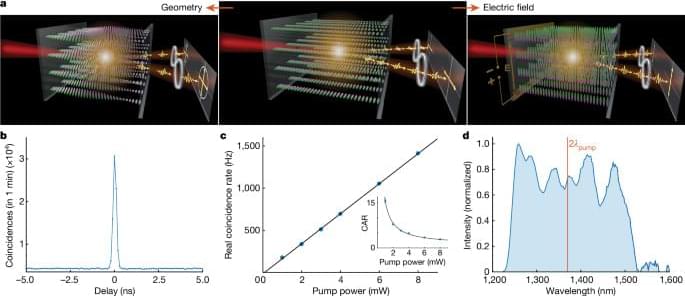
One of the most remarkable features discovered in these experiments is the unprecedented tunability of the two-photon state, achieved by manipulating the LC molecular orientation. By re-orienting the molecules through the application of an electric field, we can dynamically switch the polarization state of the generated photon pairs. This level of control over the photon pairs’ polarization properties is a crucial advancement, offering opportunities for quantum-state engineering in the sources with pixelwise-tunable optical properties, both linear and nonlinear.
Alternatively, we can manipulate the polarization state by implementing a molecular orientation twist along the sample. This approach adds versatility to the design and utilization of LC-based photon-pair sources. Moreover, a strong twist along the sample can markedly increase the efficiency of a macroscopically large source, similar to the periodic poling of bulk crystals and waveguides, but much simpler technologically, as the structure is self-assembled and may be tuned with temperature and electric field39. Owing to their nonlinear coefficient comparable to the best nonlinear crystals, such as lithium niobate, and high damage threshold, FNLCs are perfectly suitable for practical applications. Furthermore, high-quality LC devices such as LC displays are made on an industrial scale, which, combined with our work, opens a path to scalable and cheap production of quantum light sources while exceeding the existing ones in efficiency and functionality.
In the future, the electric-field tuning could be expanded to multi-pixel devices, which have the potential to generate tunable high-dimensional entanglement and multiphoton states. Furthermore, FNLCs can self-assemble in a variety of complex topological structures, which are expected to emit photon pairs in complex, spatially varying beams (structured light), such as vector and vortex beams40. The liquid nature of FNLCs opens a path to their integration with existing optical platforms such as fibres41, waveguides42 and metasurfaces43.