How can the United States foster a robust commercialization ecosystem for fusion energy?


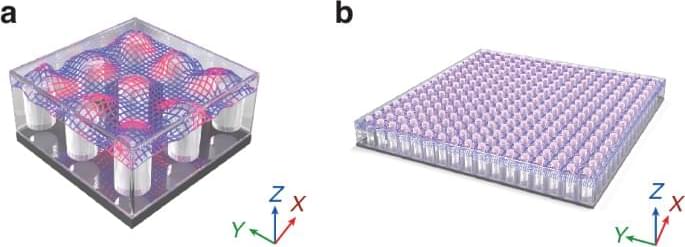
Transparent ceramic infinite speed computer.
Jiang, WX. Highly homogeneous zero-index metamaterials make devices more compact and perform better. Light Sci Appl 13, 104 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1038/s41377-024-01458-6

Dutch astrophysicists have observed the collision of two neutron stars, capturing unprecedented data that offers new insights into the formation of black holes.
The team, based at the Niels Bohr Institute at the University of Copenhagen, documented the birth of the smallest black hole ever recorded through their observations. Their findings, published in Astronomy and Astrophysics, illuminate the immense cosmic forces at play and how such events have shaped the universe and the creation of atoms.
Microorganisms—bacteria, viruses and other tiny life forms—may drive biological variation in visible life as much, if not more, than genetic mutations, creating new lineages and even new species of animals and plants, according to Seth Bordenstein, director of Penn State’s One Health Microbiome Center, professor of biology and entomology, and the Dorothy Foehr Huck and J. Lloyd Huck Endowed Chair in Microbiome Sciences.
Bordenstein and 21 other scientists from around the world published a paper in Science, summarizing research that they said drives a deeper understanding of biological variation by uniting life’s seen and unseen realms.
The authors explained that this newly described concept—holobiont biology —underpins a multidisciplinary and holistic understanding of how life’s forms and functions, from human disease to agricultural output, depend upon the relationships between microorganisms and their hosts. Penn State News spoke with Bordenstein about the paper and the emerging field of holobiont biology.
Spanning 18 kilometers, the new Fehmarn Belt fixed link between Germany and Denmark will be the world’s longest and deepest underwater tunnel, combining road and rail.
Once completed, the tunnel promises to reduce travel time, strengthen ties between Scandinavia and Central Europe, form a greener traffic lane, and boost train transport. The ten billion euro price tag, therefore, promises to be worth it and has the stamp of approval from the European Commission’s Ten-T Programme.
The underwater fixed link tunnel will consist of two two-lane highways divided by a service passage and two separate railways.

A patient’s own blood could be used to help create a material potentially capable of repairing their broken bones, new research suggests.
Scientists have transformed blood into a substance which successfully repaired bones in animals, paving the way for personalised 3D-printed implants.
They suggest the new material has the potential to create regenerative blood products that could be used as effective therapies to treat injury and disease.

CIEMAT scientists advance fusion energy for efficient reactors.
For decades, scientists have been working to develop reactors that can achieve fusion to meet the increasing need for clean and limitless energy.
The success of such experiments depends on multiple key factors, including optimized magnetic fields that could display enhanced fusion plasma confinement.
Introduced by researchers at Laboratorio Nacional de Fusión–CIEMAT, the new family of magnetic fields is claimed to be better suited for confining particles in fusion devices.
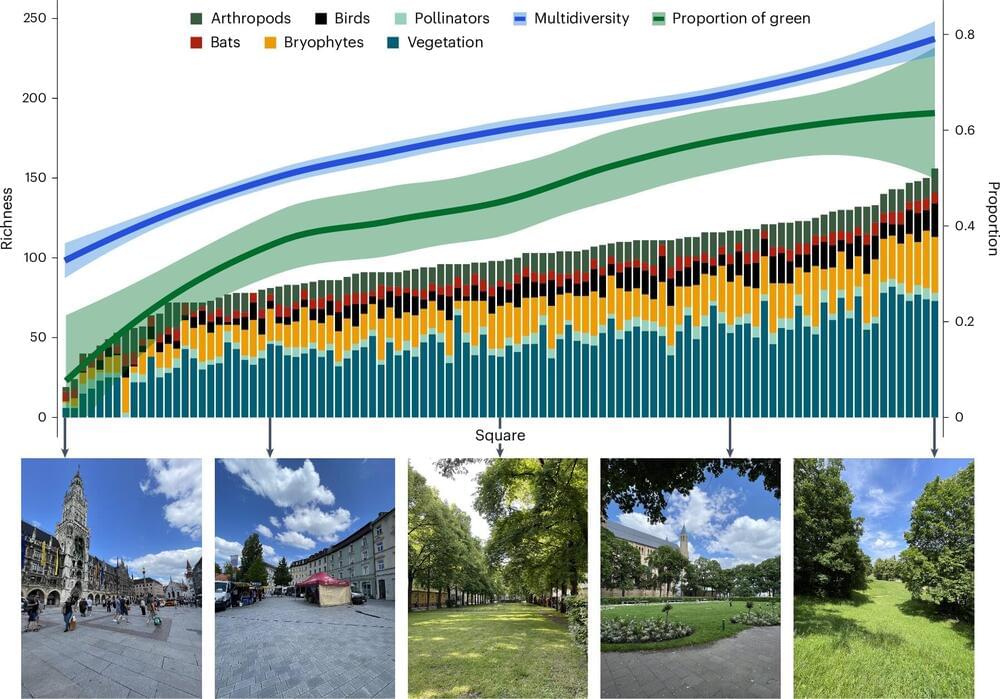
Animals and plants also live and thrive on public squares. This creates opportunities for greater biodiversity and well-being for the human population. Researchers at the Technical University of Munich (TUM) have studied at 103 locations in Munich how various factors affect flora and fauna.
They advocate a close examination of local conditions and a more nature-focused approach to the design of public spaces. Their results are published in Nature Cities.
Biodiversity is the foundation of functional ecosystems: diverse ecosystems are more stable and have greater resiliency to the effects of climate change. However, humans also benefit directly from having a wide range of plant and animal life in their surroundings.