Researchers at the Max-Planck-Institute (MPL) proposed a novel way to entangle optical photons with phonons.


Unveiling faster and smarter reasoning in AI:*
Researchers have introduced a breakthrough in AI reasoning, specifically for Large Language Models (LLMs), with a method called*.
Interpretable Contrastive Monte Carlo Tree Search Reasoning — zitian-gao/SC-MCTS.
Discover how a revolutionary lunar spaceline could slash space travel costs and unlock new frontiers in exploration.
The group’s Aftershock II rocket reached an altitude of 470,000 feet (143,250 meters) last month.

Researchers from Baylor College of Medicine, Stanford University School of Medicine, and their collaborators have identified a novel compound called BHB-Phe, which is naturally produced by the body. Published in the journal Cell, their findings reveal that BHB-Phe regulates appetite and body weight by interacting with neurons in the brain.
Until now, BHB has been known as a compound produced by the liver to be used as fuel. However, in recent years, scientists have found that BHB increases in the body after fasting or exercise, prompting interest in investigating potential beneficial applications in obesity and diabetes.

Scientists have pioneered a new material based on ruthenium that demonstrates complex, disordered magnetic properties akin to those predicted for quantum spin liquids, an elusive state of matter.
This breakthrough in the study indicates significant potential for the development of quantum materials that transcend classical physical laws, providing new insights and applications in the quantum realm.
Novel Quantum Materials

The AI was forced to watch millions of hours of Minecraft footage, like a parent of any 8-year-old.
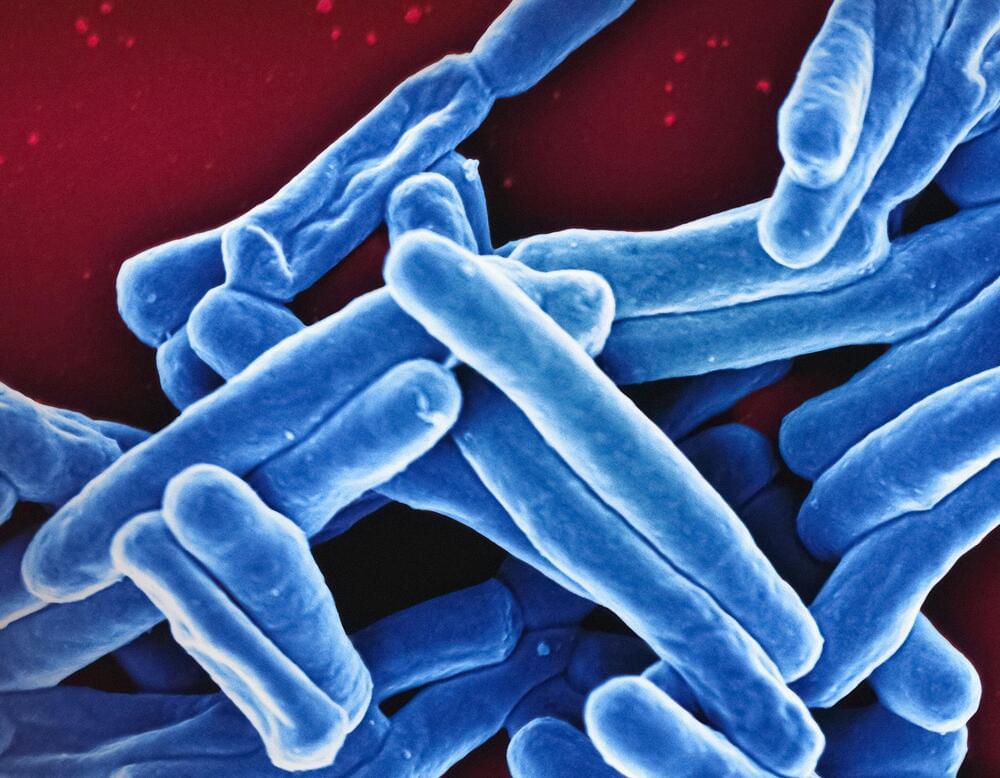
The rod-shaped tuberculosis (TB) bacterium, which the World Health Organization has once again ranked as the top infectious disease killer globally, is the first single-celled organism ever observed to maintain a consistent growth rate throughout its life cycle. These findings, reported by Tufts University School of Medicine researchers on November 15 in the journal Nature Microbiology, overturn core beliefs of bacterial cell biology and hint at why the deadly pathogen so readily outmaneuvers our immune system and antibiotics.
“The most basic thing you can study in bacteria is how they grow and divide, yet our study reveals that the TB pathogen is playing by a completely different set of rules compared to easier-to-study model organisms,” said Bree Aldridge, a professor of molecular biology and microbiology at the School of Medicine and a professor of biomedical engineering at the School of Engineering, as well as one of the paper’s co-senior authors along with Ariel Amir of the Weizmann Institute of Science.
TB bacteria are successful at surviving in humans because some parts of the infection can quickly evolve within their host, allowing these outliers to avoid detection or resist treatment. If someone has TB, it takes months of various antibiotics to be cured, and even then, this approach is only successful in 85% of patients. Aldridge and her colleagues hypothesize that gaps in our understanding of the basic biology behind this phenomenon have been holding back the development of more effective treatments.