Japan’s new state-of-the-art supercomputer, which is due to cost more than $750 million to build, is set to turn on by 2030.


If you’ve ever seen yourself through a thermal imaging camera, you’ll know that your body produces lots of heat. This is in fact a waste product of our metabolism. Every square foot of the human body gives off heat equivalent to about 19 matches per hour.
Unfortunately, much of this heat simply escapes into the atmosphere. Wouldn’t it be great if we could harness it to produce energy? My research has shown this would indeed be possible. My colleagues and I are discovering ways of capturing and storing body heat for energy generation, using eco-friendly materials.
The goal is to create a device that can both generate and store energy, acting like a built-in power bank for wearable tech. This could allow devices such as smart watches, fitness trackers, or GPS trackers to run much longer, or even indefinitely, by harnessing our body heat.
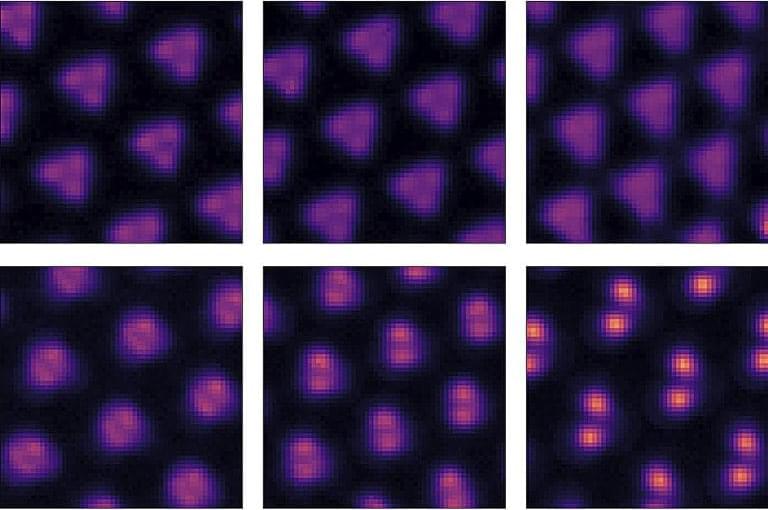
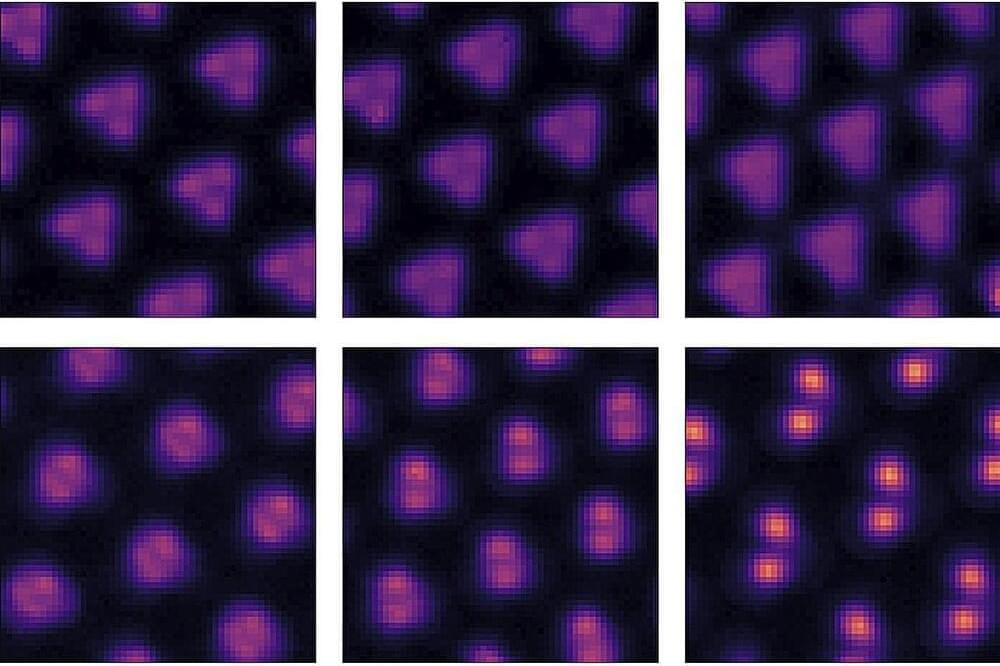
The composition of the products varies depending on the starting materials. Pure methane reacts—with very low yield—to give ethane, propane and hydrogen. The addition of oxygen increases the conversion, resulting mainly in CO2 as well as CO, ethylene, and water.
In the presence of water, aqueous methane reacts to give acetone and tertiary butyl alcohol; in the gas phase, it gives ethane and propane. When both water and oxygen are added, the reactions are strongly accelerated. In the aqueous phase, formaldehyde, acetic acid, and acetone are formed. If ammonia is also added, acetic acid forms glycine, an amino acid also found in space.
“Under gamma radiation, glycine can be made from methane, oxygen, water, and ammonia, molecules that are found in large amounts in space,” says Huang. The team developed a reaction scheme that explains the routes by which the individual products are formed. Oxygen (∙O2−) and ∙OH radicals play an important role in this. The rates of these radical reaction mechanisms are not temperature-dependent and could thus also take place in space.

Swedish scientists report a new breakthrough in technology that could transform optical communication in deep space, according to recently published research.
In a study led by a team at Chalmers University of Technology in Sweden, researchers have developed a silent amplifier and ultra-sensitive receiver that can facilitate high-fidelity transmissions over vast distances, showing promise for long-distance space communication.
Optica l Communication Through Deep Space


True humility is rare today. It takes courage and a strong stance. It’s the story of Grigori Perelman, who proved the Poincaré conjecture — the only one of the seven Millennium Prize Problems solved by humanity. 1️⃣ In 1990s, Perelman worked at UC Berkeley. Top universities tried to hire him. A hiring committee at Stanford asked him for a C.V. to include with requests for letters of recommendation. But Perelman said: “If they know my work, they don’t need my C.V. If they need my C.V., they don’t know my work.” he received several job offers. But he declined them all. 2️⃣ In 2002–2003, he posted three manuscripts on arXiv where he solved the Poincare problem. On a PREPRINT server. Not in a journal! He did not care about publishing them in Nature. He did not care about getting them peer reviewed. He just wanted to make his work publicly available. Several leading math groups immediately started checking his proof. 3️⃣ In 2006, he was awarded a Fields Medal for his work on the Ricci flow and Poincare conjecture. But Perelman declined it: “[The prize] was completely irrelevant for me. Everybody understood that if the proof is correct, then no other recognition is needed.” He did not attend the ceremony. He was the only person to have ever declined the prize. 4️⃣ In 2010, Perelman was awarded a Millennium Prize ($1,000,000). He did not attend a ceremony in Paris as well. He considered the decision of the Clay Institute unfair because he wanted to share the prize with Richard Hamilton (who had a big influence on Perelman in 1990s). “The main reason is my disagreement with the organized mathematical community. I don’t like their decisions, I consider them UNJUST.” ❗️Why I am writing all this? Because: There’s no fairness in academia. It’s unjust and often illogical. It’s full of competition and unkindness. Perelman was very sensitive to it. So, he left mathematics… IF we don’t want to lose brilliant minds like this… IF we want our kids to love science as they grow up… Then we should focus on making it a better place. Less pressure on tenure track professors. No pursuit of metrics. No emphasis on awards. More mentorship and quality research. We need it. #science #research #engineering #mathematics #scienceandtechnology
Can someone smarter than I tell me if this has any implications regarding the Covid vaccine?
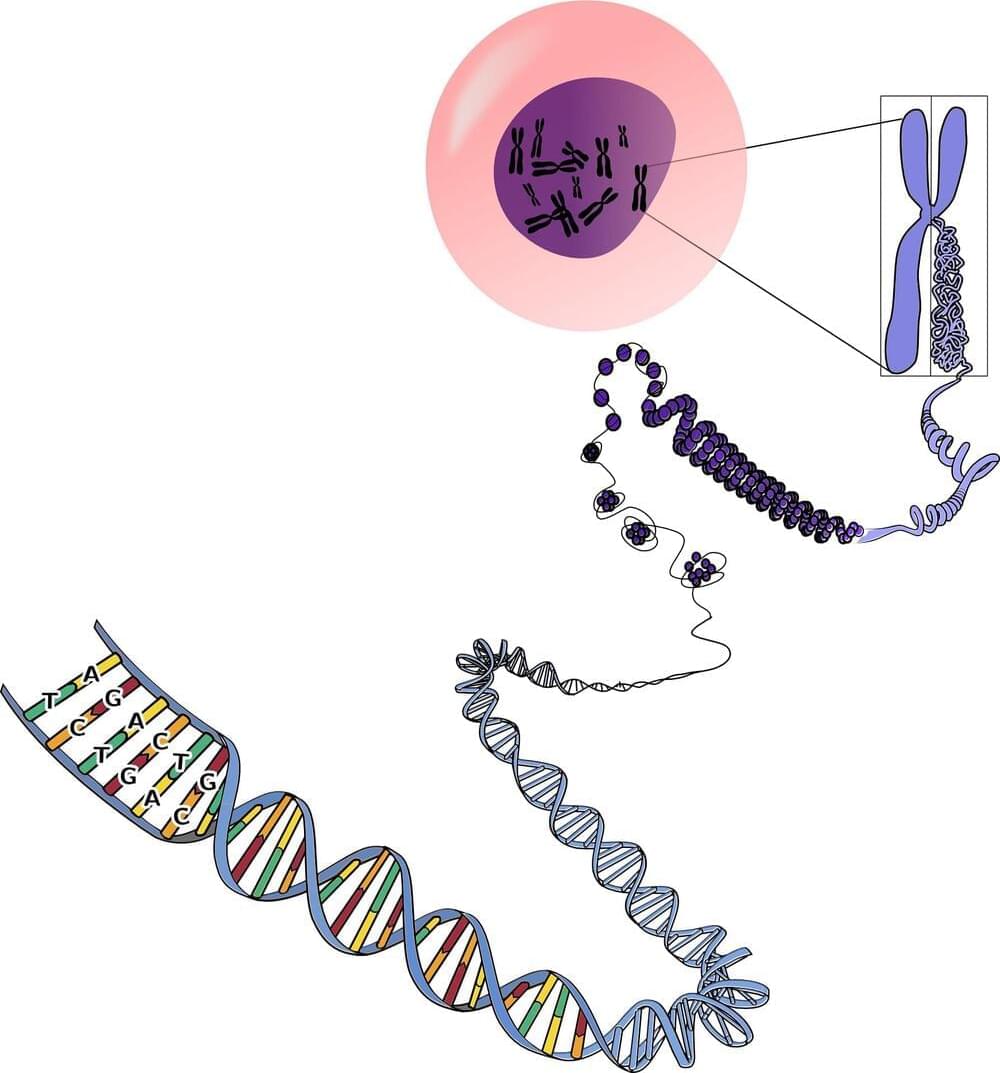
Genes contain instructions for making proteins, and a central dogma of biology is that this information flows from DNA to RNA to proteins. But only two percent of the human genome actually encodes proteins; the function of the remaining 98% remains largely unknown.