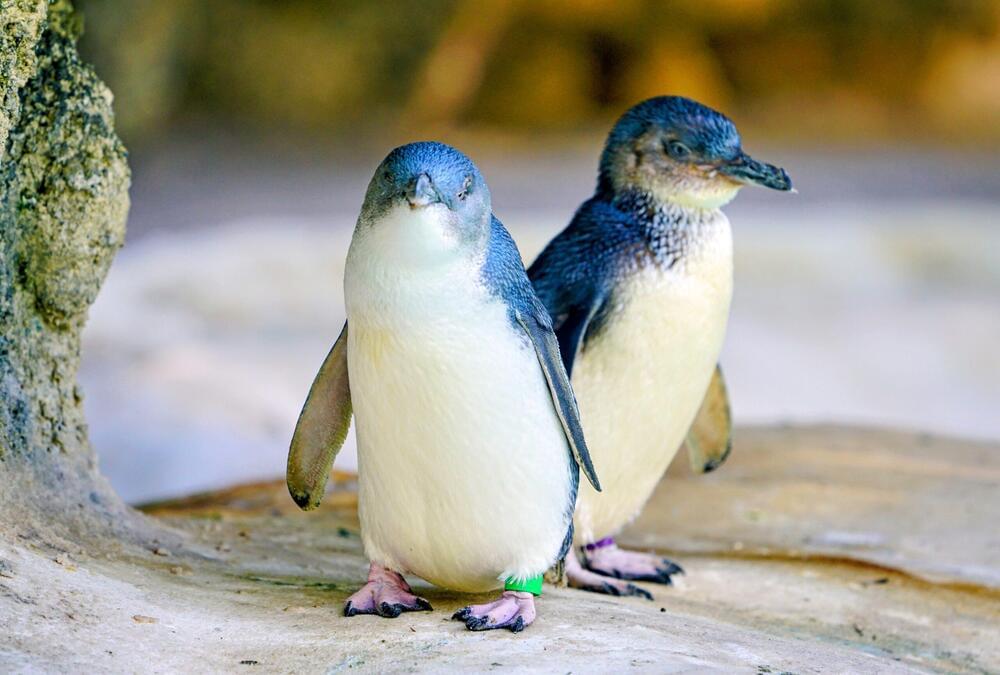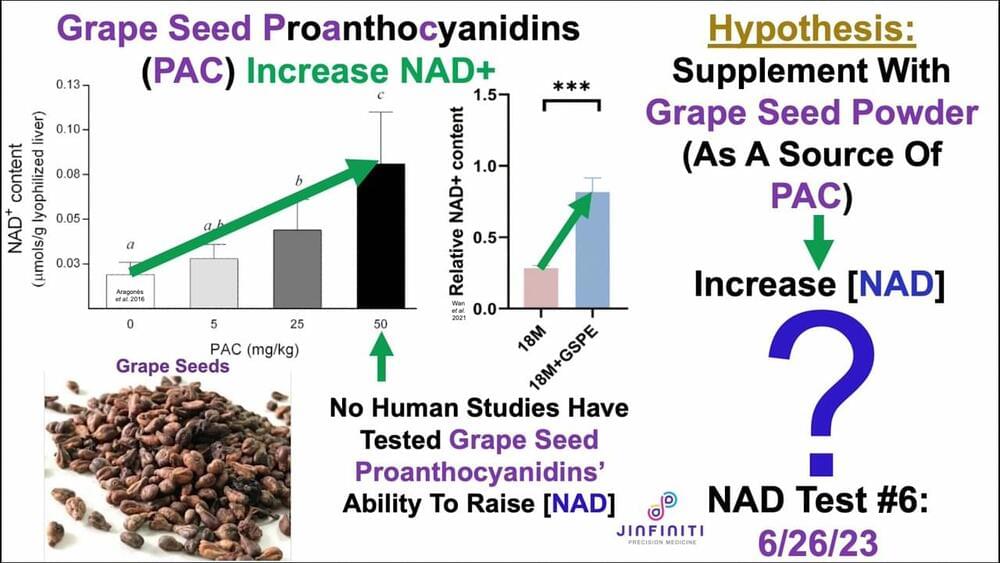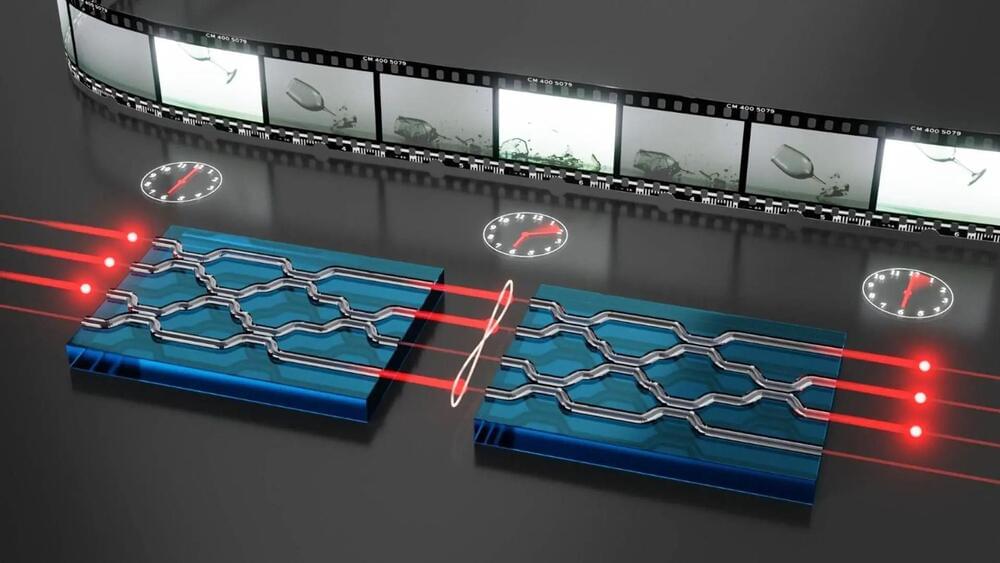
It seems quantum mechanics and thermodynamics cannot be true simultaneously. In a new publication, University of Twente researchers use photons in an optical chip to demonstrate how both theories can be true at the same time.
In quantum mechanics, time can be reversed and information is always preserved. That is, one can always find back the previous state of particles. It was long unknown how this could be true at the same time as thermodynamics. There, time has a direction and information can also be lost. “Just think of two photographs that you put in the sun for too long, after a while you can no longer distinguish them,” explains author Jelmer Renema.
There was already a theoretical solution to this quantum puzzle and even an experiment with atoms, but now the University of Twente (UT) researchers have also demonstrated it with photons. “Photons have the advantage that it is quite easy to reverse time with them,” explains Renema. In the experiment, the researchers used an optical chip with channels through which the photons could pass. At first, they could determine exactly how many photons there were in each channel, but after that, the photons shuffled positions.





 עברית (Hebrew)
עברית (Hebrew)