The CEO also talked about how much AI computing power increased in the past 10 years and Nvidia’s single greatest contribution to AI.
Get the latest international news and world events from around the world.
SRSOS — Information Control
The battle was lost long ago.
Removal of the Fairness Doctrine.
Citizens United.
The Telecom Act.
We serve at the leisure of our corporate masters.
We are the product.
Powered by Roland, Korg and Behringer.
Copyright Ⓒ 2019 — 2025 by.
SRSOS.COM/SRSOS.ORG MUSIC LLC

2nd India CGT Symposium 2024
Bio-Rad invites you to our 2nd India Cell Gene Therapy Symposium 2024 After many decades of effort, the future of cell and gene therapies (CGT) is incredibly promising. A flurry of recent successes has led to the approval of several life changing treatments for patients and many more therapies are in development. CGT seek to correct the root cause of an illness at the molecular level. These game changing medicines are reshaping how we address previously uncurable illnesses — transforming people’s lives.
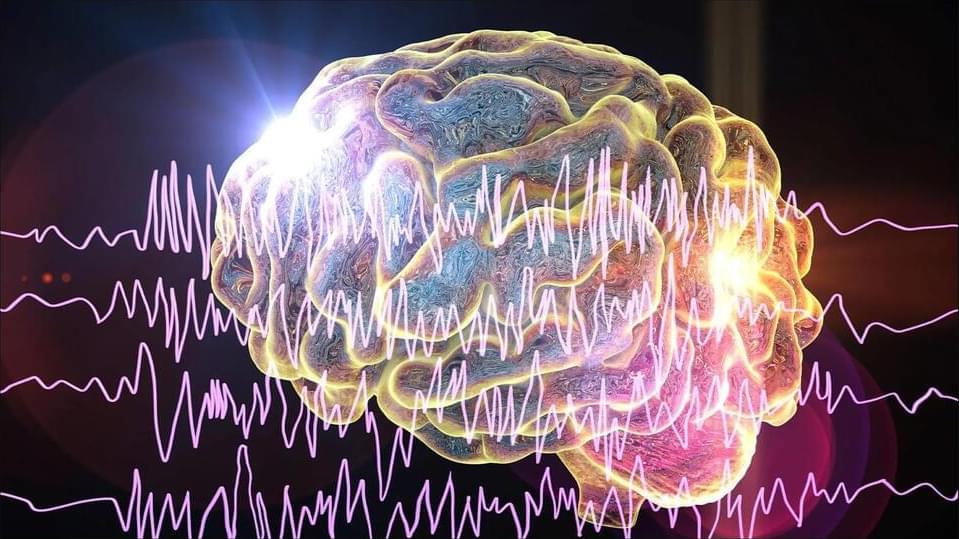
Mayo Clinic researchers develop new AI tools to reveal seizure hotspots, improve patient care
Mayo Clinic researchers have developed new artificial intelligence (AI)-based tools to pinpoint specific regions of the brain with seizure hotspots more quickly and accurately in patients with drug-resistant epilepsy. Their study, published in Nature Communications Medicine, highlights the potential of AI to revolutionize epilepsy treatment by interpreting brain waves during electrode implantation surgery. This transformative approach could significantly reduce the time patients spend in the hospital, accelerating the identification and removal of seizure-generating brain regions.
“This innovative approach could enable more rapid and accurate identification of seizure-generating areas during stereo-electroencephalography (EEG) implantation surgery, potentially reducing the cost and risks of prolonged monitoring,” says Nuri Ince, Ph.D., senior author of the study and a consultant in the Mayo Clinic Department of Neurologic Surgery.
Drug-resistant epilepsy often requires surgical removal of the seizure-causing brain tissue. A first step in that treatment is typically a surgery that involves implanting electrodes in the brain and monitoring neural activity for several days or weeks to identify the location of the seizures.

Meet ‘Blackbird’: A flying taxi that spins and moves in any direction thanks to new propulsion system
CycloTech’s all-electric flying vehicle is capable of controlled descents even in stormy weather with motors similar to those used for tug boats.
Researchers uncover link between quantum information theory and particle and condensed matter physics
Theoretical physicists have established a close connection between the two rapidly developing fields in theoretical physics, quantum information theory and non-invertible symmetries in particle and condensed matter theories, after proving that any non-invertible symmetry operation in theoretical physics is a quantum operation. The study was published in Physical Review Letters as an Editors’ Suggestion on November 6.
In physics, symmetry provides an important clue to the properties of a theory. For example, if the N-poles in a magnetic field are replaced by the S-poles, and the S-poles by the N-poles all at once, the forces on objects and the energy stored in the magnetic field remain the same, even though the direction of the magnetic field has now become reversed. This is because the equations describing the magnetic field are symmetric with respect to the operation of swapping the N and S poles.
Over the past few years, the concept of symmetries has received generalization in various directions in the theoretical study of particle physics and condensed matter physics, becoming an active area of research. One such generalization is non-invertible symmetry. The operation of conventional symmetries is always invertible. There exists a reverse operation to undo it. Non-invertible symmetry, on the other hand, allows certain non-invertibility in such symmetry operations.
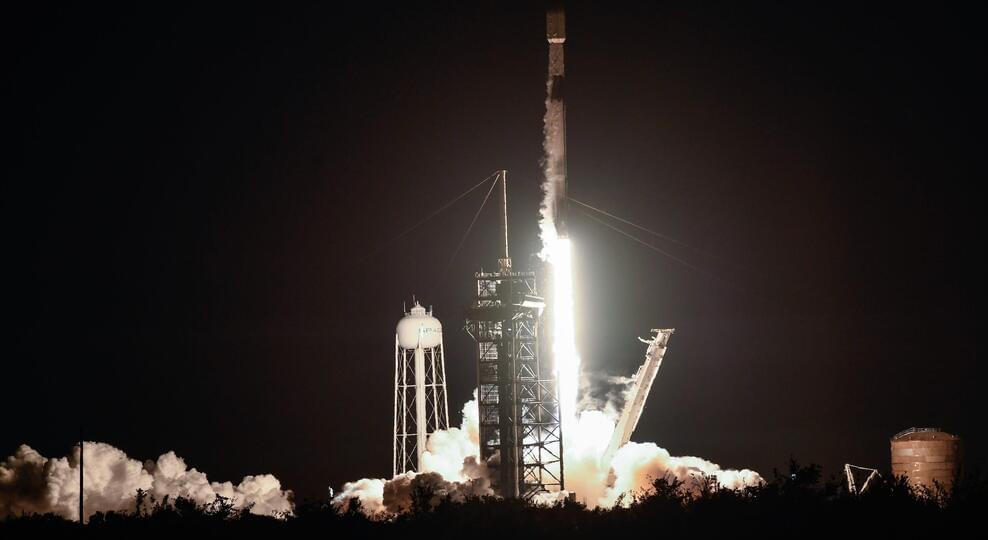

SpaceX launch overnight: Everything to know about the Starlink launch from Cape Canaveral
The Space Force’s 45th Weather Squadron pegs the odds of “go for launch” weather at 85%. Chief meteorological risks include thick cloud layers and liftoff winds, coupled with a low-to-moderate risk of upper-level wind shear.
Check back for live FLORIDA TODAY Space Team launch coverage updates on this page, starting about 90 minutes before the launch window opens. When SpaceX’s live webcast kicks off about five minutes before liftoff, look for it posted below the countdown clock.