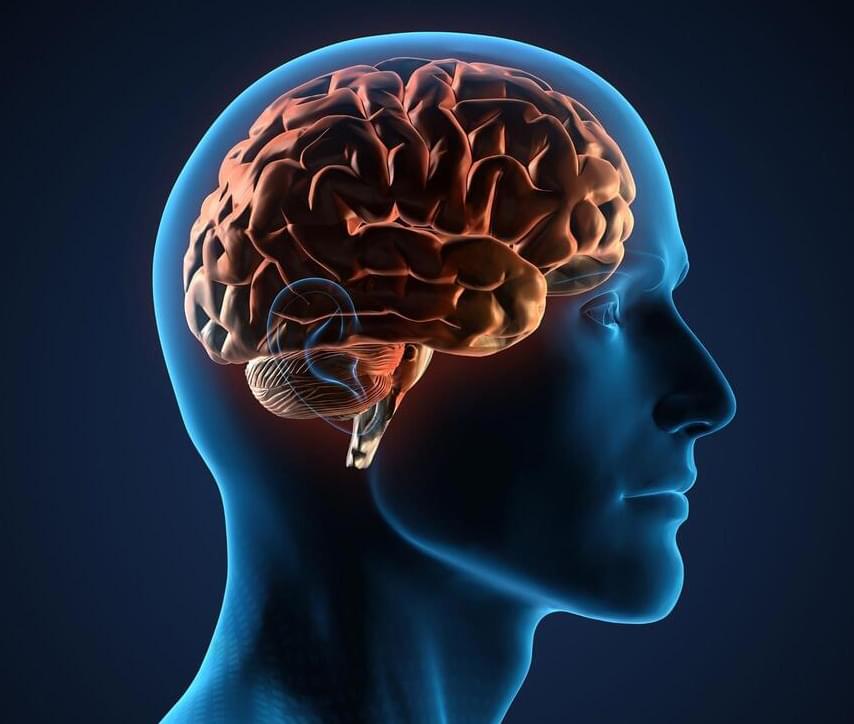
Researchers at FutureNeuro, the SFI Research Centre for Translational Brain Science, and RCSI University of Medicine and Health Sciences, in collaboration with international partners, have developed a revolutionary technique to profile gene activity in the living human brain.
This innovative approach, published in JCI Insight, opens new avenues for understanding and treating neurological conditions like epilepsy.
Studying gene activity in the brain without requiring invasive tissue samples from surgery or post-mortem donation has been a long-standing challenge in neuroscience. By analyzing molecular traces – specifically RNA and DNA – collected from electrodes implanted in the brains of patients with epilepsy and linking these with electrical recordings from the brain, the researchers were able to take a ‘snapshot’ of gene activity in the living brain.