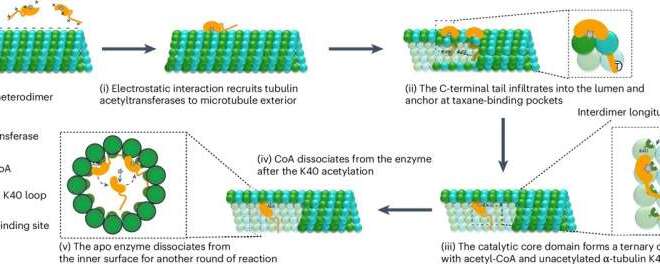
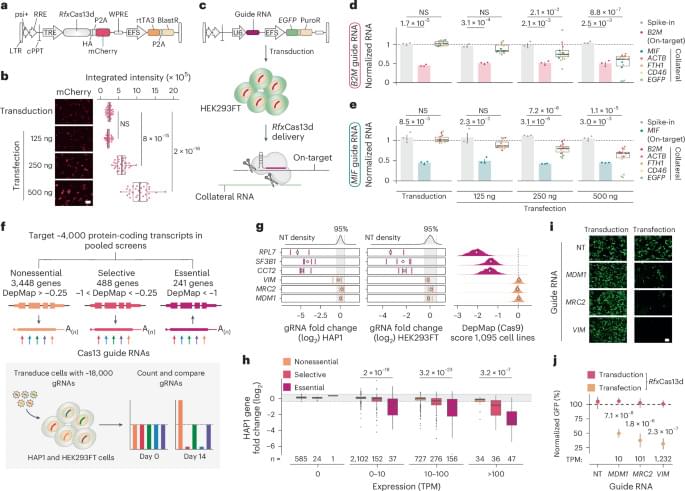
Careful selection of Cas13 variants and delivery methods minimizes collateral RNA degradation.

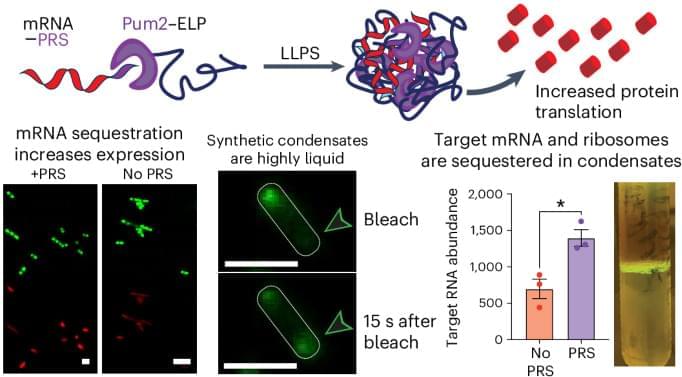
Formation of biomolecular condensates composed of proteins and RNA facilitates the regulation of gene expression by modulating translation or facilitating RNA processing. Now, synthetic ribonucleoprotein granules created with engineered intrinsically disordered proteins selectively sequester mRNA and enhance protein translation in cells. These highly liquid-like condensates exchange biomolecules across the cell and facilitate target mRNA and ribosome partitioning.
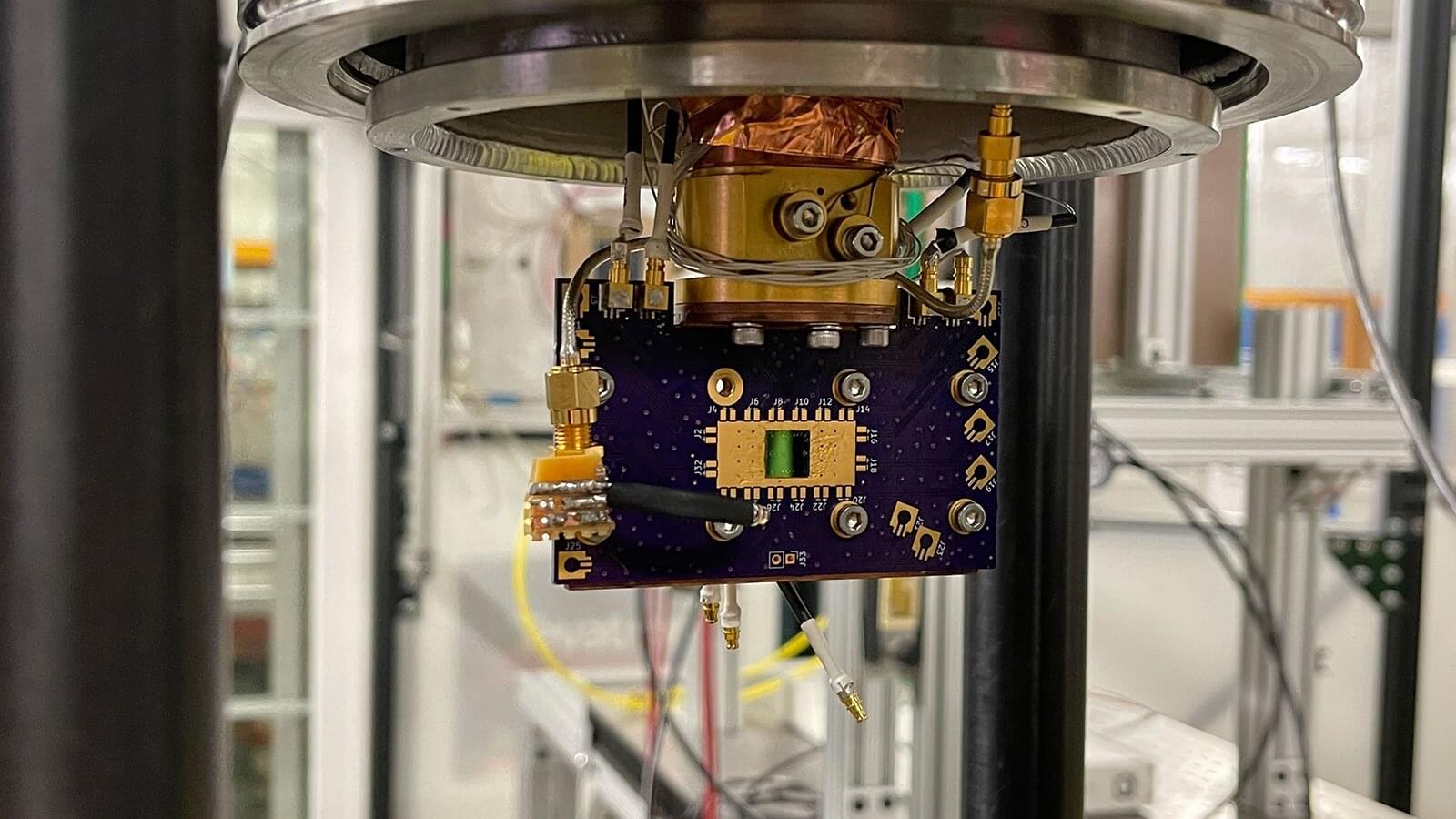

Particle detectors play a crucial role in our understanding of the fundamental building blocks of the universe. They allow scientists to study the behavior and properties of the particles produced in high-energy collisions. Such particles are boosted to near the speed of light in large accelerators and then smashed into targets or other particles where they are then analyzed with detectors. Traditional detectors, however, lack the needed sensitivity and precision for certain types of research.
Researchers at the U.S. Department of Energy’s (DOE) Argonne National Laboratory have made a significant breakthrough in the field of high-energy particle detection in recent experiments conducted at the Test Beam Facility at DOE’s Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory (Fermilab).
They have found a new use for the superconducting nanowire photon detectors (SNSPDs) already employed for detecting photons, the fundamental particles of light. These incredibly sensitive and precise detectors work by absorbing individual photons. The absorption generates small electrical changes in the superconducting nanowires at very low temperatures, allowing for the detection and measurement of photons. Specialized devices able to detect individual photons are crucial for quantum cryptography (the science of keeping information secret and secure), advanced optical sensing (precision measurement using light) and quantum computing.
Was born in Tambov, about 500 kilometers southeast of Moscow, in 1903. His unmarried mother, Maria Yakovlevna Kolmogorov a, died giving birth to him. [ 8 ] Andrey was raised by two of his aunts in Tunoshna (near Yaroslavl) at the estate of his grandfather, a well-to-do nobleman.
How does a tech-guru billionaire anti-gravity developer wind up in jail headed to prison?
A new paper in Nature Physics shows that by cramming lots of rare-earth ions into a crystal, some will form pairs that act as highly coherent qubits, thus debunking the idea that solid-state qubits need to be super dilute in an ultra-clean material to achieve long lifetimes.
According to the study’s authors, one of the major barriers to practical quantum computing has been how to make qubits that retain their quantum information long enough to be useful.
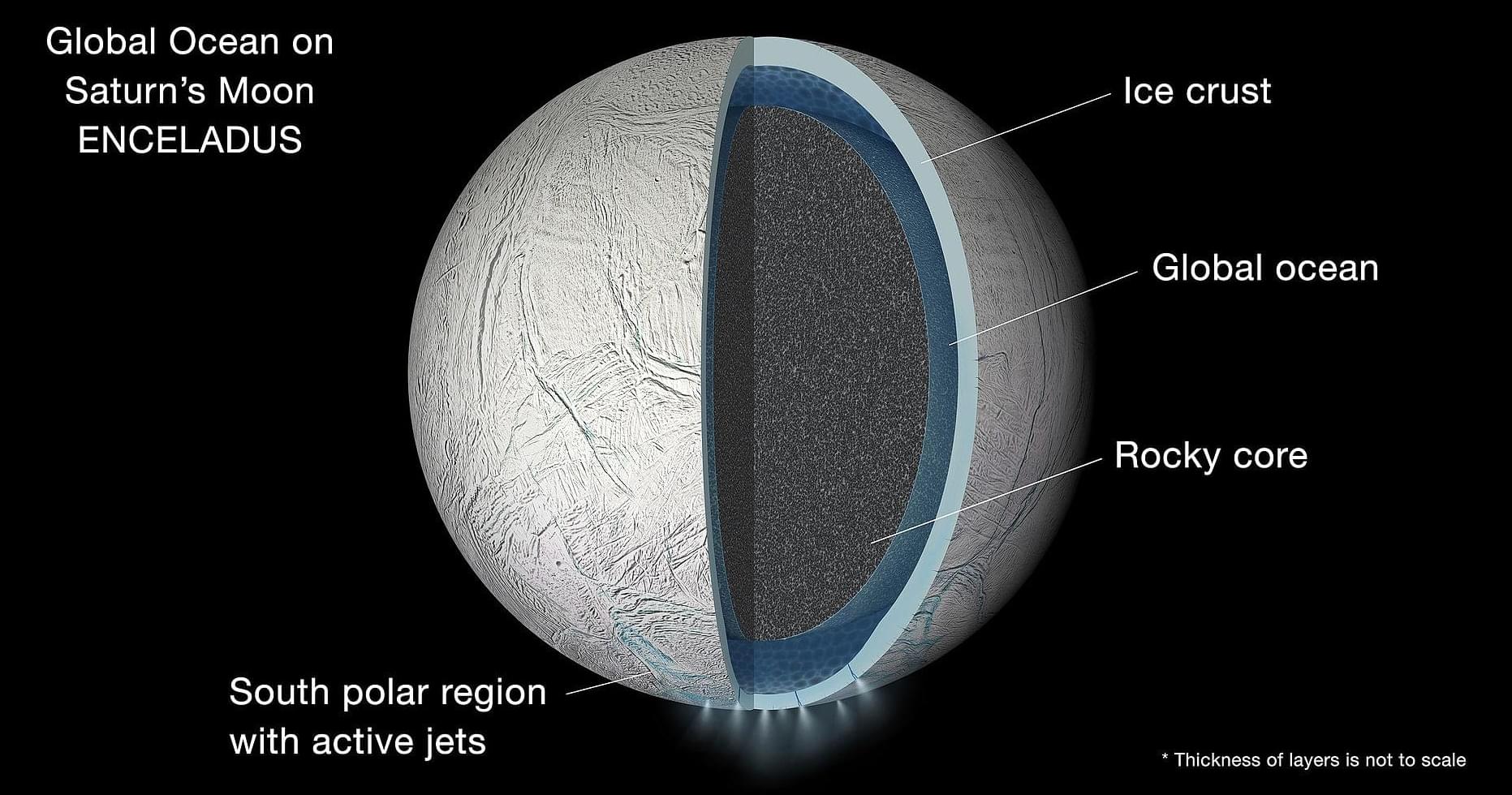
“We’ve found that Enceladus’ ocean should behave like oil and water in a jar, with layers that resist vertical mixing,” said Flynn Ames.
Could finding life in alien oceans be harder than previously thought? This is what a recent study published in Communications Earth & Environment hopes to address as a team of researchers from the United Kingdom investigated how life that might exist in the depths of alien oceans like Saturn’s moon, Enceladus, could take time to reach the surface for sampling, which could potentially pose problems for future sample return missions to these intriguing worlds.
For the study, the researchers used a series of computer models to simulate the various layers that could exist between the liquid ocean of Enceladus and the plumes that discharge from its south polar regions, nicknamed “tiger stripes” for its giant ice cracks. Given the sampling potential of the plumes, especially with NASA’s Cassini spacecraft having flown through the plumes during its mission, the researchers wanted to ascertain the length of time material from potential hydrothermal vents at the bottom of the ocean would reach the surface to be discharged by the plumes and sampled for signs of life. In the end, the researchers found that material from the bottom of Enceladus’ would take several centuries to reach a plausible depth to be discharged by the plumes.