“Genesis” can compress training times from decades into hours using 3D worlds conjured from text.
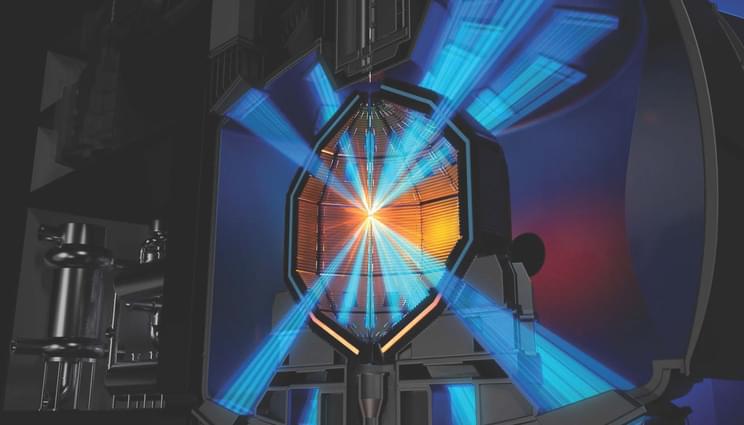



When Lawrence Livermore National Laboratory (LLNL) achieved fusion ignition at the National Ignition Facility (NIF) in December 2022, the world’s attention turned to the prospect of how that breakthrough experiment — designed to secure the nation’s nuclear weapons stockpile — might also pave the way for virtually limitless, safe and carbon-free fusion energy.
Advanced 3D printing offers one potential solution to bridging the science and technology gaps presented by current efforts to make inertial fusion energy (IFE) power plants a reality.
“Now that we have achieved and repeated fusion ignition,” said Tammy Ma, lead for LLNL’s inertial fusion energy institutional initiative, “the Lab is rapidly applying our decades of know-how into solving the core physics and engineering challenges that come with the monumental task of building the fusion ecosystem necessary for a laser fusion power plant. The mass production of ignition-grade targets is one of these, and cutting-edge 3D printing could help get us there.”

The Hubble Space Telescope has captured imagery of the R Aquarii binary star system from 2014–2023. The images have been time-lapsed here to show the evolution of the region.
Credit: NASA, ESA, M. Stute, M. Karovska, D. de Martin \& M. Zamani (ESA/Hubble) | edited by Space.com.
Music: You Want Dark Tunes? by Ave Air / courtesy of http://www.epidemicsound.com


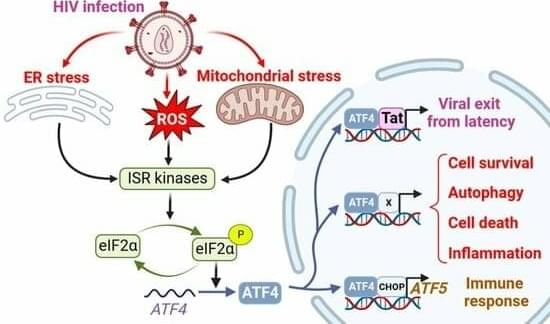
Cellular integrated stress response (ISR), the mitochondrial unfolded protein response (UPRmt), and IFN signaling are associated with viral infections. Activating transcription factor 4 (ATF4) plays a pivotal role in these pathways and controls the expression of many genes involved in redox processes, amino acid metabolism, protein misfolding, autophagy, and apoptosis. The precise role of ATF4 during viral infection is unclear and depends on cell hosts, viral agents, and models. Furthermore, ATF4 signaling can be hijacked by pathogens to favor viral infection and replication. In this review, we summarize the ATF4-mediated signaling pathways in response to viral infections, focusing on human immunodeficiency virus 1 (HIV-1). We examine the consequences of ATF4 activation for HIV-1 replication and reactivation.
Understanding the behavior of the molecules and cells that make up our bodies is critical for the advancement of medicine. This has led to a continual push for clear images of what is happening beyond what the eye can see. In a study recently published in Science Advances, researchers from Osaka University have reported a method that gives high-resolution Raman microscopy images.
Raman microscopy is a useful technique for imaging biological samples because it can provide chemical information about specific molecules—such as proteins—that take part in the body’s processes. However, the Raman light that comes from biological samples is very weak, so the signal can often get swamped by the background noise, leading to poor images.
The researchers have developed a microscope that can maintain the temperature of previously frozen samples during the acquisition. This has allowed them to produce images that are up to eight times brighter than those previously achieved with Raman microscopy.
Link :
Imagine a life where your body’s internal “battery” runs low every single day, demanding constant recharging just to keep going. For millions of people living with Type 1 diabetes, this is the exhausting reality—one where insulin injections act as the lifeline, replacing what the body can no longer produce on its own. But what if the body could be taught to recharge itself again?
In a world-first medical breakthrough, this question has moved from possibility to reality. A woman’s own stem cells have been successfully used to reverse her Type 1 diabetes, a condition once thought to be irreversible. Scientists turned her blood stem cells into insulin-producing powerhouses, effectively “rebooting” her pancreas and allowing her body to produce insulin naturally for the first time in years.
This achievement isn’t just a milestone for one patient; it’s a bold step toward a future where Type 1 diabetes may no longer require a lifetime of management. So, how did this groundbreaking transformation happen? And what does it mean for millions waiting for a cure?