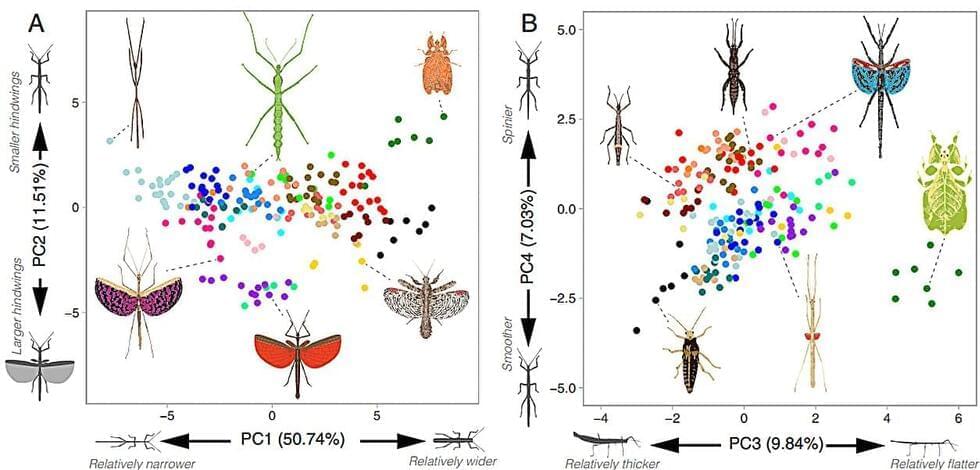
A team of biologists in Montana and Germany has found that, regardless of type, those insects that express a protective stick-or leaf-like appearance all evolved the same basic body parts. In their study, published in the journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, Romain Boisseau, Douglas Emlen and Sven Bradler measured and compared characteristics from 1,359 stick insects covering 212 stick and leaf species and assessed the possibility of predicting evolutionary change.
Prior evidence has shown that similar physical characteristics can evolve in unrelated creatures, a process called convergent evolution. For this new study, the researchers looked at two specific types of insects to learn more about how convergence works. They discovered that stick-and leaf-imitating insects had all evolved the same 20 basic body features, including body shape, head shape and lobster-like features. In all cases, they noted, the features had evolved to help the insects blend into the background to avoid being eaten by predators.
Something else the team learned was that because the same body parts kept evolving in different insects, they could predict how some modern insects will evolve. The key was looking at the environmental factors that led to changes that had already occurred. Creatures that live in similar environments, they note, tend to evolve in similar ways, including their means of camouflage. This tends to be the best way to avoid predators.