Spintronics relies on the transport of spin currents for computing and communication applications. New device designs would be possible if this spin transport could be carried out by both electrons and magnetic waves called magnons. But spin transport via magnons typically requires electrically insulating magnets—materials that cannot be easily integrated with silicon electronics. A way to bypass that requirement has now been found by Matthias Althammer at the Bavarian Academy of Sciences and Humanities in Germany and his colleagues [1]. The researchers say that this finding could have important implications for both spintronic applications and fundamental research on spin transport.
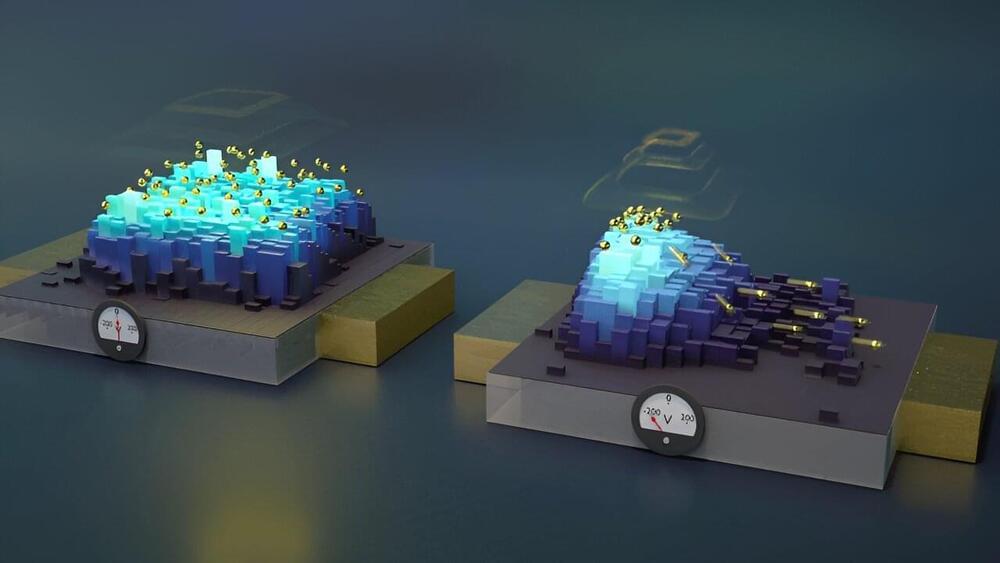
To demonstrate their concept, Althammer and his colleagues placed two magnetic, metallic strips—each hosting coupled electrons and magnons—on a nonmagnetic, insulating substrate. In the first strip, the researchers converted electron charge currents to electron spin currents. These spin currents were transferred first to the magnons in the same strip, then across the substrate to the magnons in the second strip, and finally to the electrons in the second strip. The researchers detected this spin transport by converting the electron spin currents in the second strip to charge currents.
Althammer and his colleagues studied how the spin transport between the two strips depended on temperature and strip separation. These measurements suggested that the transport was achieved via a magnetic dipole–dipole interaction between the strips. But the researchers could not rule out the possibility that it partly or mainly occurred via crystal vibrations in the substrate. Solving this open problem, which the researchers plan to do in upcoming work, will help in optimizing devices based on this principle.