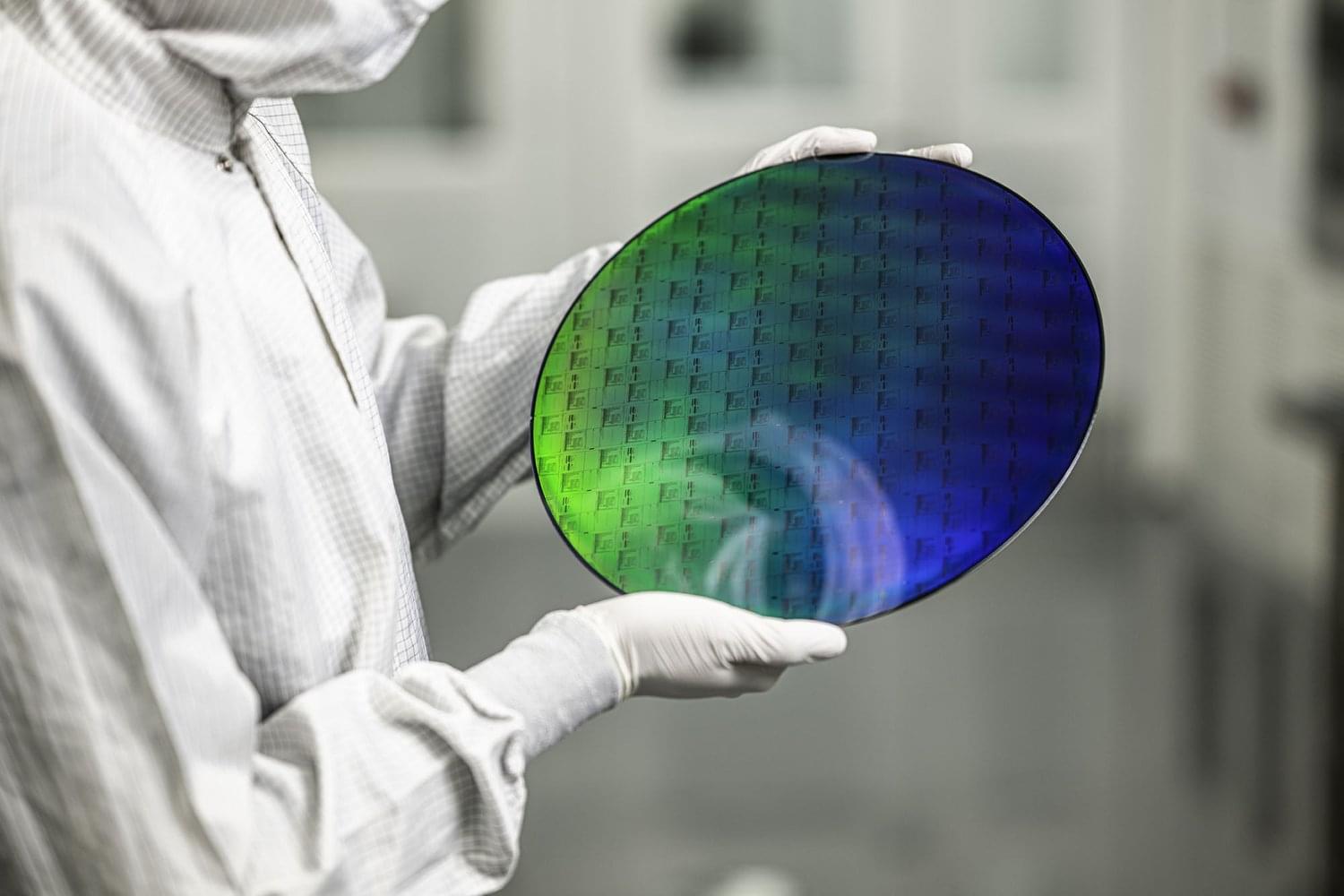
PsiQuantum unveiled Omega, a quantum photonic chipset designed for large-scale quantum computing. This development, detailed in a Nature publication, marks a significant milestone in the mass production of quantum chips. Manufactured in partnership with GlobalFoundries at their Albany, New York facility, Omega integrates advanced components essential for constructing million-qubit quantum computers. The chipset employs photonics technology, manipulating single photons for computations, which offers advantages such as simplified cooling mechanisms. PsiQuantum has achieved manufacturing yields comparable to standard semiconductors, producing millions of these chips. The company plans to establish two Quantum Compute Centers in Brisbane, Australia, and Chicago, Illinois, aiming for operational facilities by 2027. This progress positions PsiQuantum at the forefront of the quantum computing industry, alongside other major companies making significant strides in the field. Summary of the paper in Nature: For decades, scientists have dreamed of building powerful quantum computers using light—photonic quantum computers. These machines could solve complex problems far beyond the reach of today’s most advanced supercomputers. However, a major roadblock has been the sheer difficulty of manufacturing the components required at the necessary scale. Now, researchers have developed a manufacturable platform for photonic quantum computing, marking a significant breakthrough. Their system is built using silicon photonics, a technology that integrates optical components directly onto a chip, much like modern semiconductor chips. The team demonstrated key capabilities: * Ultra-precise qubits: They achieved a stunning 99.98% accuracy in preparing and measuring quantum states. * Reliable quantum interference: Independent photon sources interacted with a visibility of 99.50%, crucial for quantum logic operations. * High-fidelity entanglement: A critical quantum process, known as two-qubit fusion, reached 99.22% accuracy. * Seamless chip-to-chip connections: The team linked quantum chips with 99.72% fidelity, a crucial step for scaling up quantum systems. Looking ahead, the researchers highlight new technologies that will further improve performance, including better photon sources, advanced detectors, and high-speed switches. This work represents a major step toward large-scale, practical quantum computing, bringing us closer to a future where quantum machines tackle problems that are impossible today.
PsiQuantum’s focus is now on wiring these chips together across racks, into increasingly large-scale multi-chip systems – work the company is now expanding through its partnership with the U.S. Department of Energy at SLAC National Accelerator Laboratory in Menlo Park, California as well as a new manufacturing and testing facility in Silicon Valley. While chip-to-chip networking remains a hard research problem for many other approaches, photonic quantum computers have the intrinsic advantage that photonic qubits can be networked using standard telecom optical fiber without any conversion between modalities, and PsiQuantum has already demonstrated high-fidelity quantum interconnects over distances up to 250m.
In 2024, PsiQuantum announced two landmark partnerships with the Australian Federal and Queensland State governments, as well as the State of Illinois and the City of Chicago, to build its first utility-scale quantum computers in Brisbane and Chicago. Recognizing quantum as a sovereign capability, these partnerships underscore the urgency and race towards building million-qubit systems. Later this year, PsiQuantum will break ground on Quantum Compute Centers at both sites, where the first utility-scale, million-qubit systems will be deployed.