Artificial neural networks (ANNs) show a remarkable pattern when trained on natural data irrespective of exact initialization, dataset, or training objective; models trained on the same data domain converge to similar learned patterns. For example, for different image models, the initial layer weights tend to converge to Gabor filters and color-contrast detectors. Many such features suggest global representation that goes beyond biological and artificial systems, and these features are observed in the visual cortex. These findings are practical and well-established in the field of machines that can interpret literature but lack theoretical explanations.
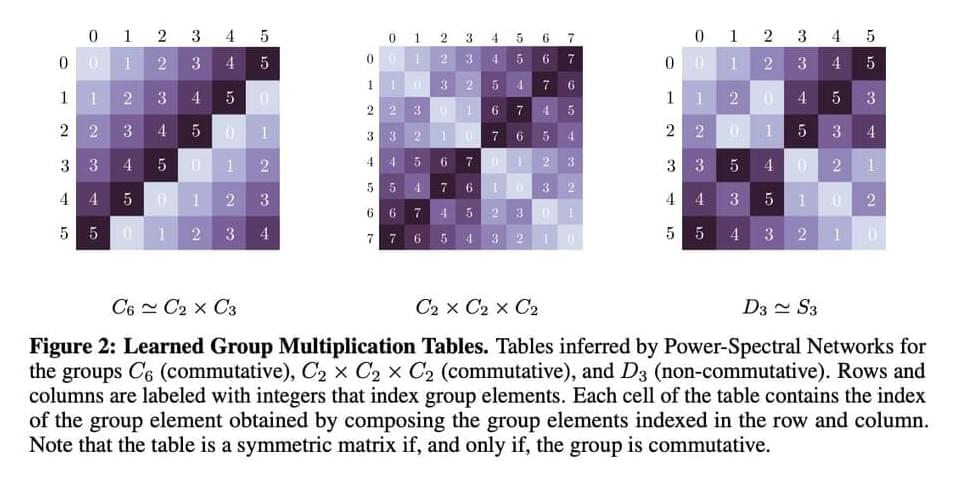
Localized versions of canonical 2D Fourier basis functions are the most observed universal features in image models, e.g. Gabor filters or wavelets. When vision models are trained on tasks like efficient coding, classification, temporal coherence, and next-step prediction goals, these Fourier features pop up in the model’s initial layers. Apart from this, Non-localized Fourier features have been observed in networks trained to solve tasks where cyclic wraparound is allowed, for example, modular arithmetic, more general group compositions, or invariance to the group of cyclic translations.
Researchers from KTH, Redwood Center for Theoretical Neuroscience, and UC Santa Barbara introduced a mathematical explanation for the rise of Fourier features in learning systems like neural networks. This rise is due to the downstream invariance of the learner that becomes insensitive to certain transformations, e.g., planar translation or rotation. The team has derived theoretical guarantees regarding Fourier features in invariant learners that can be used in different machine-learning models. This derivation is based on the concept that invariance is a fundamental bias that can be injected implicitly and sometimes explicitly into learning systems due to the symmetries in natural data.