The work outlines a detailed blueprint for the creation of an Artificial General Intelligence system with capability at the human level and ultimately beyond, according to the Cog Prime AGI design and the Open Cog software architecture.




This book is a collection of writings by active researchers in the field of Artificial General Intelligence, on topics of central importance in the field. Each chapter focuses on one theoretical problem, proposes a novel solution, and is written in sufficiently non-technical language to be understandable by advanced undergraduates or scientists in allied fields.
This book is the very first collection in the field of Artificial General Intelligence (AGI) focusing on theoretical, conceptual, and philosophical issues in the creation of thinking machines. All the authors are researchers actively developing AGI projects, thus distinguishing the book from much of the theoretical cognitive science and AI literature, which is generally quite divorced from practical AGI system building issues.
Go to https://ground.news/sabine to get 40% off the Vantage plan and see through sensationalized reporting. Stay fully informed on events around the world with Ground News.
Over the past few decades, the idea that gravity is not a fundamental interaction but is instead caused by the increase of entropy has become increasingly popular in the world of physics. Today, we have a paper from a group of physicists who claim that entropic gravity might be the result of space being full of qubits. Let’s take a look.
Paper: https://journals.aps.org/prx/abstract… Check out my new quiz app ➜ http://quizwithit.com/ 📚 Buy my book ➜ https://amzn.to/3HSAWJW 💌 Support me on Donorbox ➜ https://donorbox.org/swtg 📝 Transcripts and written news on Substack ➜ https://sciencewtg.substack.com/ 👉 Transcript with links to references on Patreon ➜ / sabine 📩 Free weekly science newsletter ➜ https://sabinehossenfelder.com/newsle… 👂 Audio only podcast ➜ https://open.spotify.com/show/0MkNfXl… 🔗 Join this channel to get access to perks ➜
/ @sabinehossenfelder #science #sciencenews #physics #gravity.
🤓 Check out my new quiz app ➜ http://quizwithit.com/
📚 Buy my book ➜ https://amzn.to/3HSAWJW
💌 Support me on Donorbox ➜ https://donorbox.org/swtg.
📝 Transcripts and written news on Substack ➜ https://sciencewtg.substack.com/
👉 Transcript with links to references on Patreon ➜ / sabine.
📩 Free weekly science newsletter ➜ https://sabinehossenfelder.com/newsle…
👂 Audio only podcast ➜ https://open.spotify.com/show/0MkNfXl…
🔗 Join this channel to get access to perks ➜
/ @sabinehossenfelder.
#science #sciencenews #physics #gravity

The prevalence of Alzheimer’s disease (AD) is approximately two times higher in African Americans (AA) compared to white/European-ancestry (EA) individuals living in the U.S. Some of this is due to social determinants of health such as disparities in health care access and quality of education, biases in testing and higher rates of AD risk factors such as cardiovascular disease and diabetes in those who identify as African American.
Although many studies have examined differences in gene expression (a measure of the amount of protein encoded by a gene) in brain tissue from AD cases and controls in EA or mixed ancestry cohorts, the number of AA individuals in these studies was unspecified or too small to identify significant findings within this group alone.
In the largest AD study conducted in brain tissue from AA donors, researchers from Boston University Chobanian & Avedisian School of Medicine have identified many genes, a large portion of which had not previously been implicated in AD by other genetic studies, to be significantly more or less active in tissue from AD cases compared to controls. The most notable finding was a 1.5 fold higher level of expression of the ADAMTS2 gene in brain tissue from those with autopsy-confirmed AD.
One of the newest weapons that scientists have developed against cancer is a type of engineered immune cell known as CAR-NK (natural killer) cells. Similar to CAR-T cells, these cells can be programmed to attack cancer cells.
MIT and Harvard Medical School researchers have now come up with a new way to engineer CAR-NK cells that makes them much less likely to be rejected by the patient’s immune system, which is a common drawback of this type of treatment.
The new advance may also make it easier to develop “off-the-shelf” CAR-NK cells that could be given to patients as soon as they are diagnosed. Traditional approaches to engineering CAR-NK or CAR-T cells usually take several weeks.
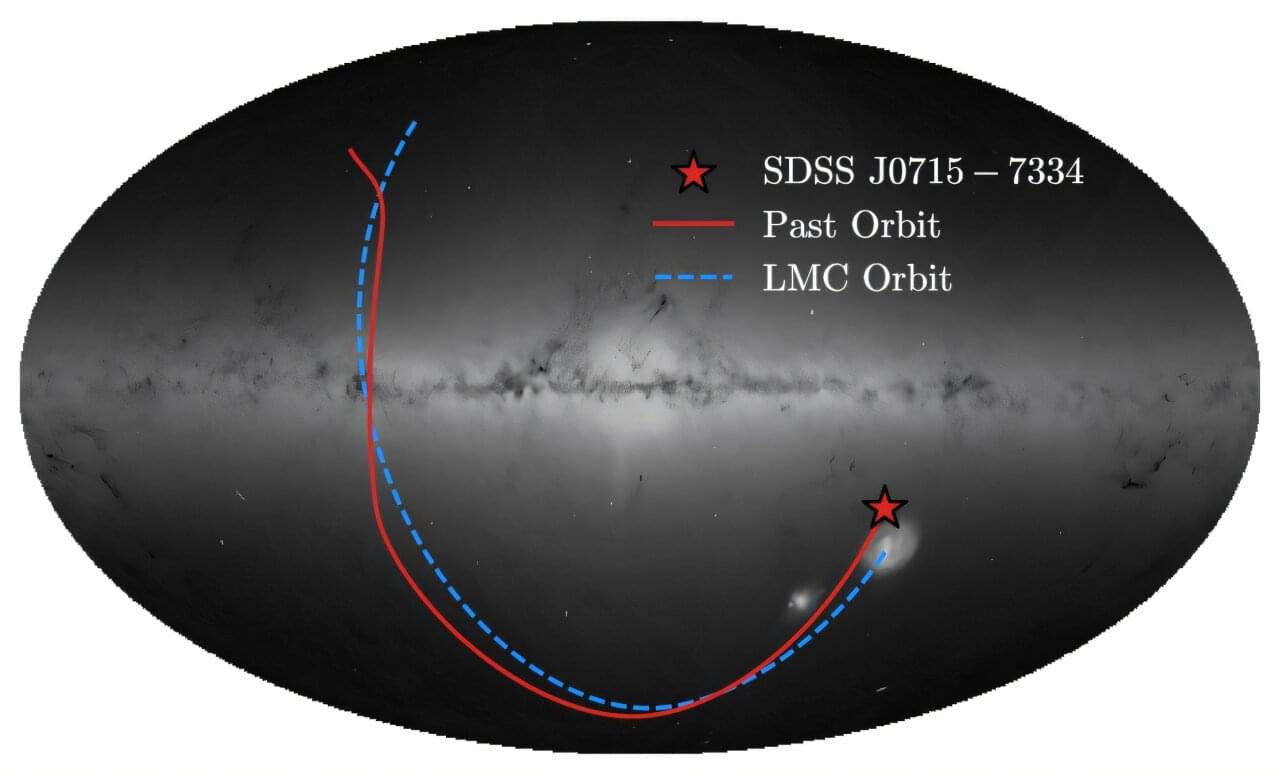
Not all stars are created equally. Astronomers believe that the first stars to form after the Big Bang were mostly made of only hydrogen and helium with trace amounts of lithium, as the heavier elements formed later on by nuclear fusion inside the stars. When these stars went supernova, heavier elements spread throughout space and formed more stars. Each successive generation contained more heavy elements, and these elements also became successively heavier.
While most stars still contain mostly hydrogen and helium, they now contain many heavy elements as well, especially as they get older. These elements show up in spectrographic data when astronomers gather light from these distant stars. Stars are considered “pristine” when the data shows a lack of heavy elements—meaning they are likely very rare, older stars from earlier generations. And now, a group of astronomers, led by Alexander Ji from the University of Chicago, believe they have found the most pristine star on record. The group has documented their findings on the arXiv preprint server.
The star, referred to as SDSS J0715-7334, is a red giant purported to have the lowest metallicity—or heavy element content—ever found. The team’s detailed spectral and chemical analysis shows that SDSS J0715-7334 has a total metallicity “Z” of less than 7.8 × 10-7. This is compared to the next lowest metallicity star currently known, a star located in the Milky Way with a total metallicity of around 1.4 × 10-6.

People who sleep poorly are more likely than others to have brains that appear older than they actually are. This is according to a comprehensive brain imaging study from Karolinska Institutet, published in the journal eBioMedicine. The paper is titled “Poor sleep health is associated with older brain age: the role of systemic inflammation.”
Increased inflammation in the body may partly explain the association.
Poor sleep has been linked to dementia, but it is unclear whether unhealthy sleep habits contribute to the development of dementia or whether they are rather early symptoms of the disease.