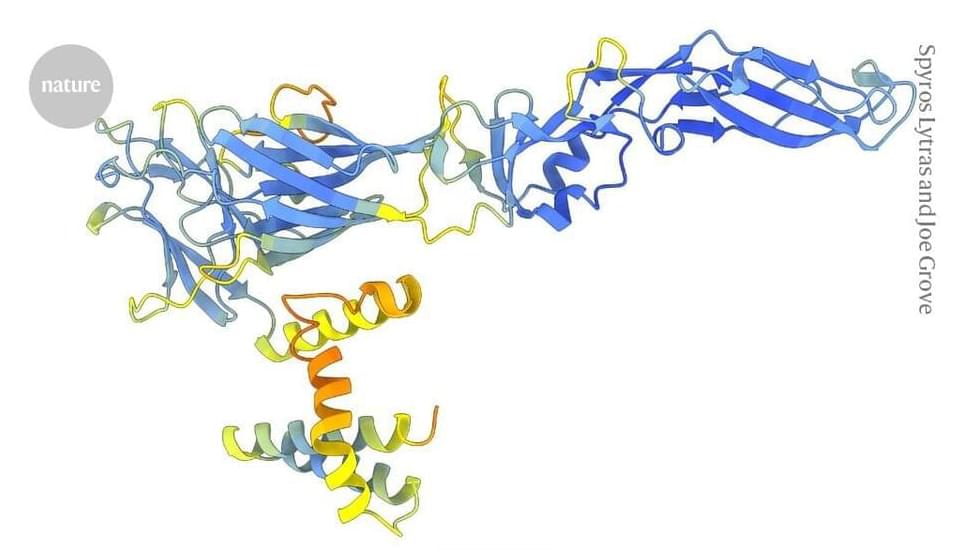
Protein structures predicted by artificial intelligence have charted the evolution of the virus family responsible for dengue and hepatitis C.

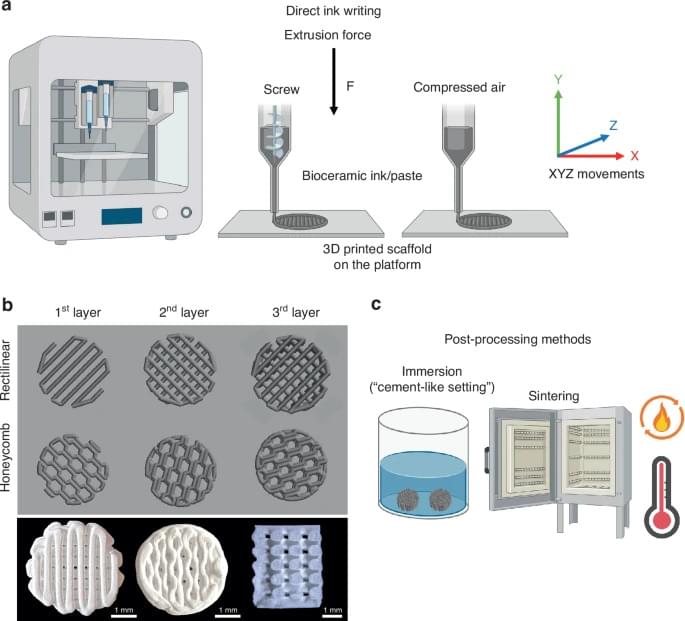
Researchers have unveiled a groundbreaking approach to facial bone reconstruction using 3D-printed ceramic materials that can be precisely customized to each patient’s needs. The comprehensive review, published in the International Journal of Oral Science, demonstrates how advanced manufacturing techniques are transforming the treatment of complex facial bone defects.
The traditional approach of harvesting bone from elsewhere in the patient’s body – long considered the gold standard – may soon give way to these sophisticated synthetic alternatives. These new materials not only eliminate the need for a second surgical site but can also be tailored to match the intricate anatomy of facial bones.
“3D printing enables the production of personalized grafts that perfectly fit the bone defect,” explains Marco C. Bottino, one of the study’s lead researchers. The technology allows surgeons to create exact replicas of the desired bone structure based on detailed medical imaging.


NVIDIA is set to accelerate its development of humanoid robots in the next year, as Team Green is preparing to release dedicated compact computers under the “Jetson Thor” series.
NVIDIA Is Prepared To Capitalize On The “Humanoid Robotics” Hype As The Industry Is Expected To Grow Up To $195 Billion By 2029
When we talk about how AI is going to evolve from hereon, the one discussion in everyone’s mind is automated robots, primarily since AGI has taken over the industry. Now, in a report by the Financial Times, it seems like the upcoming year will likely mark the next phase of the AI hype, where robotics will play a huge role in driving the markets further on. Team Green is rumored to introduce their next-gen “Jetson Thor” computing lineup in the first half of 2025, likely acting as a catalyst in the development of humanoid robots.
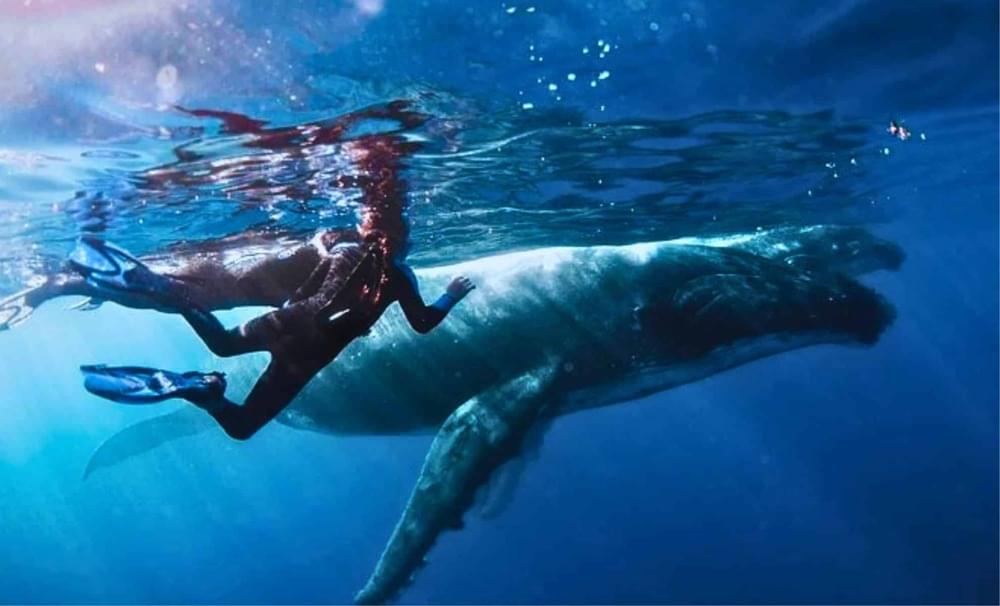

What if humans could truly talk to animals? Thanks to groundbreaking AI technology, researchers recently achieved something extraordinary—a 20-minute interaction with a humpback whale named Twain. But what exactly did this ‘conversation’ reveal? And how could it change the way we understand intelligence on Earth—and beyond? The answers may redefine our relationship with nature.


The U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS) has proposed updates to the Health Insurance Portability and Accountability Act of 1996 (HIPAA) to secure patients’ health data following a surge in massive healthcare data leaks.
These stricter cybersecurity rules, proposed by the HHS’ Office for Civil Rights (OCR) and expected to be published as a final rule within 60 days, would require healthcare organizations to encrypt protected health information (PHI), implement multifactor authentication, and segment their networks to make it harder for attackers to move laterally through them.
“In recent years, there has been an alarming growth in the number of breaches affecting 500 or more individuals reported to the Department, the overall number of individuals affected by such breaches, and the rampant escalation of cyberattacks using hacking and ransomware,” the HHS’ proposal says.
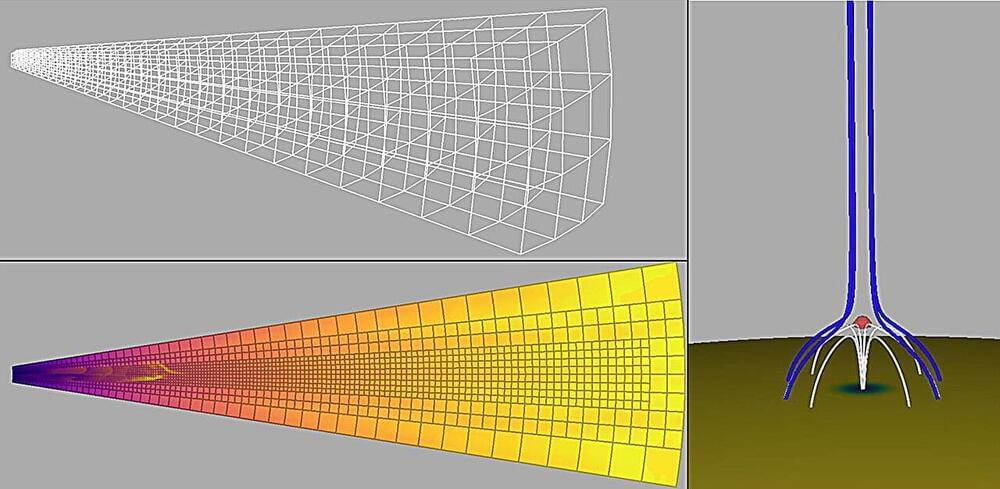
NASA’s Parker Solar Probe mission has detected magnetic distortions in solar wind, known as switchbacks. To better understand these phenomena, whose origins remain uncertain, a study was conducted by a network of collaborators. This study, published in the journal Astronomy & Astrophysics, reveals that solar jets can create similar disturbances without causing a complete reversal of the magnetic field.
NASA’s Parker Solar Probe mission revealed the presence of switchbacks, sudden and rapid reversals of the magnetic field in the solar wind. These peculiar phenomena, rarely observed near Earth, have captivated the scientific community due to their enigmatic origins. A leading theory suggests that switchbacks originate from solar jets, which are ubiquitous in the lower atmosphere of the sun.
To investigate their origins, a team of researchers from LPP, LPC2E, FSLAC, the University of Dundee and Durham University conducted 3D numerical simulations to replicate plasma behavior in the sun’s atmosphere. These simulations modeled solar jets and studied their propagation in solar wind.

Background and objectives: Aging clocks are computational models designed to measure biological age and aging rate based on age-related markers including epigenetic, proteomic, and immunomic changes, gut and skin microbiota, among others. In this narrative review, we aim to discuss the currently available aging clocks, ranging from epigenetic aging clocks to visual skin aging clocks.
Methods: We performed a literature search on PubMed/MEDLINE databases with keywords including: “aging clock,” “aging,” “biological age,” “chronological age,” “epigenetic,” “proteomic,” “microbiome,” “telomere,” “metabolic,” “inflammation,” “glycomic,” “lifestyle,” “nutrition,” “diet,” “exercise,” “psychosocial,” and “technology.”
Results: Notably, several CpG regions, plasma proteins, inflammatory and immune biomarkers, microbiome shifts, neuroimaging changes, and visual skin aging parameters demonstrated roles in aging and aging clock predictions. Further analysis on the most predictive CpGs and biomarkers is warranted. Limitations of aging clocks include technical noise which may be corrected with additional statistical techniques, and the diversity and applicability of samples utilized.