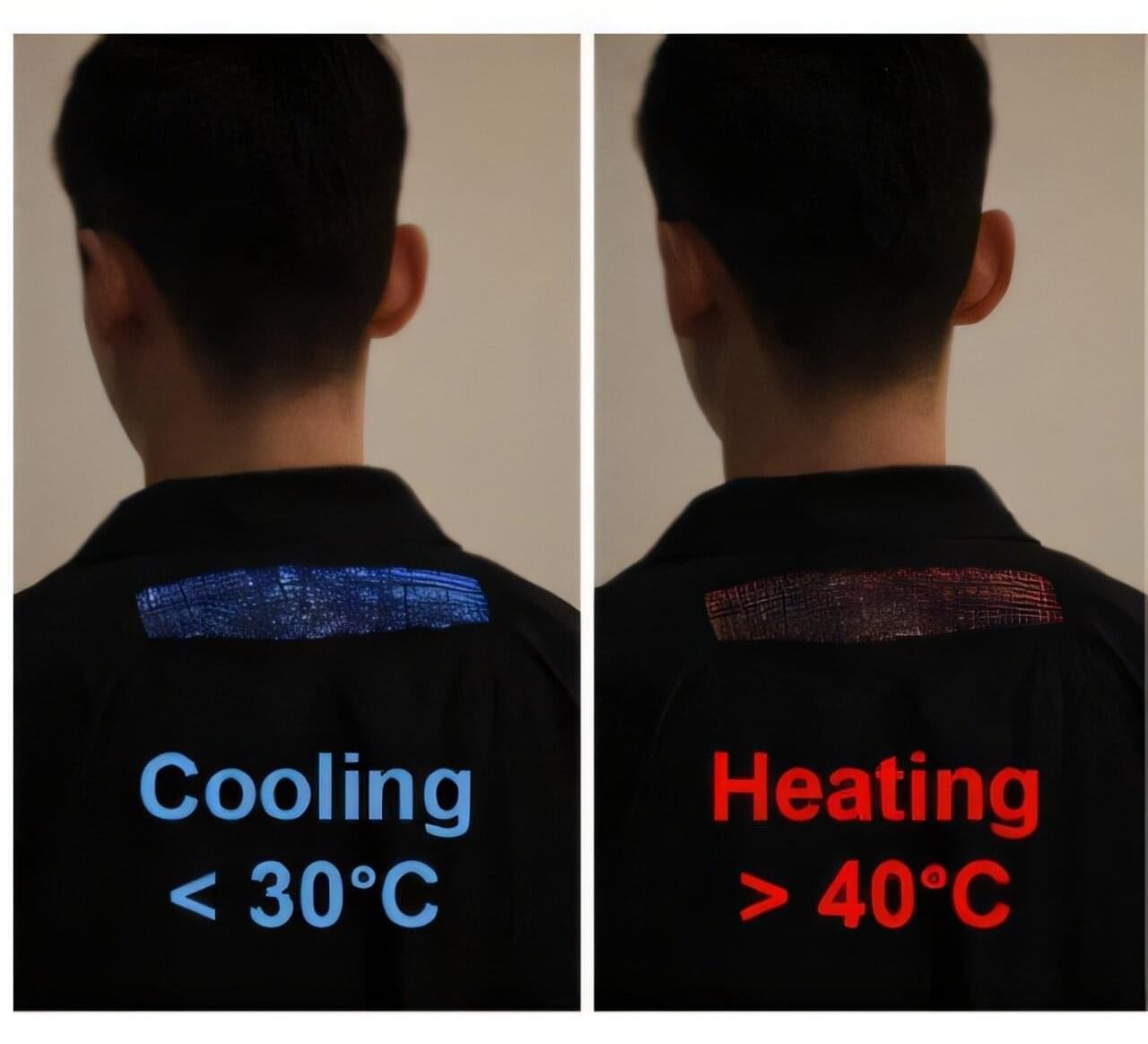
In Europe alone, approximately 2 million people live with chronic inflammatory bowel diseases (IBD), and their incidence has been rising steadily in recent decades. However, a small proportion of the European population carries a genetic variant that provides natural protection against IBD.
A newly published study in the journal eBioMedicine explores how this protective variant can be leveraged to develop modern therapies, demonstrating the potential of evolutionary medicine in addressing chronic diseases of the modern era.
The study, led by the Institute of Clinical Molecular Biology (IKMB) at Kiel University, brought together researchers from genetics, medicine, and archaeology.