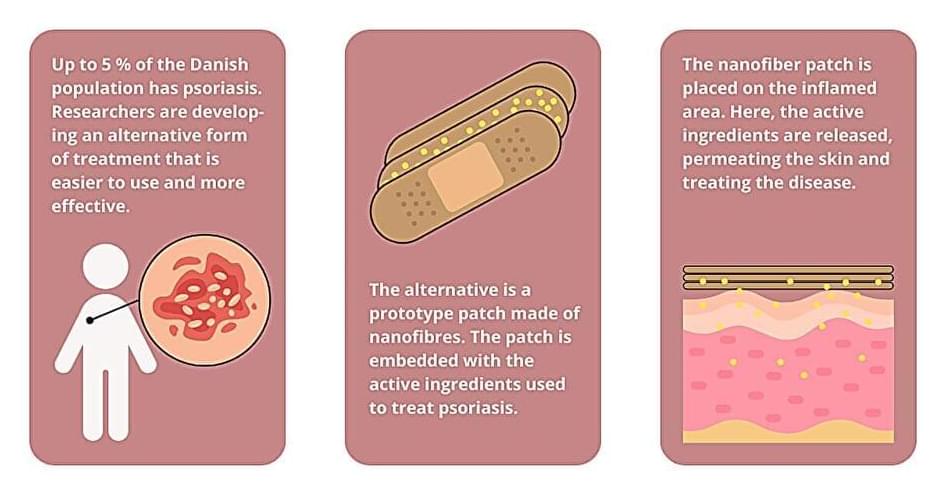
The researchers used electrospinning to produce the patch—a method where high voltage is applied to a polymer solution to produce synthetic nanofibers. The fibers are then used to make a fiber mat that may be attached to the skin like a plaster.
The researchers are still working on the patch. More research, product development and clinical trials are needed before the method is ready for use.
According to Andrea Heinz, though, it has great potential that extends beyond psoriasis treatment, “A patch containing active ingredients may be an alternative to creams and ointments in the treatment of other inflammatory skin diseases, for instance atopic eczema. It may also be useful in connection with wound healing.”