A new type of OLED (organic light emitting diode) could replace bulky night vision goggles with lightweight glasses, making them cheaper and more practical for prolonged use, according to University of Michigan researchers.

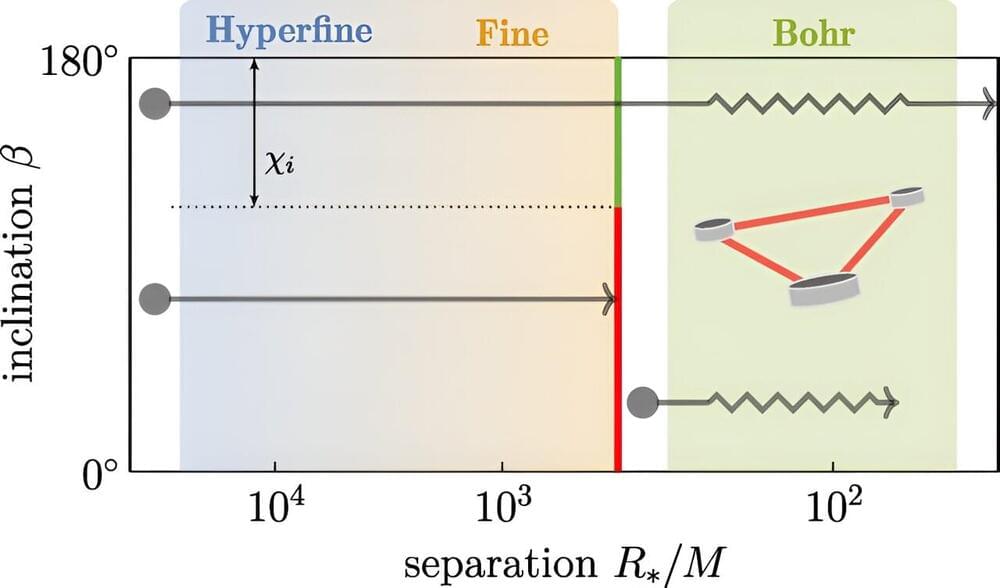
In a paper published in Physical Review Letters this week, physicists from Amsterdam and Copenhagen argue that close observations of merging black hole pairs may unveil information about potential new particles. The research combines several new discoveries made by UvA scientists over the past six years.
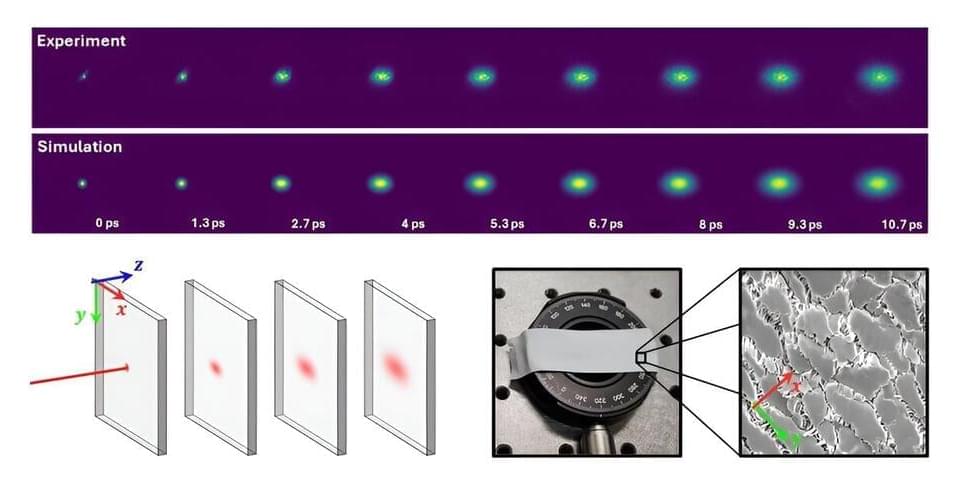
Understanding how light travels through various materials is essential for many fields, from medical imaging to manufacturing. However, due to their structure, materials often show directional differences in how they scatter light, known as anisotropy. This complexity has traditionally made it difficult to accurately measure and model their optical properties. Recently, researchers have developed a new technique that could transform how we study these materials.
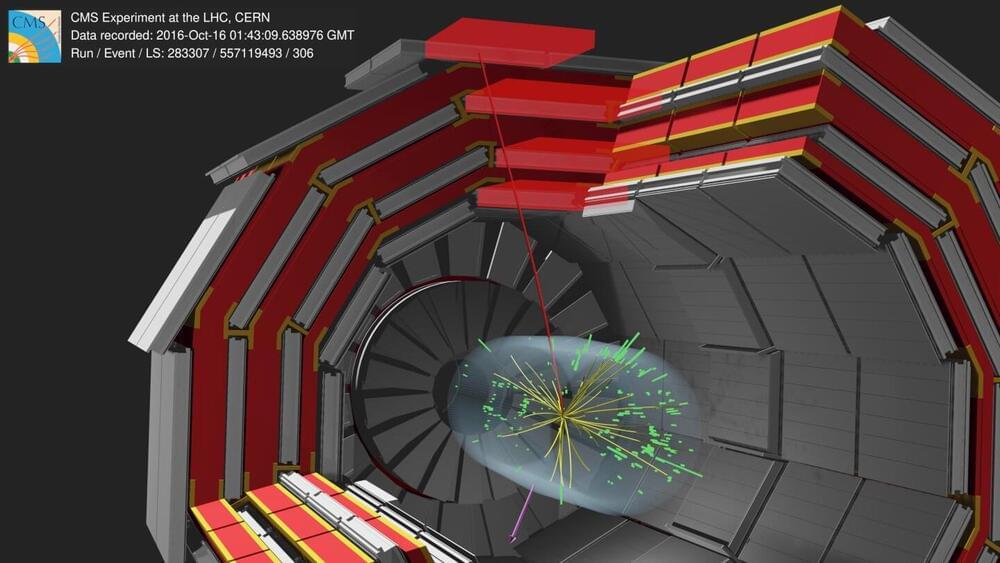
In 2023, the ATLAS collaboration, which provided its first W boson mass measurement in 2017, released an improved measurement based on a reanalysis of proton–proton collision data from the first run of the LHC. This improved result, 80,366.5 MeV with an uncertainty of 15.9 MeV, lined up with all previous measurements except the CDF measurement, which remains the most precise to date, with a precision of 0.01%.
The CMS experiment has now contributed to this global endeavor with its first W boson mass measurement. The keenly anticipated result, 80,360.2 with an uncertainty of 9.9 MeV, has a precision comparable to that of the CDF measurement and is in line with all previous measurements except the CDF result.
“The wait for the CMS result is now over. After carefully analyzing data collected in 2016 and going through all the cross checks, the CMS W mass result is ready,” says outgoing CMS spokesperson Patricia McBride. “This analysis is the first attempt to measure the W mass in the harsh collision environment of the second running period of the LHC. And all the hard work from the team has resulted in an extremely precise W mass measurement and the most precise measurement at the LHC.”
After about 6 prompts, ChatGPT o1’s preview and mini create a running version of the code described from the methods section of my research paper. I do want to emphasize that while the skeletal code does emulate what my code does, it did use its own synthetic data I asked for it to create as opposed to real astronomical data that would be used in a real paper. Nevertheless, the potential it has is incredible, to effectively accomplish what I struggled for about 10 months in my first year of my PhD. I am excited to apply o1 for other use cases. Thank you to everyone who tuned in live last night! #ai #openaio1 ##chatgpt
Enjoy the videos and music you love, upload original content, and share it all with friends, family, and the world on YouTube.
Kolmogorov-Arnold Transformer.
Xingyi Yang, Xinchao Wang National University of Singapore 2024 https://arxiv.org/abs/2409.10594 code: https://github.com/Adamdad/kat.
This study introduces the Kolmogorov–Arnold Transformer (KAT), a novel architecture that integrates Kolmogorov-Arnold Networks (KANs)…
Contribute to Adamdad/kat development by creating an account on GitHub.