Don Pettit packed a home-made tracker to space, allowing him to bless our timelines with long-exposure images.


A new USC Stem Cell study published in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences has identified key gene regulators that enable some deafened animals—including fish and lizards—to naturally regenerate their hearing. The findings could guide future efforts to stimulate the regeneration of sensory hearing cells in patients with hearing loss and balance disorders.
Led by first author Tuo Shi and co-corresponding authors Ksenia Gnedeva and Gage Crump at the Keck School of Medicine of USC, the study focuses on two cell types in the inner ear: the sensory cells that detect sound, and the supporting cells that create an environment where sensory cells can thrive.
In highly regenerative species such as fish and lizards, supporting cells can also transform into replacement sensory cells after injury—a capacity absent in humans, mice and all other mammals.

Researchers have developed a new computational method to explore the neutron matter inside neutron stars at densities higher than previously studied.
This method provides insights into the behavior of neutrinos during supernova explosions, enhancing the accuracy of simulations and potentially improving our understanding of such cosmic events.
Advances in Neutron Matter Simulation.
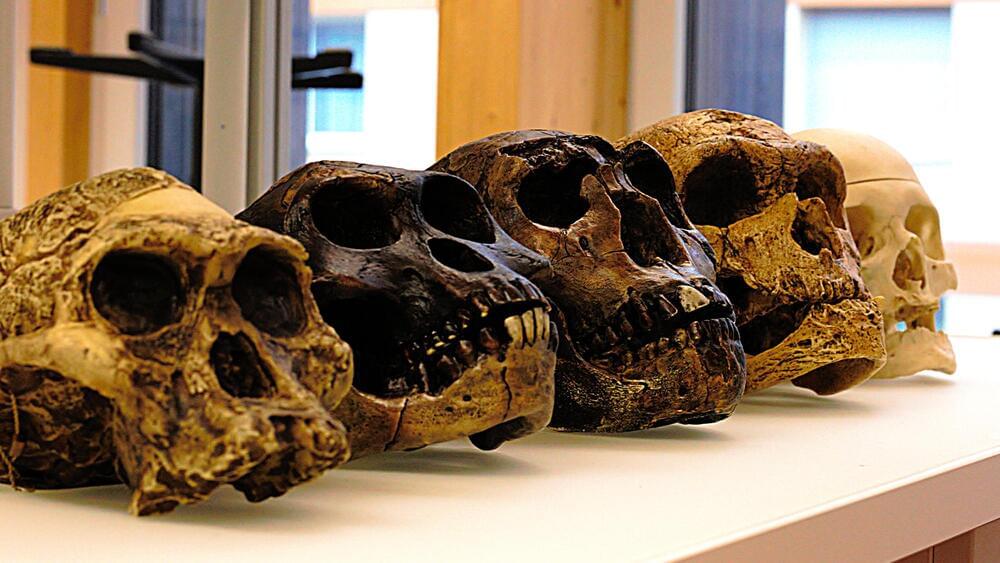

A team of scientists from the United States, Italy, and China may have finally explained a large gap in the African and Eurasian fossil record. According to a model in a study published August 31 in the journal Science, the population of human ancestors crashed between 800,000 and 900,000 years ago. They estimate that there were only 1,280 breeding individuals alive during this transition between the early and middle Pleistocene. About 98.7 percent of the ancestral population was lost at the beginning of this ancestral bottleneck that lasted for roughly 117,000 years, according to the study.
[Related: Want more eye-opening science stories? Sign up for a PopSci newsletter.].

There are contexts where human cognitive and emotional intelligence takes precedence over AI, which serves a supporting role in decision-making without overriding human judgment. Here, AI “protects” human cognitive processes from things like bias, heuristic thinking, or decision-making that activates the brain’s reward system and leads to incoherent or skewed results. In the human-first mode, artificial integrity can assist judicial processes by analyzing previous law cases and outcomes, for instance, without substituting a judge’s moral and ethical reasoning. For this to work well, the AI system would also have to show how it arrives at different conclusions and recommendations, considering any cultural context or values that apply differently across different regions or legal systems.
4 – Fusion Mode:
Artificial integrity in this mode is a synergy between human intelligence and AI capabilities combining the best of both worlds. Autonomous vehicles operating in Fusion Mode would have AI managing the vehicle’s operations, such as speed, navigation, and obstacle avoidance, while human oversight, potentially through emerging technologies like Brain-Computer Interfaces (BCIs), would offer real-time input on complex ethical dilemmas. For instance, in unavoidable crash situations, a BCI could enable direct communication between the human brain and AI, allowing ethical decision-making to occur in real-time, and blending AI’s precision with human moral reasoning. These kinds of advanced integrations between humans and machines will require artificial integrity at the highest level of maturity: artificial integrity would ensure not only technical excellence but ethical robustness, to guard against any exploitation or manipulation of neural data as it prioritizes human safety and autonomy.
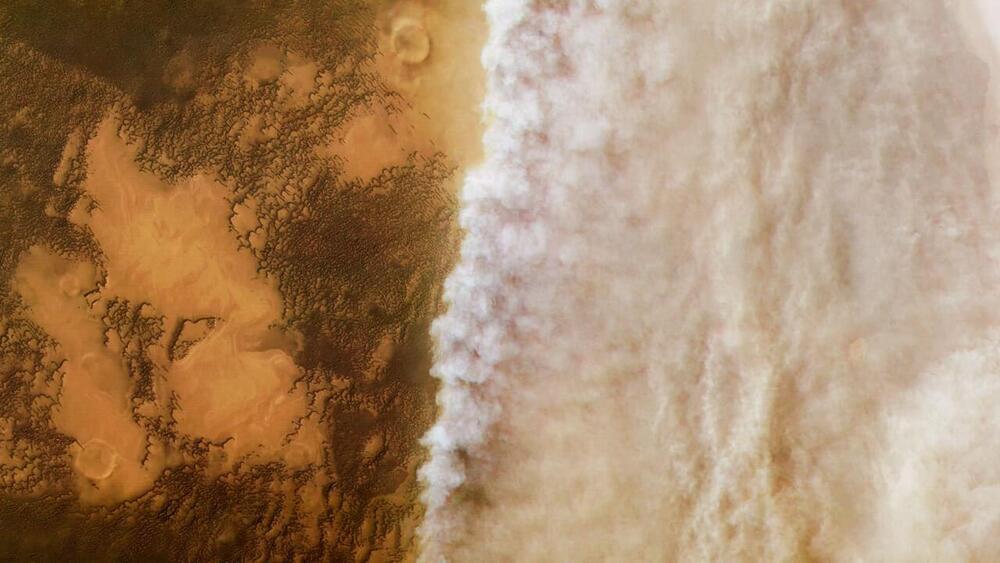

What processes are responsible for dust storms on Mars? This is what a study presented today at the American Geophysical Union 2024 Fall Meeting hopes to address as a pair of researchers from the University of Colorado Boulder (CU Boulder) investigated the causes behind the massive dust storms on Mars, which periodically grow large enough to engulf the entire planet. This study holds the potential to help researchers predict dust storms on Mars, which could help current and future robotic missions survive these calamities, along with future human crews to the Red Planet.
“Dust storms have a significant effect on rovers and landers on Mars, not to mention what will happen during future crewed missions to Mars,” said Heshani Pieris, who is a PhD Candidate in planetary science at CU Boulder and lead author of the study. “This dust is very light and sticks to everything.”
For the study, the researchers examined 15 (Earth) years of data obtained from NASA’s Mars Reconnaissance Orbiter (MRO) to ascertain the processes responsible for kickstarting dust storms. After analyzing countless datasets of Martian surface temperatures, the researchers found that 68 percent of large dust storms on Mars resulted from spikes in surface temperatures during periods of increased sunlight through Mars’ thin atmosphere.

They say beauty is in the eye of the beholder – and for physicists, beauty is in numbers.
Pedro Vieira, Clay Riddell Dirac Chair in Theoretical Physics at Perimeter Institute, is currently teaching a non-credit minicourse about ‘beautiful’ papers in physics. The course alternates between lectures on nine influential papers and student-led presentations about how these monumental papers influenced physics.
This is Vieira’s second time running the course and his first time offering it at Perimeter. He says the course is a way to cover spectacular papers while helping students understand the language of quantum field theory.
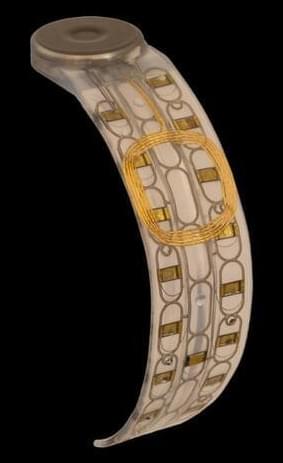
A year later, he got a myoelectric arm, a type of prosthetic powered by the electrical signals in his residual limb’s muscles. But Smith hardly used it because it was “very, very slow” and had a limited range of movements. He could open and close the hand, but not do much else. He tried other robotic arms over the years, but they had similar problems.
“They’re just not super functional,” he says. “There’s a massive delay between executing a function and then having the prosthetic actually do it. In my day-to-day life, it just became faster to figure out other ways to do things.”
Recently, he’s been trying out a new system by Austin-based startup Phantom Neuro that has the potential to provide more lifelike control of prosthetic limbs. The company is building a thin, flexible muscle implant to allow amputees a wider, more natural range of movement just by thinking about the gestures they want to make.
Water electrolysis is a cornerstone of global sustainable and renewable energy systems, facilitating the production of hydrogen fuel. This clean and versatile energy carrier can be utilized in various applications, such as chemical CO2 conversion, and electricity generation. Utilizing renewable energy sources such as solar and wind to power the electrolysis process may help reduce carbon emissions and promote the transition to a low-carbon economy.
The development of efficient and stable anode materials for the Oxygen Evolution Reaction (OER) is essential for advancing Proton Exchange Membrane (PEM) water electrolysis technology. OER is a key electrochemical reaction that generates oxygen gas (O₂) from water (H₂O) or hydroxide ions (OH⁻) during water splitting.
This seemingly simple reaction is crucial in energy conversion technologies like water electrolysis as it is hard to efficiently realize and a concurrent process to the wanted hydrogen production. Iridium (Ir)-based materials, particularly amorphous hydrous iridium oxide (am-hydr-IrOx), are at the forefront of this research due to their high activity. However, their application is limited by high dissolution rates of the precious iridium.
