Transformers have gained significant attention due to their powerful capabilities in understanding and generating human-like text, making them suitable for various applications like language translation, summarization, and creative content generation. They operate based on an attention mechanism, which determines how much focus each token in a sequence should have on others to make informed predictions. While they offer great promise, the challenge lies in optimizing these models to handle large amounts of data efficiently without excessive computational costs.
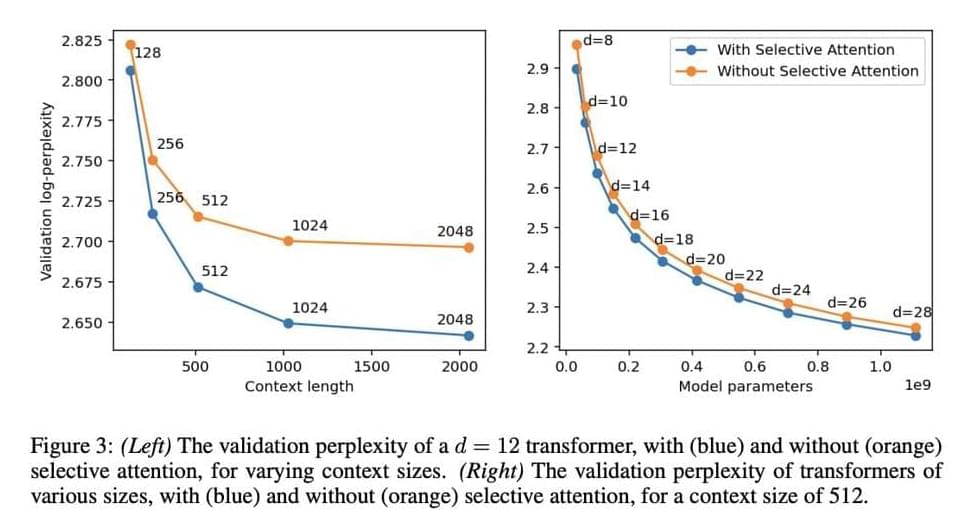
A significant challenge in developing transformer models is their inefficiency when handling long text sequences. As the context length increases, the computational and memory requirements grow exponentially. This happens because each token interacts with every other token in the sequence, leading to quadratic complexity that quickly becomes unmanageable. This limitation constrains the application of transformers in tasks that demand long contexts, such as language modeling and document summarization, where retaining and processing the entire sequence is crucial for maintaining context and coherence. Thus, solutions are needed to reduce the computational burden while retaining the model’s effectiveness.
Approaches to address this issue have included sparse attention mechanisms, which limit the number of interactions between tokens, and context compression techniques that reduce the sequence length by summarizing past information. These methods attempt to reduce the number of tokens considered in the attention mechanism but often do so at the cost of performance, as reducing context can lead to a loss of critical information. This trade-off between efficiency and performance has prompted researchers to explore new methods to maintain high accuracy while reducing computational and memory requirements.