Vo1d malware infects 1.3M Android TV boxes in 197 countries. Learn about this new backdoor threat and how it compromises device security.




The FBI says that 2023 was a record year for cryptocurrency fraud, with total losses exceeding $5.6 billion, based on nearly 70,000 reports received through the Internet Crime Complaint Center (IC3).
This marks a 45% increase in losses compared to the previous year, driven primarily by investment fraud, which accounted for 71% of the total cryptocurrency losses. Other types of fraud contributing to the statistics include tech support scams, call center fraud, and government impersonation.
The vast majority of the reported losses ($4.8 billion) were incurred by U.S. citizens, followed by Cayman Islands ($196M), Mexico ($127M), Canada ($72M), the UK ($59M), India ($44M), and Australia ($25M).
A novel acoustic attack named ‘PIXHELL’ can leak secrets from air-gapped and audio-gapped systems, and without requiring speakers, through the LCD monitors they connect to.
In a PIXHELL attack, malware modulates the pixel patterns on LCD screens to induce noise in the frequency range of 0–22 kHz, carrying encoded signals within those acoustic waves that can be captured by nearby devices such as smartphones.
The researchers’ tests showed that data exfiltration is possible at a maximum distance of 2 meters (6.5 ft), achieving a data rate of 20 bits per second (bps).


“Traditional measures of chirality have struggled to identify the concentration of right-and left-handed molecules in samples containing almost equal amounts of both,” says physicist Nicola Mayer, from the Max Born Institute.
“With our new method, a tiny excess in the concentration of either mirror twin can be detected, possibly enough to make a life-changing difference.”
We’re not sure how chirality first emerged, but it may have originated from deep space, before going on to play a profound role in so many different aspects of life on Earth. Having instruments that can better detect chiral molecules would be a major step forward.
ChatGPT creator OpenAI on Thursday released a new series of artificial intelligence models designed to spend more time thinking—in hopes that generative AI chatbots provide more accurate and beneficial responses.
The new models, known as OpenAI o1-Preview, are designed to tackle complex tasks and solve more challenging problems in science, coding and mathematics, something that earlier models have been criticized for failing to provide consistently.
Unlike their predecessors, these models have been trained to refine their thinking processes, try different methods and recognize mistakes, before they deploy a final answer.

Dr. Tim Brown.
Taking…
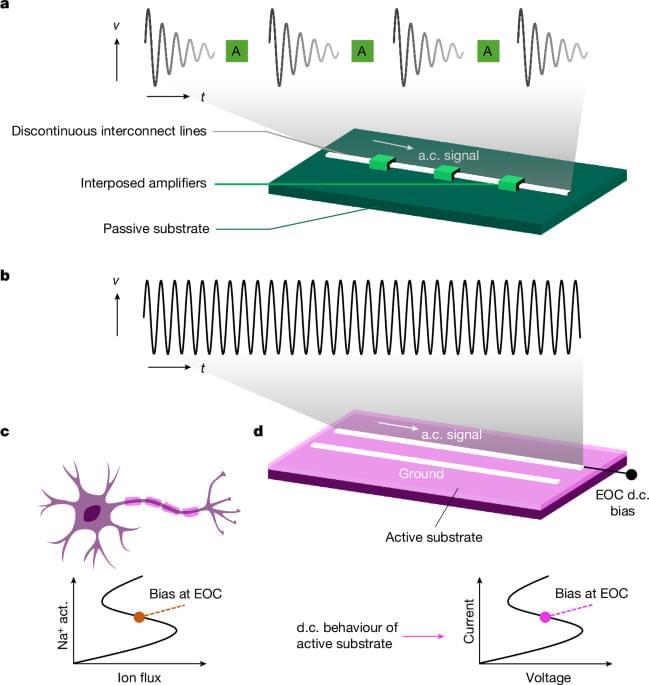
Axon-mimicking Materials for Computing https://engineering.tamu.edu/news/2024/09/axon-mimicking-mat…uting.html.
Biology does things differently: some signals in the brain are also transmitted across centimeter distances, but through…
A method using semi-stable edge of chaos in LaCoO3 enables continuous signal amplification in metallic conductors without separate amplifiers, potentially revolutionizing electronic chip design.
