https://x.com/clashreport/status/1825777230569423302
This renowned Chinese creator’s tank simulator just got better.
https://x.com/clashreport/status/1825777230569423302
This renowned Chinese creator’s tank simulator just got better.
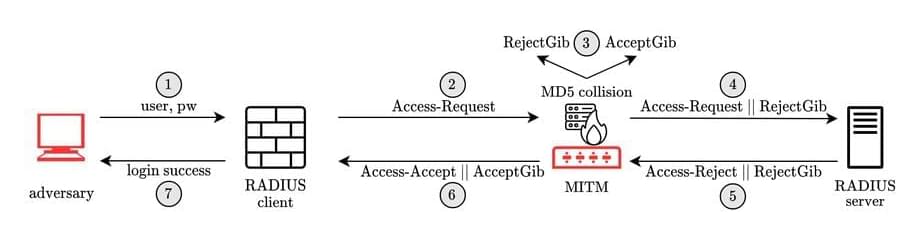
A widely used security protocol that dates back to the days of dial-up internet has vulnerabilities that could expose large numbers of networked devices to an attack and allow an attacker to gain control of traffic on an organization’s network.
A research team led by University of California San Diego computer scientists investigated the Remote Authentication Dial-In User Service (RADIUS) protocol and found a vulnerability they call Blast-RADIUS that has been present for decades. RADIUS, designed in 1991, allows networked devices such as routers, switches or mobile roaming gear to use a remote server to validate login or other credentials.
This is a common set-up in enterprise and telecommunications networks because it allows credentials to be centrally managed. As a result, RADIUS is a critical part of modern telecommunications and enterprise networks; in large enterprises, it may control access to tens of thousands of switches.


GPT-5, or ChatGPT 5, is the next big update everyone’s waiting for. But what features will it bring and when will is it expected to release?

Innovative diode laser spectroscopy provides precise monitoring of the color changes in the sweeping laser at each moment, establishing new benchmarks for frequency metrology and practical applications.
Since the laser’s debut in the 1960s, laser spectroscopy has evolved into a crucial technique for investigating the intricate structures and behaviors of atoms and molecules. Advances in laser technology have significantly expanded its potential. Laser spectroscopy primarily consists of two key types: frequency comb-based laser spectroscopy and tunable continuous-wave (CW) laser spectroscopy.
Comb-based laser spectroscopy enables extremely precise frequency measurements, with an accuracy of up to 18 digits. This remarkable precision led to a Nobel Prize in Physics in 2005 and has applications in optical clocks, gravity sensing, and the search for dark matter. Frequency combs also enable high-precision, high-speed broadband spectroscopy because they combine large bandwidth with high spectral resolution.

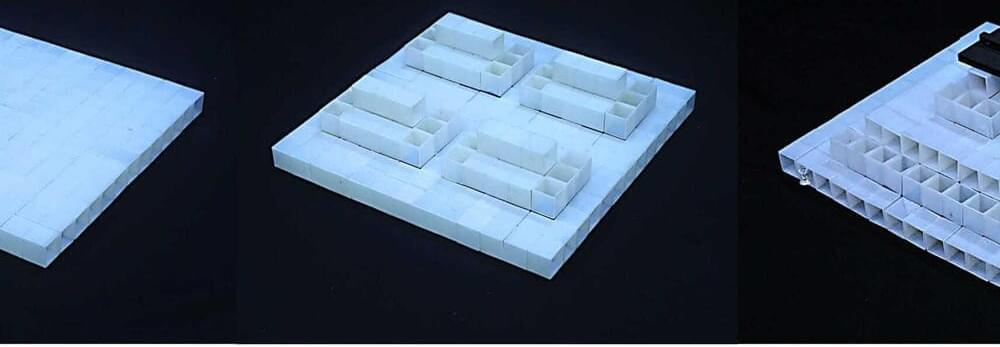
A new mechanical computer made from an array of rigid, interconnected plastic cubes can store, retrieve and erase data simply by stretching the array and manipulating the position of the cubes. The device’s construction is inspired by the ancient Japanese art of paper cutting, or kirigami, and its designers at North Carolina State University in the US say that more advanced versions could be used in stable, high-density memory and logic computing; in information encryption and decryption; and to create displays based on three-dimensional units called voxels.
Mechanical computers were first developed in the 19th century and do not contain any electronic components. Instead, they perform calculations with levers and gears. We don’t often hear about such contraptions these days, but researchers led by NC State mechanical and aerospace engineer Jie Yin are attempting to bring them back due to their stability and their capacity for storing complex information.
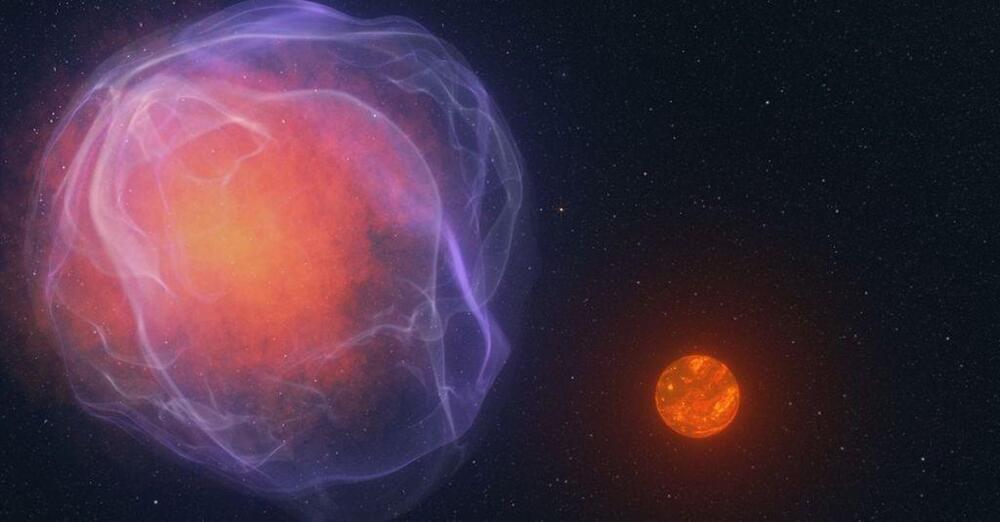
Most familiar stars peacefully orbit the center of the Milky Way. But citizen scientists working on NASA’s Backyard Worlds: Planet 9 project have helped discover an object moving so fast that it will escape the Milky Way’s gravity and shoot into intergalactic space. This hypervelocity object is the first such object found with the mass similar to or less than that of a small star.