Cell surface proteins play a crucial role in cell communication and in sensing changes in the extracellular environment.
Professor Akihiko Ito and Dr. Fuka Takeuchi from the Department of Pathology at Kindai University Faculty of Medicine, Japan, set out to seek answers to this critical question. They investigated the impact of anti-CADM1 antibodies on neuronal activity, and their findings were made available online on 22 August 2024 and published in the journal Life Sciences on 11 September 2024. the study.
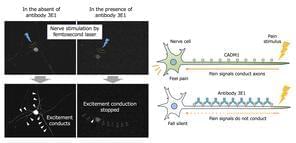
The team injected 3E1, the anti-CADM1 ectodomain antibody, under the mouse skin to study its localization on nerve fibers. Immunohistochemical and immunofluorescence studies revealed that the injected 3E1 was exclusively localized on peripheral nerves in the dermis. The lead author of the study, Prof. Ito highlights, “As CADM1 can recruit neuronal receptors to the plasma membrane, we hypothesized that this accumulation of 3E1 may blunt neuronal sensitivity, i.e., have an analgesic effect, via altering the expression of CADM1 on nerve fibers. However, to our knowledge, there have been no studies that attempted to develop drugs in terms of inhibiting CADM1 in nerves.”
Analgesic effects were tested using a formalin-induced chemical-inflammatory pain test and video-recorded behavior analysis at 6-, 12-, and 24-hours post-injection. Mice injected with 3E1 exhibited less pain-related behaviors when compared with controls, with analgesic effects lasting up to 24 hours, which is significantly longer than the duration of 5 to 8 hours reported for the local anesthetic levobupivacaine.