This study leverages single-nucleus multiomics to map cellular senescence atlas in aging human skeletal muscle and uncovers potential targets and senotherapeutics for treating age-associated sarcopenia.

Australian researchers, including those at the Charles Perkins Centre at the University of Sydney
The University of Sydney is a public research university located in Sydney, New South Wales, Australia. Founded in 1850, it is the oldest university in Australia and is consistently ranked among the top universities in the world. The University of Sydney has a strong focus on research and offers a wide range of undergraduate and postgraduate programs across a variety of disciplines, including arts, business, engineering, law, medicine, and science.
As waiting rooms fill up, doctors get increasingly burned out, and surgeries take longer to schedule and more get canceled, humanoid surgical robots offer a solution. That’s the argument that UC San Diego robotics expert Michael Yip makes in a perspective piece in Science Robotics.
Today’s surgical robots are costly pieces of equipment designed for specialized tasks and can only be operated by highly trained physicians. However, this model doesn’t scale.
Despite the drastic improvements in artificial intelligence and autonomy for industrial and humanoid robots in the past year, these improvements haven’t translated to surgical robots.
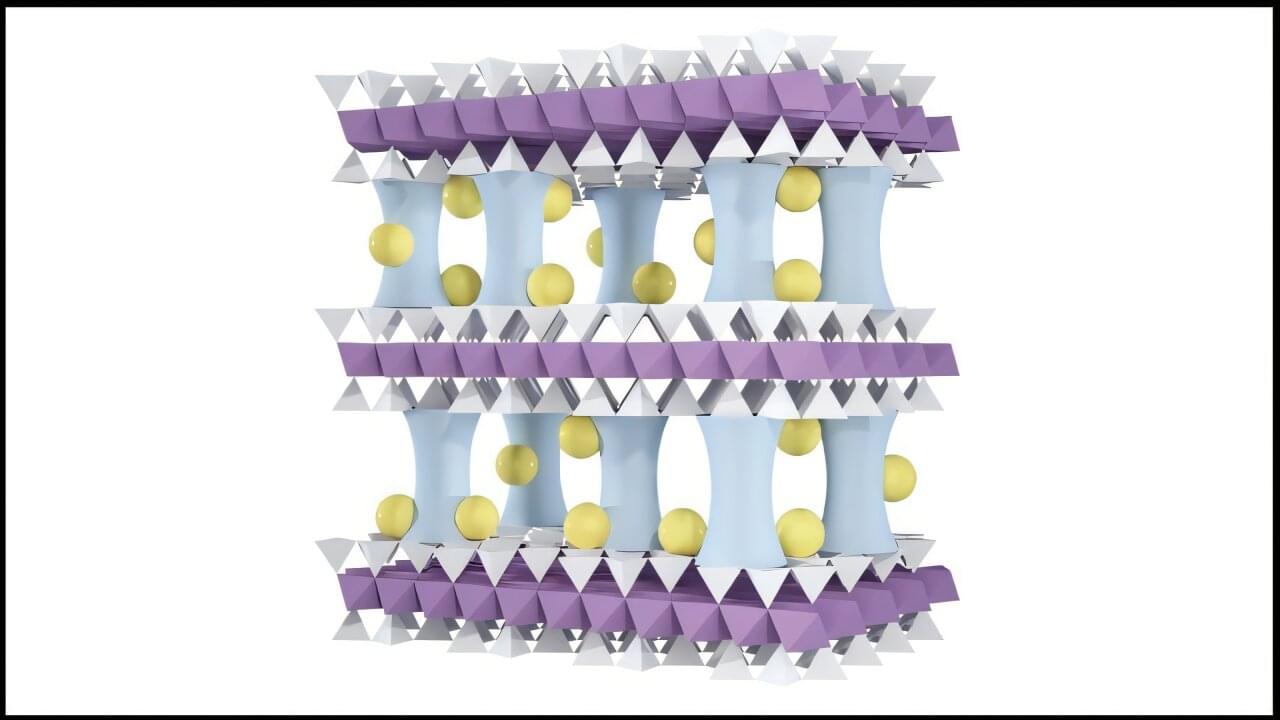
Lithium, the lightest metal on the periodic table, plays a pivotal role in modern life. Its low weight and high energy density make it ideal for electric vehicles, cellphones, laptops and military technologies where every ounce counts. As demand for lithium skyrockets, concerns about supply and reliability are growing.
To help meet surging demand and possible supply chain problems, scientists at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory have developed an innovative membrane technology that efficiently extracts lithium from water. Several team members also hold joint appointments with the Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering (PME) at the University of Chicago.
The findings appear in the journal Advanced Materials.
Researchers in Canada have developed an optical chip that harnesses the power of light to transfer data at unprecedented speed.
The world of wearable technology—such as sensors and energy-producing devices—is expanding, thanks to new research into a unique combination of materials that are flexible, safe to use on or inside the human body, and environmentally friendly.
Dr. Simon Rondeau-Gagné and a team of collaborators and graduate students have used the Canadian Light Source (CLS) at the University of Saskatchewan to show that semiconducting polymers and collagen—the main component of human skin—can be combined to create organic devices “that are more efficient, more conformable and specifically… more green as well.”
Collagen provided both the skin-like rigidity and elasticity (or bendability) the researchers were looking for in “a platform that can be integrated with something like the human body,” said Rondeau-Gagné, an associate professor in the Department of Chemistry and Biochemistry at the University of Windsor.
Join us on Patreon! https://www.patreon.com/MichaelLustgartenPhD
Discount Links/Affiliates:
Blood testing (where I get the majority of my labs): https://www.ultalabtests.com/partners/michaellustgarten.
At-Home Metabolomics: https://www.iollo.com?ref=michael-lustgarten.
Use Code: CONQUERAGING At Checkout.
Clearly Filtered Water Filter: https://get.aspr.app/SHoPY
Epigenetic, Telomere Testing: https://trudiagnostic.com/?irclickid=U-s3Ii2r7xyIU-LSYLyQdQ6…M0&irgwc=1
Use Code: CONQUERAGING
NAD+ Quantification: https://www.jinfiniti.com/intracellular-nad-test/
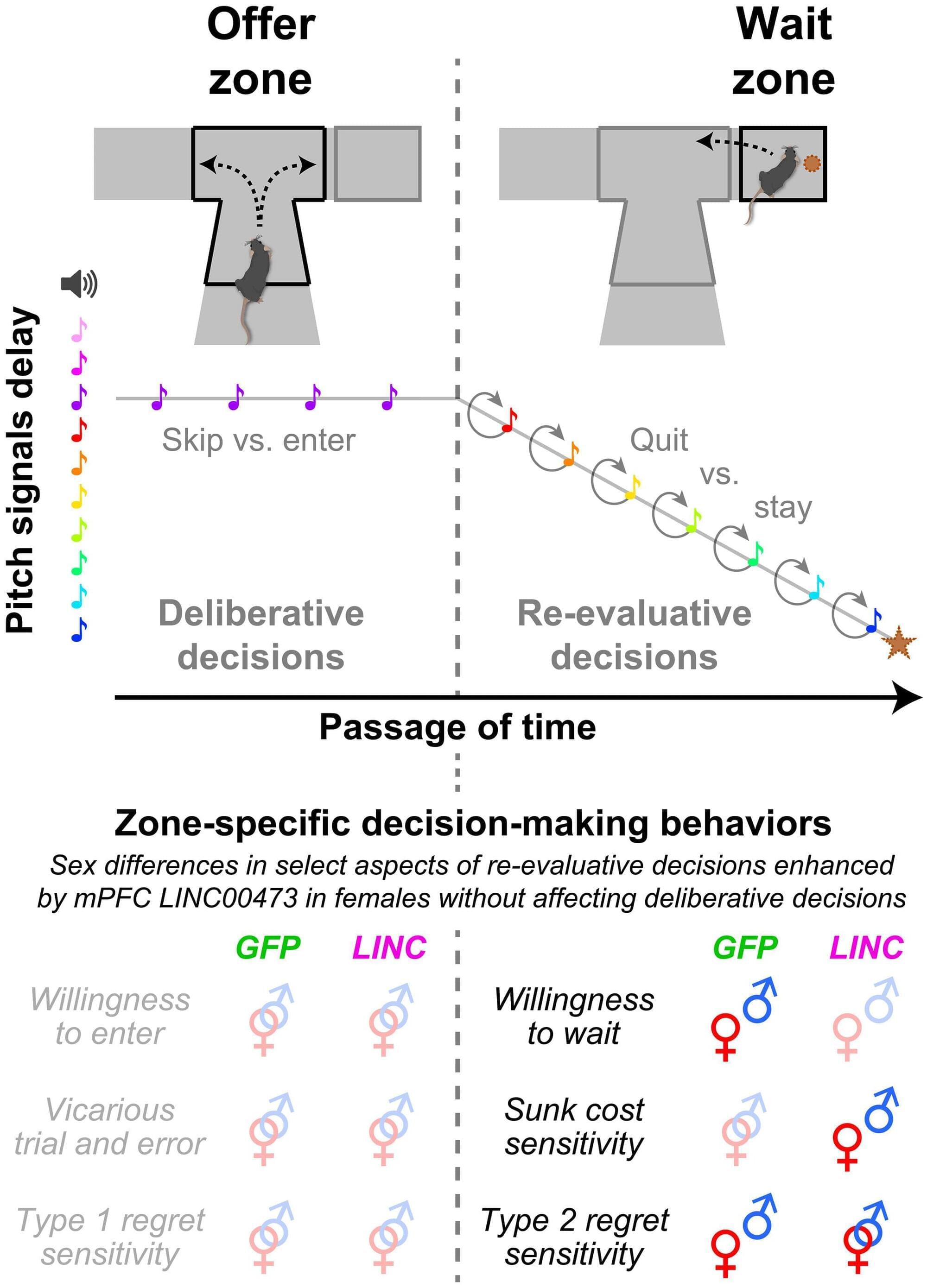
A traditionally overlooked type of RNA plays an important role in promoting resilience to depression—but only in females. According to a new study led by the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, researchers have now discovered a novel role this molecule plays in how the female brain makes decisions. The authors revealed brain-region-specific and sex-dependent effects of this biomarker, translated from humans to animals, on how individuals make only certain types of choices. This study uncovered differences in how each sex decides whether to change their minds after making mistakes, including when to cut their losses and move on as well as how they process regrets about missed opportunities.
This research sheds important light on how specific types of decisions that could negatively impact mood engage the male and female brain in very different ways. The study, published July 11 in Science Advances, using laboratory animal models, helps uncover new biological and psychological mechanisms that may be linked to psychiatric vulnerabilities.
Women are twice as likely to develop depression than men. Furthermore, depression can manifest with different symptoms between the sexes, including alterations in negative rumination on the past. However, the neurobiological mechanisms underlying these differences remain unclear.
Researchers introduce a new class of twistable materials, unlocking unprecedented quantum possibilities. Twisted materials—known as moiré structures—have revolutionized modern physics, emerging as today’s “alchemy” by creating entirely new phases of matter through simple geometric manipulation. The term “moiré” may sound familiar—it describes the st
