Artificial intelligence has the potential to significantly boost margins across various industries in the coming years, most notably software, semiconductors, and energy.
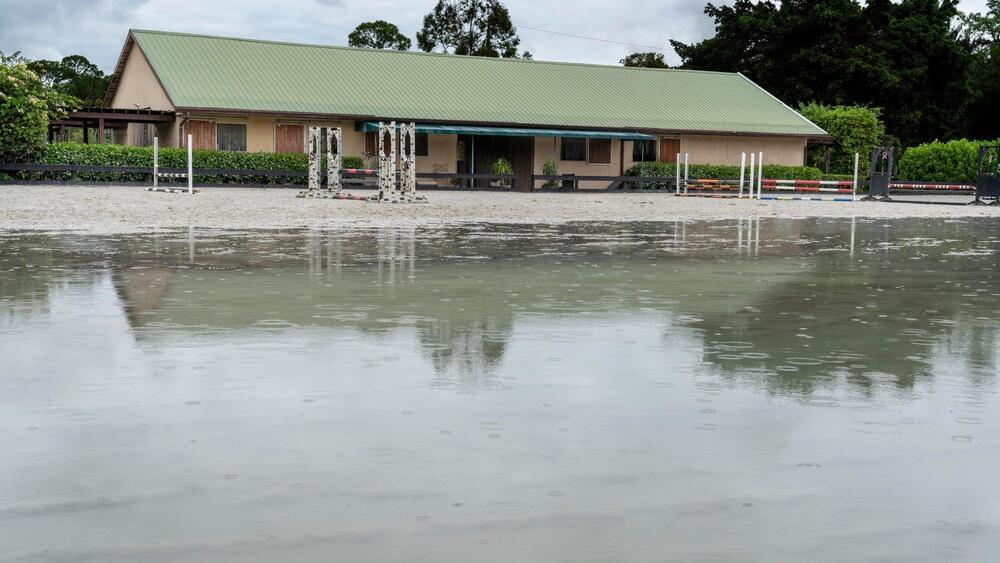



Still, damaging waters need not be a the result of a named storm or involve storm surge to destroy property, or spur flood warnings miles from the ocean. Florida’s flat, low-lying landscape, its limestone geology and its development patterns combine to present an ongoing and sometimes unpredictable threat from the wet stuff that experts fear will become more apparent with increasing temperatures and moisture.
“Virtually the entire state of Florida is a coastal plain,” said Tom Missimer, a hydrogeology professor emeritus at Florida Gulf Coast University’s College of Engineering in Fort Myers, who has been studying water movement for more than half a century. “When we get a large rainfall event, there’s not a lot of storage in the ground to absorb the new water coming in.”
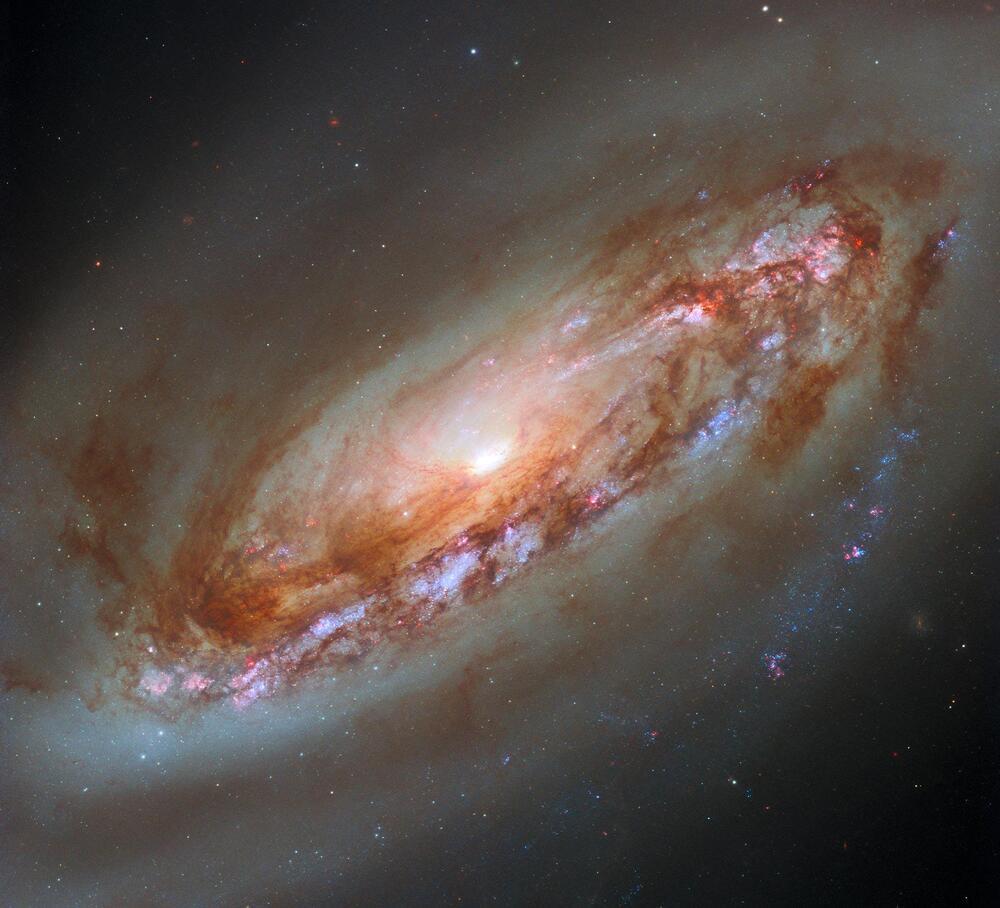


The Hubble Space Telescopes latest image of Messier 90, a spiral galaxy in the Virgo constellation, showcases advanced technological capabilities compared to earlier photographs taken in 1994.
This new image reveals the galaxy’s bright core, dusty disc, and a gaseous halo, enhanced by the Wide Field Camera 3 installed in 2010.
The stunning spiral galaxy featured in this Hubble Space Telescope image is Messier 90 (M90, also NGC 4569), located in the constellation Virgo. In 2019, Hubble released an image of M90 (see below) using data from the older Wide Field and Planetary Camera 2 (WFPC2) — data taken in 1994 soon after the camera’s installation. That image has a distinctive stair-step pattern due to the layout of WFPC2’s sensors. In 2010, WFPC2 was replaced by the more advanced Wide Field Camera 3 (WFC3), and Hubble used WFC3 when it turned its aperture to Messier 90 again in 2019 and 2023. The resulting data was processed to create this stunning new image (above), providing a much fuller view of the galaxy’s dusty disc, its gaseous halo, and its bright core.

She’s not long on charisma or passion but keeps perfect rhythm and is never prone to temperamental outbursts against the musicians beneath her three batons. Meet MAiRA Pro S, the next-generation robot conductor who made her debut this weekend in Dresden.
Her two performances in the eastern German city are intended to show off the latest advances in machine maestros, as well as music written explicitly to harness 21st-century technology. The artistic director of Dresden’s Sinfoniker, Markus Rindt, said the intention was “not to replace human beings” but to perform complex music that human conductors would find impossible.