The Advanced Research Projects Agency for Health (ARPA-H) has awarded $45 million to rapidly develop sense-and-respond implant technology that could slash U.S. cancer-related deaths by more than 50%.
Announced today, the award to a multi-institutional team of researchers, including Carnegie Mellon University, will fast-track development and testing of a new approach to cancer treatment that aims to dramatically improve immunotherapy outcomes for patients with ovarian, pancreatic, and other difficult-to-treat cancers.
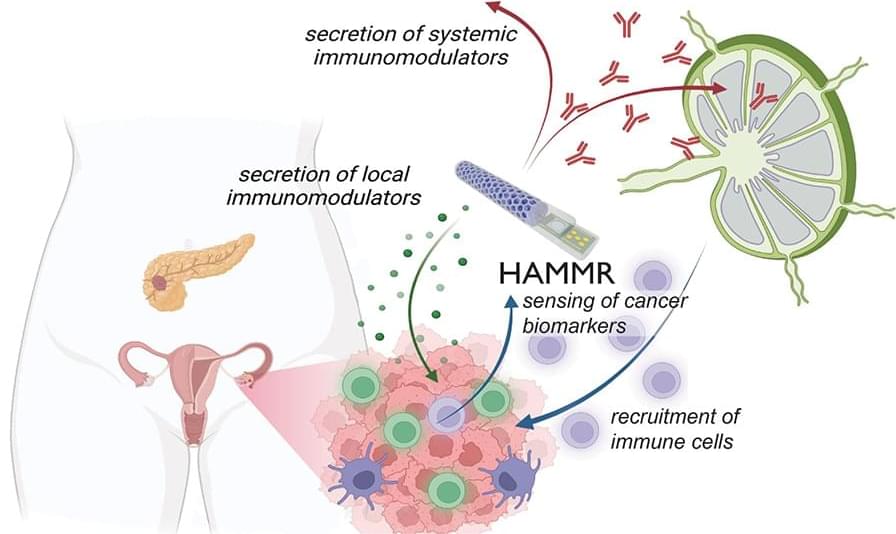
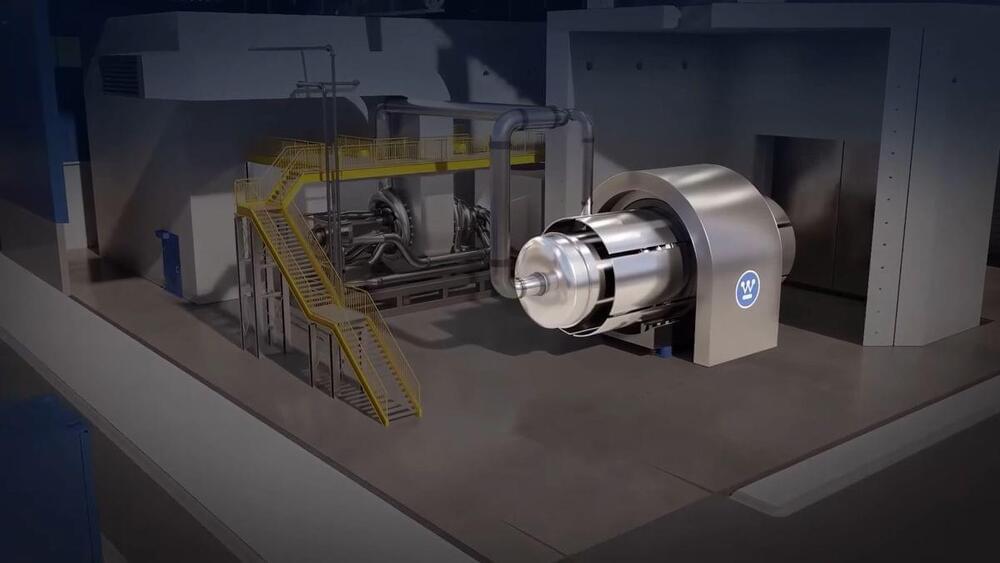
Source: Brandon Martin/Rice University. The “hybrid advanced molecular manufacturing regulator,” or HAMMR, a “closed-loop,” drug-producing implant smaller than an adult’s finger is being developed to treat ovarian, pancreatic, and other difficult-to-treat cancers. The implant, which is small enough to be implanted with minimally-invasive surgery, will be able to continuously monitor a patient’s cancer and adjust their immunotherapy dose in real time.