From punch card-operated looms in the 1800s to modern cellphones, if an object has an “on” and an “off” state, it can be used to store information.
In a computer laptop, the binary ones and zeroes are transistors either running at low or high voltage. On a compact disc, the one is a spot where a tiny indented “pit” turns to a flat “land” or vice versa, while a zero is when there’s no change.
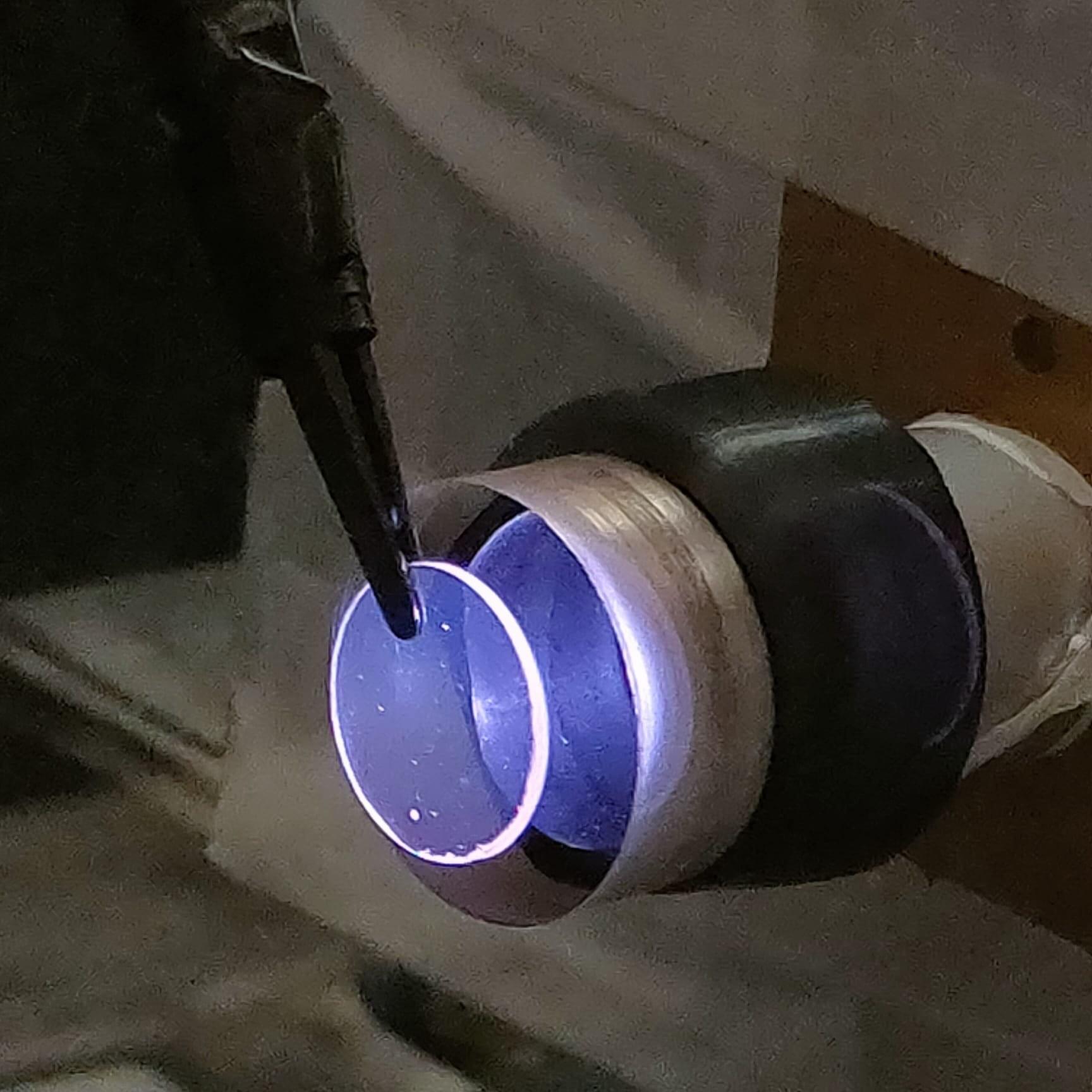
Historically, the size of the object making the “ones” and “zeroes” has put a limit on the size of the storage device. But now, University of Chicago Pritzker School of Molecular Engineering (UChicago PME) researchers have explored a technique to make ones and zeroes out of crystal defects, each the size of an individual atom for classical computer memory applications.