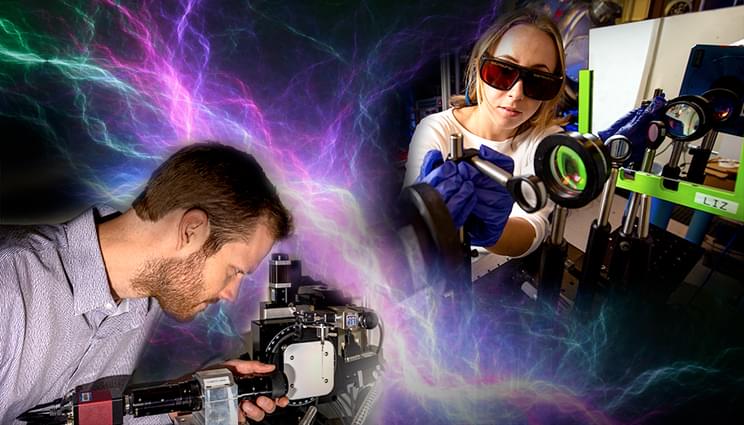
In 2019, the High Energy Density Science (HEDS) Center at Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) launched its postdoctoral fellowship program, welcoming one new scientist annually to come and conduct research for a two-year term. Supported by LLNL’s Weapons Physics and Design program, HEDS fellows are encouraged to pursue their own research agenda as it relates to the study of matter and energy under extreme conditions.
The most recent postdoctoral fellows, physicist Elizabeth “Liz” Grace (2022 fellow) and plasma physicist Graeme Sutcliffe (2023 fellow), are using high-intensity lasers and advanced diagnostics to observe the behaviors of plasma. A plasma, known as the “fourth state of matter,” is a superheated, ionized gas that makes up the majority of visible matter in the universe, like stars and nebulae. Replicating these conditions is a key step to achieving robust igniting inertial fusion designs for energy resilience.