The ASPIRE-FTD clinical trial will investigate the use of a gene therapy in people with frontotemporal dementia.


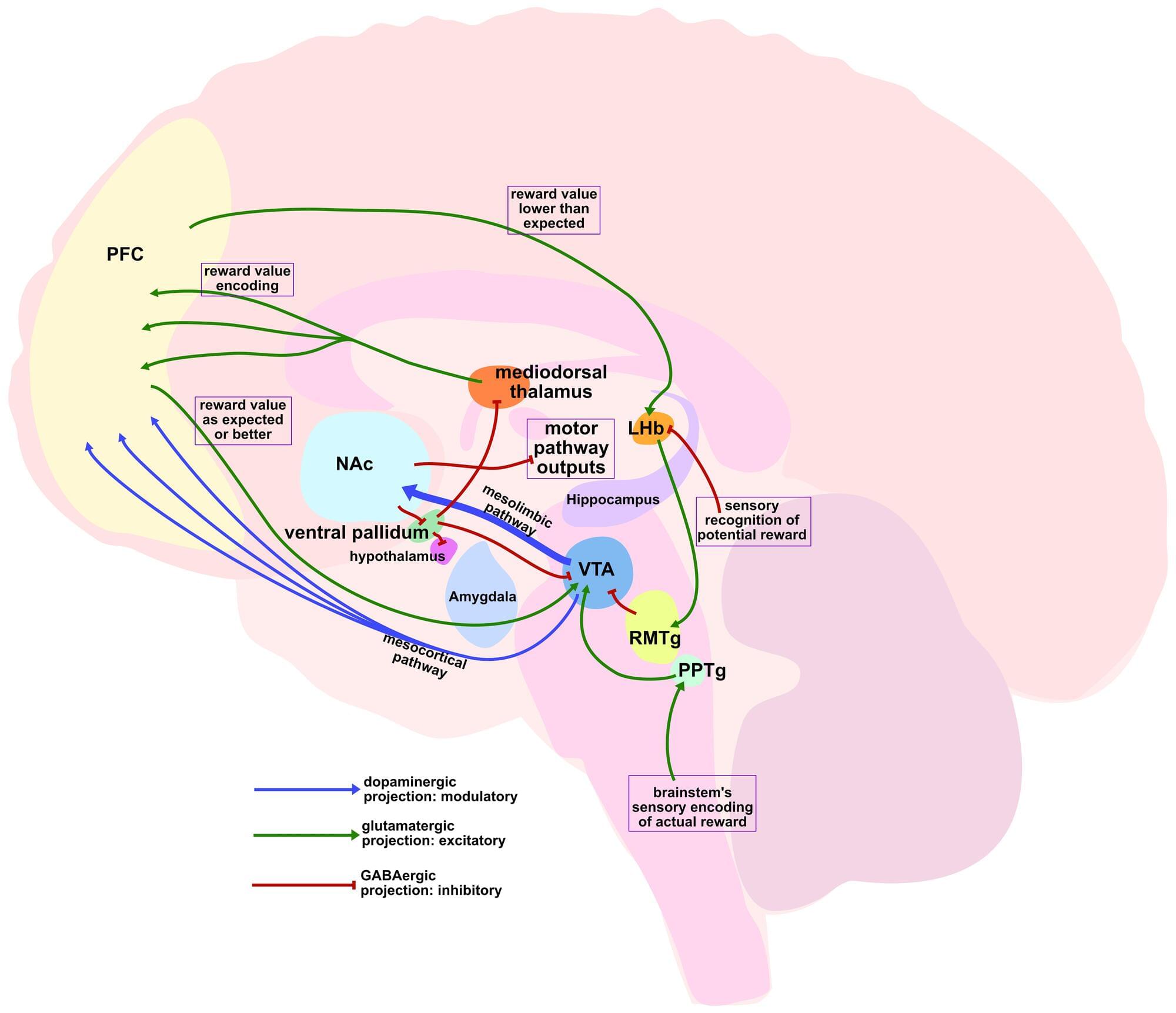
This content is also available on my website: https://logancollinsblog.com/2025/08/28/dopaminergic-neurons…epression/

The formulation of quantum field theory in Minkowski spacetime, which emerges from the unification of special relativity and quantum mechanics, is based on treating time as a parameter, assuming a fixed arrow of time, and requiring that field operators commute for spacelike separations. This procedure is questioned in the context of quantum field theory in curved spacetime (QFTCS). In 1935, Einstein and Rosen (ER), in their seminal paper [1] proposed that “a particle in the physical Universe has to be described by mathematical bridges connecting two sheets of spacetime” which involved two arrows of time. We further establish that the quantum effects at gravitational horizons aesthetically involve the physics of quantum inverted harmonic oscillators that have phase space horizons. Recently proposed direct-sum quantum theory reconciles the ER’s vision by introducing geometric superselection sectors associated with the regions of spacetime related by discrete transformations. This new understanding of the ER bridges promises a unitary description of QFTCS, along with observer complementarity. Furthermore, we present compelling evidence for our new understanding of ER bridges in the form of large-scale parity asymmetric features in the cosmic microwave background, which is statistically 650 times stronger than the standard scale-invariant power spectrum from the typical understanding of inflationary quantum fluctuations when compared with the posterior probabilities associated with the model given the data. We finally discuss the implications of this new understanding in combining gravity and quantum mechanics.
Gravity and quantum mechanics.
Questions to inspire discussion.
💰 Q: What gives Tesla an edge over competitors like Waymo in the robotaxi market? A: Tesla has a significant cost advantage and superior scalability compared to competitors, allowing for faster expansion and potentially lower operating costs.
🔄 Q: How does Tesla’s rapid scaling affect its competition? A: Tesla’s ability to rapidly scale its robotaxi service puts competitors like Waymo in “big trouble” due to Tesla’s expanding coverage and potential market dominance.
Market Impact.
📈 Q: Why is Tesla’s robotaxi expansion considered a “big deal”? A: The rapid scale and massive expansion of Tesla’s robotaxi service area in Austin demonstrates the company’s ability to quickly deploy and grow autonomous ride-hailing services, potentially disrupting the transportation industry.
🔮 Q: What does this expansion suggest about Tesla’s future in the robotaxi market? A: Tesla’s aggressive expansion suggests it’s positioning itself as a dominant player in the emerging robotaxi market, with the potential to outpace and outperform established competitors like Waymo.

A new study by researchers at Baylor College of Medicine brings hope for a more personalized approach to treating estrogen receptor-positive (ER+) breast cancer, the most common type of this cancer. The team identified a biomarker in preclinical ER+ breast cancer models that indicates that the tumor is more likely to respond to treatment with CDK4/6 inhibitors.
The findings support further clinical studies to determine whether this marker may help identify patients who could benefit from CDK4/6 inhibitors. The study appears in Science Translational Medicine.
ER+ breast cancers rely on estrogen to grow and are typically treated by endocrine therapies that block the effects of estrogen. To improve outcomes, drugs called CDK4/6 inhibitors, such as abemaciclib and ribociclib, are added to endocrine therapy to prevent relapse.

Enjoy the videos and music that you love, upload original content and share it all with friends, family and the world on YouTube.