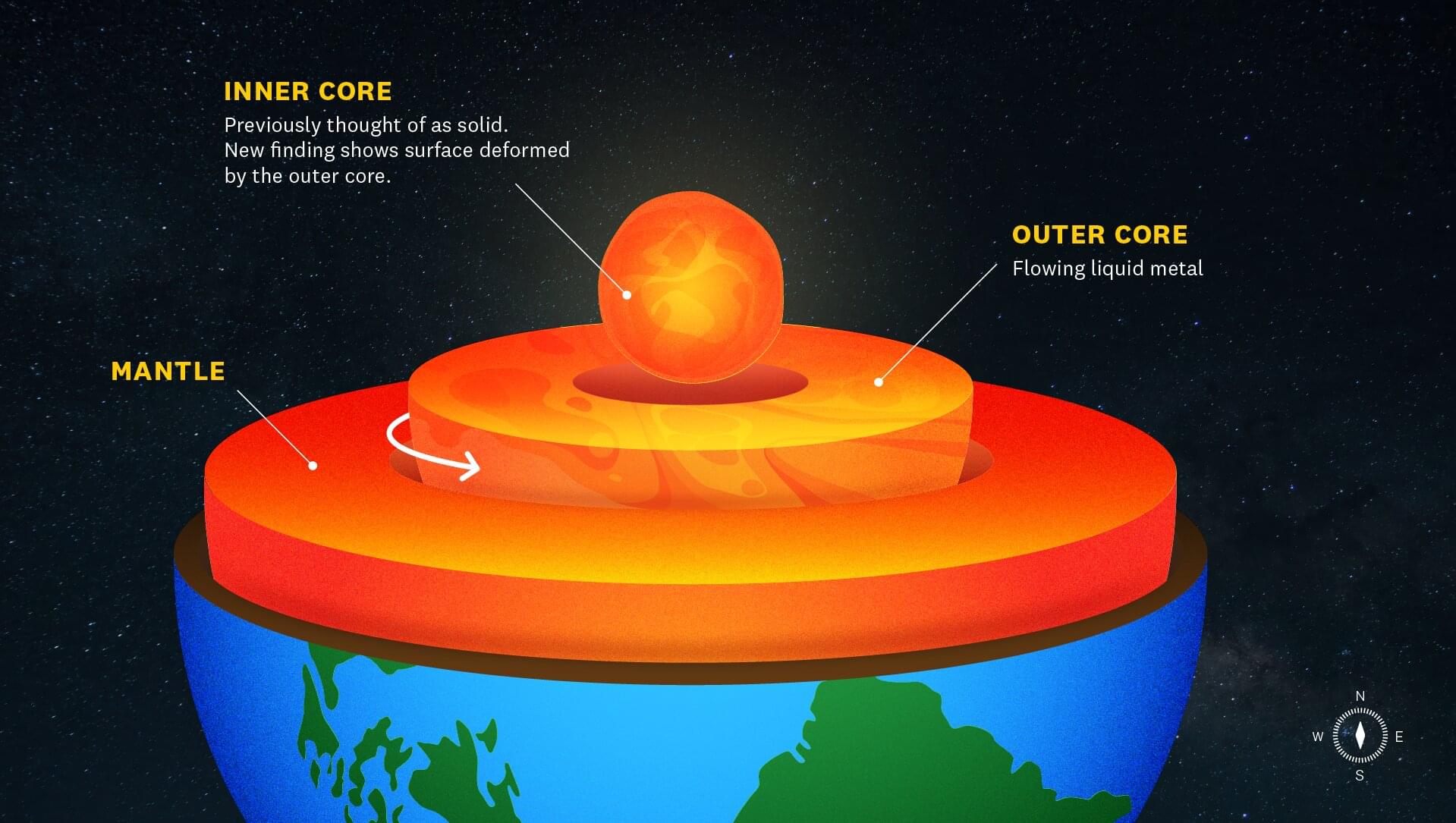
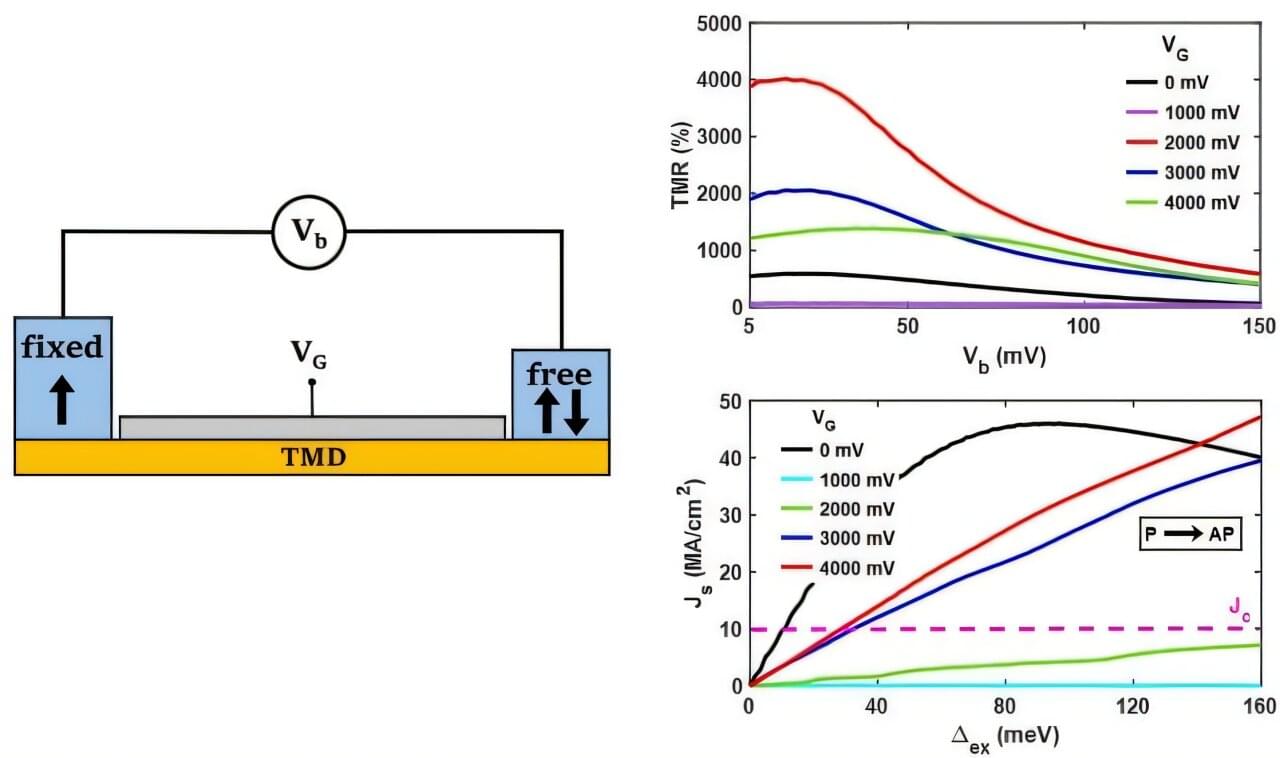
The surface of the Earth’s inner core may be changing, as shown by a new study by USC scientists that detected structural changes near the planet’s center, published in Nature Geoscience.
The changes of the inner core have long been a topic of debate for scientists. However, most research has been focused on assessing rotation. John Vidale, Dean’s Professor of Earth Sciences at the USC Dornsife College of Letters, Arts and Sciences and principal investigator of the study, said the researchers “didn’t set out to define the physical nature of the inner core.”
“What we ended up discovering is evidence that the near surface of Earth’s inner core undergoes structural change,” Vidale said. The finding sheds light on the role topographical activity plays in rotational changes in the inner core that have minutely altered the length of a day and may relate to the ongoing slowing of the inner core.