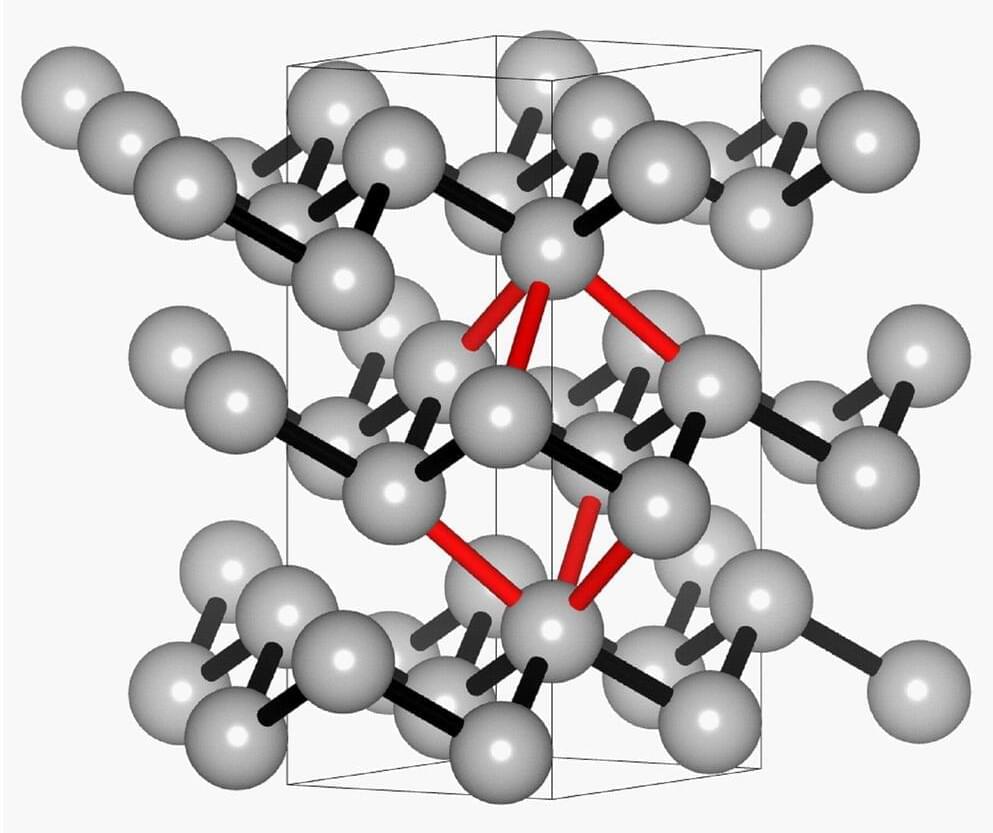
A new study that provides unprecedented insights into the chemical bonding of antimony could have a profound impact on materials research. The collaboration between scientists from Leipzig University, RWTH Aachen University and the DESY synchrotron in Hamburg combined experimental measurements with theoretical calculations.
The findings will help scientists to better understand phase change materials and, in particular, improve their application in data storage and thermoelectrics. The research has now been published in Advanced Materials.
The study combined experimental measurements with theoretical calculations, with the aim of analyzing the nature and strength of the chemical bonding in antimony. “The strength of a bond depends directly on the distance between the atoms,” says Professor Claudia S. Schnohr of the Felix Bloch Institute for Solid State Physics at Leipzig University, adding that comparisons with other materials such as metals and semiconductors show that this distance dependence is characteristic of the type of chemical bond.