Магнитная буря, накрывшая Землю, из средней стала сильной, сообщил ведущий специалист центра погоды “Фобос” Михаил Леус в Telegram-канале. РИА Новости, 12.08.
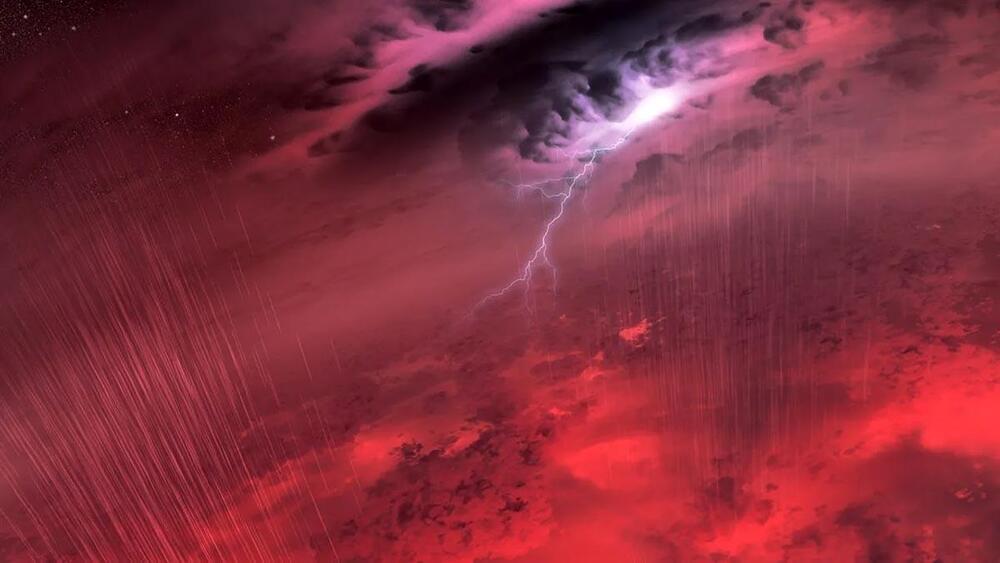




Astronomers used the James Webb Space Telescope to create a comprehensive weather report for two brown dwarfs located about six light years from Earth.
Researchers have created the most detailed weather report ever for two distant worlds beyond our own solar system.
The international study – the first of its kind – reveals the extreme atmospheric conditions on the celestial objects, which are swathed in swirling clouds of hot sand amid temperatures of 950°C (1750°F).

Quantum computers have the potential of outperforming conventional computers on some practically relevant information processing problems, possibly even in machine learning and optimization. Yet their large-scale deployment is not yet feasible, largely due to their sensitivity to noise, which causes them to make errors.

The Russian government and IT organizations are the target of a new campaign that delivers a number of backdoors and trojans as part of a spear-phishing campaign codenamed EastWind.
The attack chains are characterized by the use of RAR archive attachments containing a Windows shortcut (LNK) file that, upon opening, activates the infection sequence, culminating in the deployment of malware such as GrewApacha, an updated version of the CloudSorcerer backdoor, and a previously undocumented implant dubbed PlugY.
PlugY is “downloaded through the CloudSorcerer backdoor, has an extensive set of commands and supports three different protocols for communicating with the command-and-control server,” Russian cybersecurity company Kaspersky said.
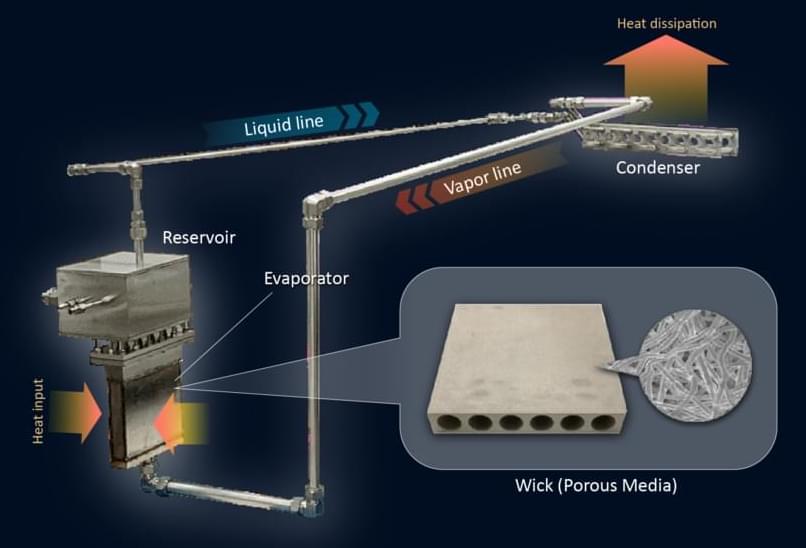
This LHP (loop heat pipe) is unprecedented in transporting such a large amount of heat without electricity.
In a groundbreaking development, scientists at Nagoya University in Japan have created the world’s most powerful loop heat pipe (LHP), capable of transporting an astounding 10 kilowatts of heat without using any electricity. This innovation promises to revolutionize energy efficiency across multiple industries, from electric vehicles to data centers.
Understanding Loop Heat Pipes
Before delving into the significance of this breakthrough, let’s explore what loop heat pipes are and how they work. LHPs are passive heat transfer devices that use the principles of phase change and capillary action to move heat from one place to another. They consist of an evaporator, a condenser, and connecting pipes filled with a working fluid.

Link to newsletter:
Dear Subscribers, please see the latest Security & tech Insights newsletter covering emerging issues, trends and potential solutions in the world of cybersecurity. Thanks for reading and stay safe! Best, Chuck Brooks PS checkout my new book on Amazon: Inside Cyber: How AI, 5G, and Quantum Computing Will Transform Privacy and Our Security Amazon.com : Inside Cyber: How AI, 5G, and Quantum Computing Will Transform Privacy and Our Security: 9781394254941: Brooks, Chuck: Books.