W/ Dr. Emma Pierson of UC Berkeley.
Speakers: Emma Pierson, Cecile Tamura
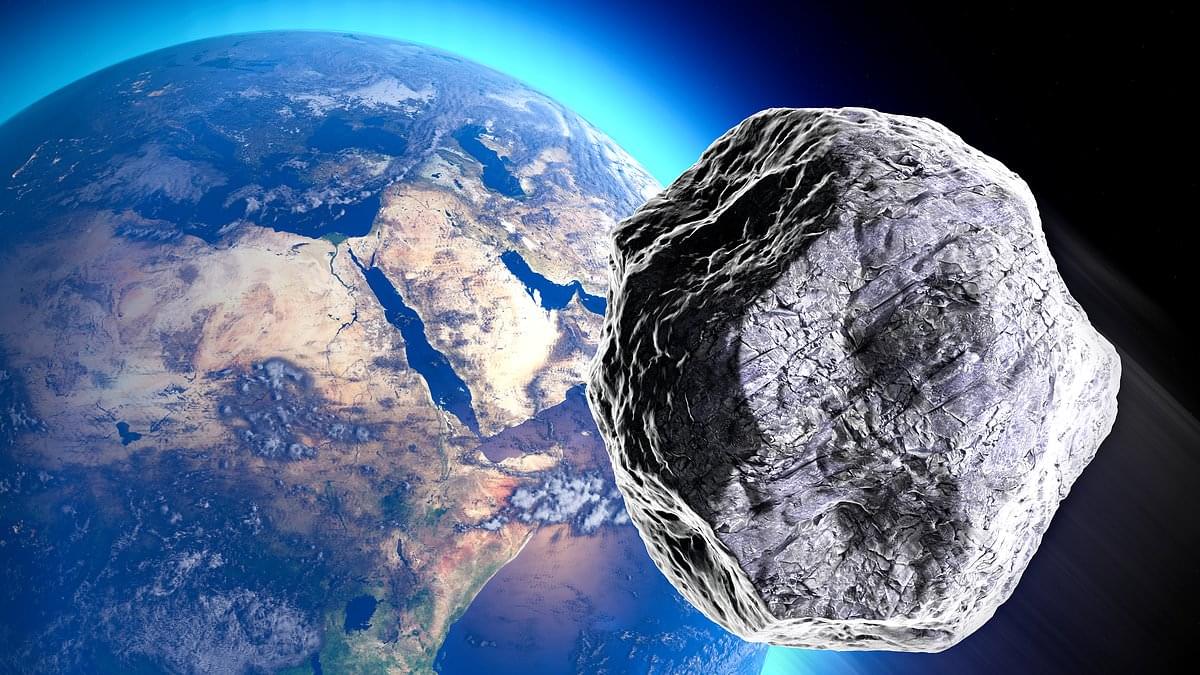


2.4 billion years from now there will be a black hole colliding with the Milky Way.
A supermassive black hole hidden in the Large Magellanic Cloud is on a collision course with the Milky Way! Scientists discovered it using hypervelocity stars, and in 2.4 billion years, it will merge with Sagittarius A at our galaxy’s center. This event could reshape our galaxy and trigger gravitational waves! 🌌 Want to know what happens next? Watch the full video to explore the science behind this cosmic collision. Don’t miss it—subscribe now for more space discoveries! 🚀
Paper link: https://arxiv.org/abs/2502.
Chapters:
00:00 Introduction.
00:30 The Discovery and Characteristics of the Supermassive Black Hole.
03:11 The LMC-Milky Way Collision and Its Consequences.
05:34 Other Famous Supermassive Black Holes and What They Teach Us.
07:23 Outro.
07:35 Enjoy.
MUSIC TITLE : Starlight Harmonies.

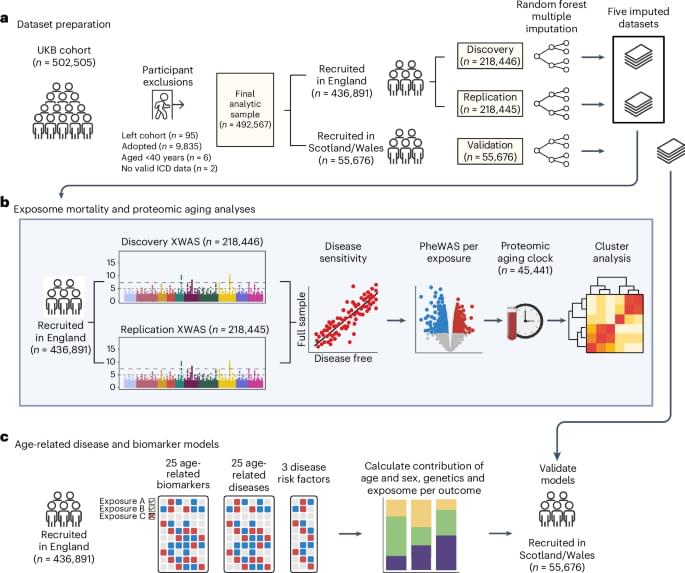
Based on a systematic analysis of environmental exposures associated with aging and mortality in the UK Biobank, the relative contributions of such exposures and genetic risk for mortality and a range of age-related diseases were compared, highlighting the potential beneficial effects of environment-focused interventions.

“ tabindex=”0” accuracy and scale, brings scientists closer to understanding how neurons connect and communicate.
Mapping Thousands of Synaptic Connections
Harvard researchers have successfully mapped and cataloged over 70,000 synaptic connections from approximately 2,000 rat neurons. They achieved this using a silicon chip capable of detecting small but significant synaptic signals from a large number of neurons simultaneously.

Summary: Researchers analyzed human motivation from an evolutionary perspective, identifying 15 key motives that drive behavior. These motives, grouped into five categories—environmental, physiological, reproductive, psychological, and social—reflect adaptations that helped early humans survive.
The study used network analysis of survey responses to reveal how these motives interconnect and influence one another. Notably, Status and Play emerged as central to motivational structures, facilitating resource access and skill development.
Findings also showed age and gender differences in motivational priorities, with younger individuals focusing on Status and Play, while older adults prioritize Comfort and Fear. The results have broad applications in marketing, AI, and mental health, helping tailor strategies to different motivational needs.
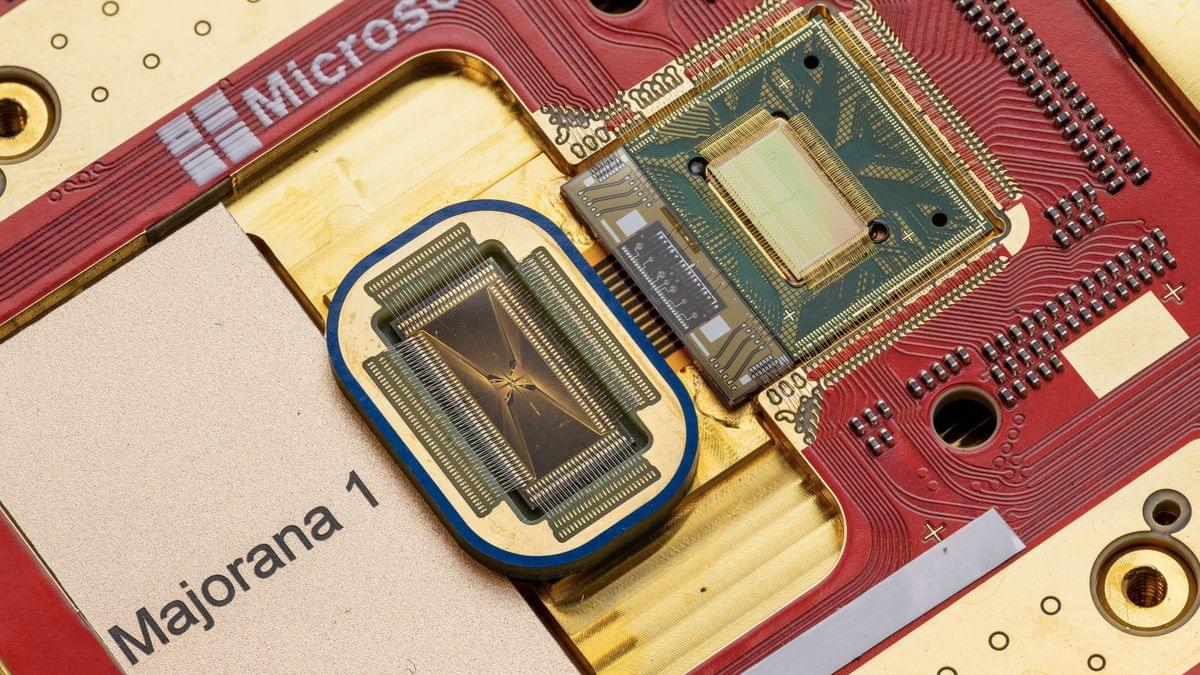
Majorana’s theory proposed that a particle could be its own antiparticle. That means it’s theoretically possible to bring two of these particles together, and they will either annihilate each other in a massive release of energy (as is normal) or can coexist stably when pairing up together — priming them to store quantum information.
These subatomic particles do not exist in nature, so to nudge them into being, Microsoft scientists had to make a series of breakthroughs in materials science, fabrication methods and measurement techniques. They outlined these discoveries — the culmination of a 17-year-long project — in a new study published Feb. 19 in the journal Nature.
Chief among these discoveries was the creation of this specific topoconductor, which is used as the basis of the qubit. The scientists built their topoconductor from a material stack that combined a semiconductor made of indium arsenide (typically used in devices like night vision goggles) with an aluminum superconductor.
When discussing motors, most people think of those in vehicles or machines. However, biological motors have existed for millions of years in microorganisms. Many bacteria use tail-like structures called flagella, which rotate to propel them through fluids. This movement is driven by a protein complex known as the flagellar motor.
The flagellar motor has two key components: the rotor and the stators. The rotor, a large rotating structure anchored to the cell membrane, drives flagellum movement. The stators, smaller structures surrounding the rotor, contain ion pathways that transport protons or sodium ions, depending on the bacterial species.
A species is a group of living organisms that share a set of common characteristics and are able to breed and produce fertile offspring. The concept of a species is important in biology as it is used to classify and organize the diversity of life. There are different ways to define a species, but the most widely accepted one is the biological species concept, which defines a species as a group of organisms that can interbreed and produce viable offspring in nature. This definition is widely used in evolutionary biology and ecology to identify and classify living organisms.
