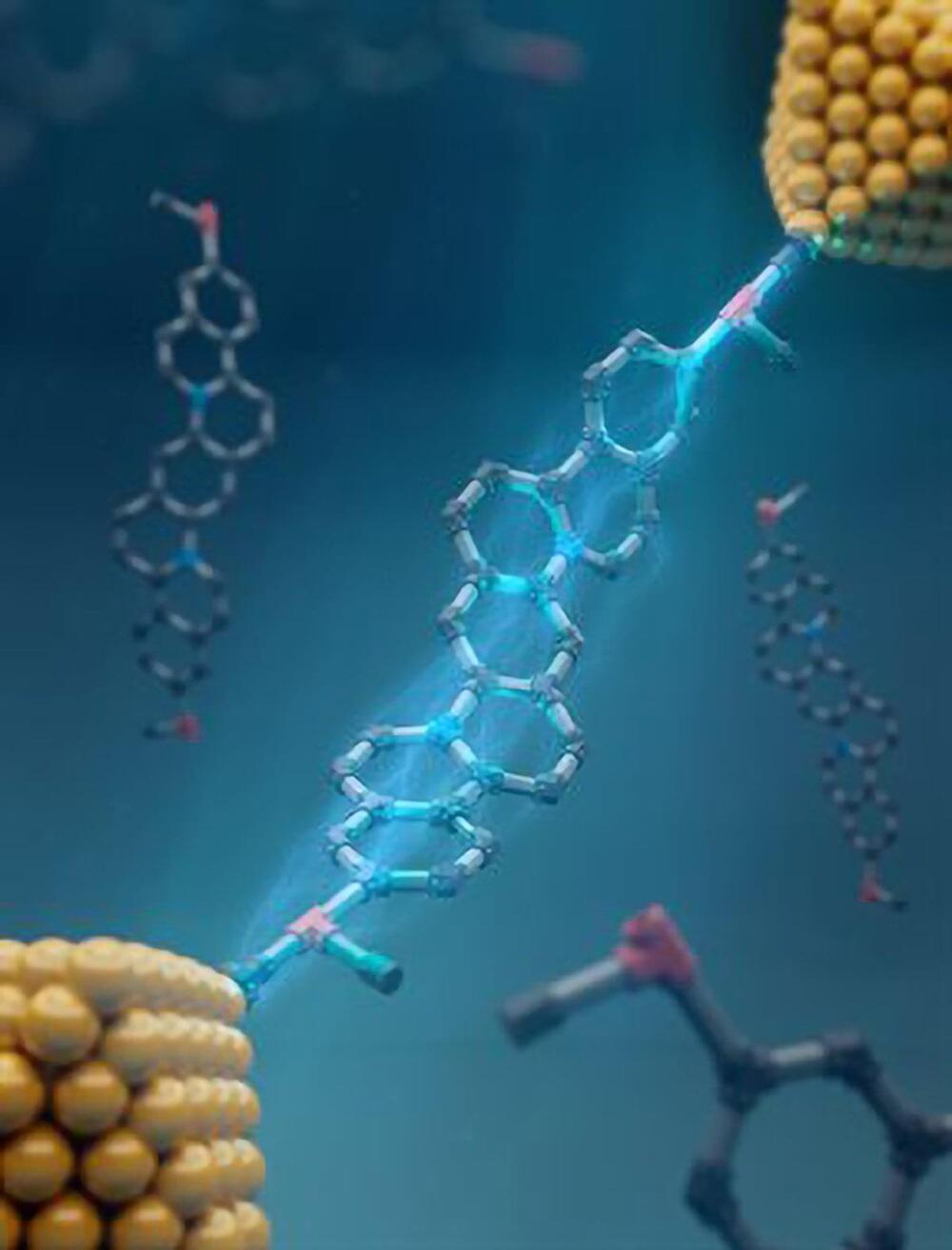
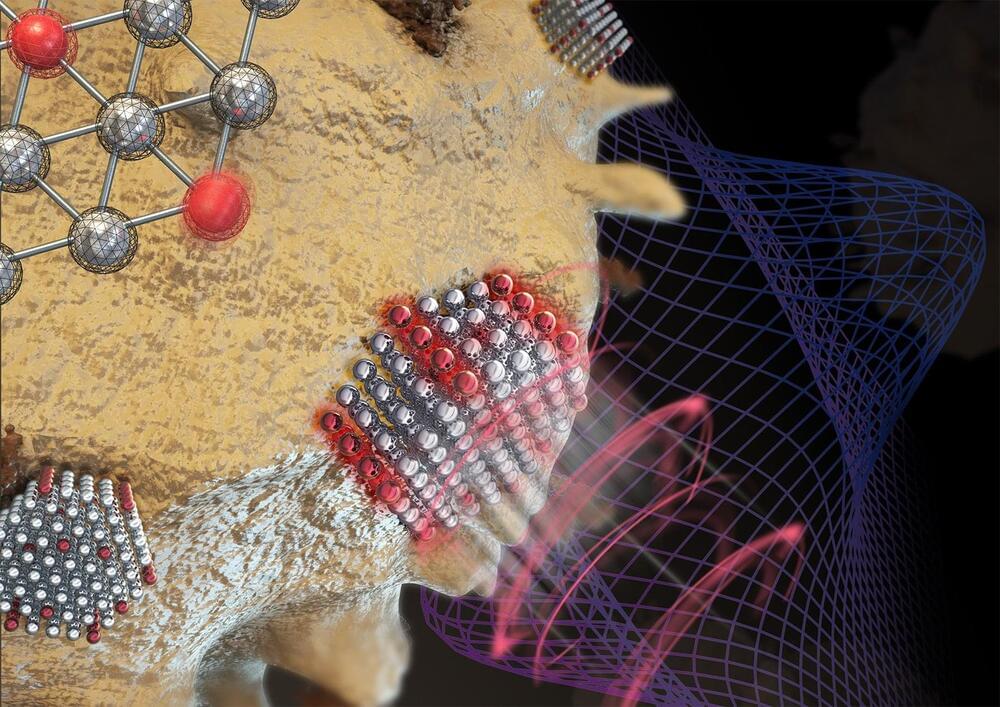
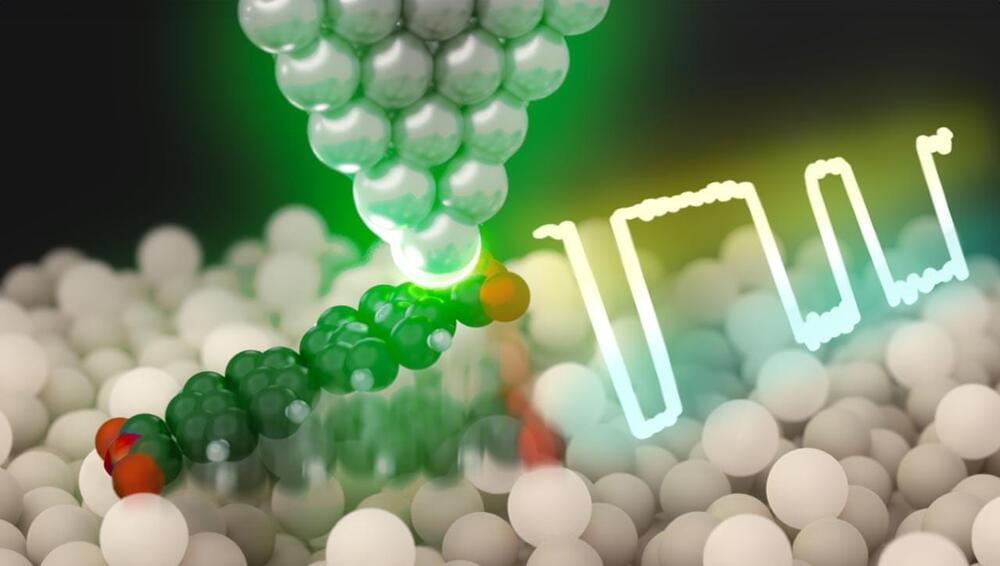
University of Illinois researchers have innovated in molecular electronics by creating stable, shape-persistent molecules with controlled conductance, using a new synthesis method, paving the way for more reliable miniaturized electronic devices.
As electronic devices keep shrinking, physical size limitations are starting to hinder the trend of doubling transistor density on silicon-based microchips every two years, as predicted by Moore’s law. Molecular electronics, which involves using single molecules as the fundamental components of electronic devices, presents a promising avenue for further miniaturizing small-scale electronics.
Devices that utilize molecular electronics require precise control over the flow of electrical current. However, the dynamic nature of these single molecule components affects device performance and impacts reproducibility.