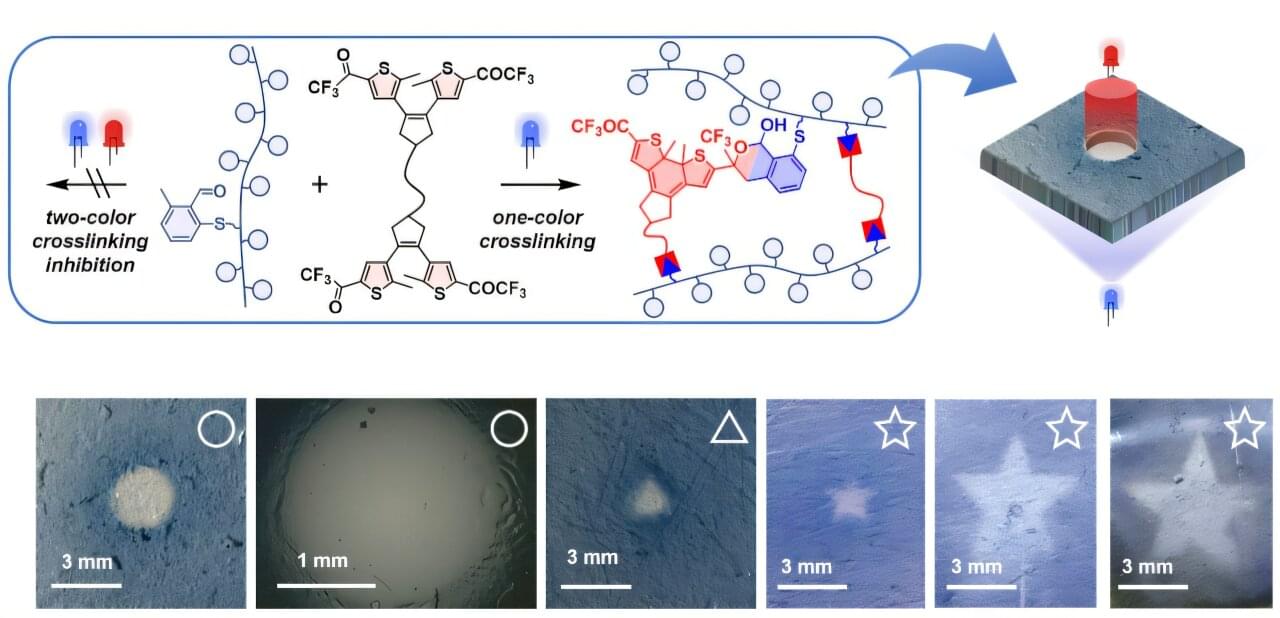
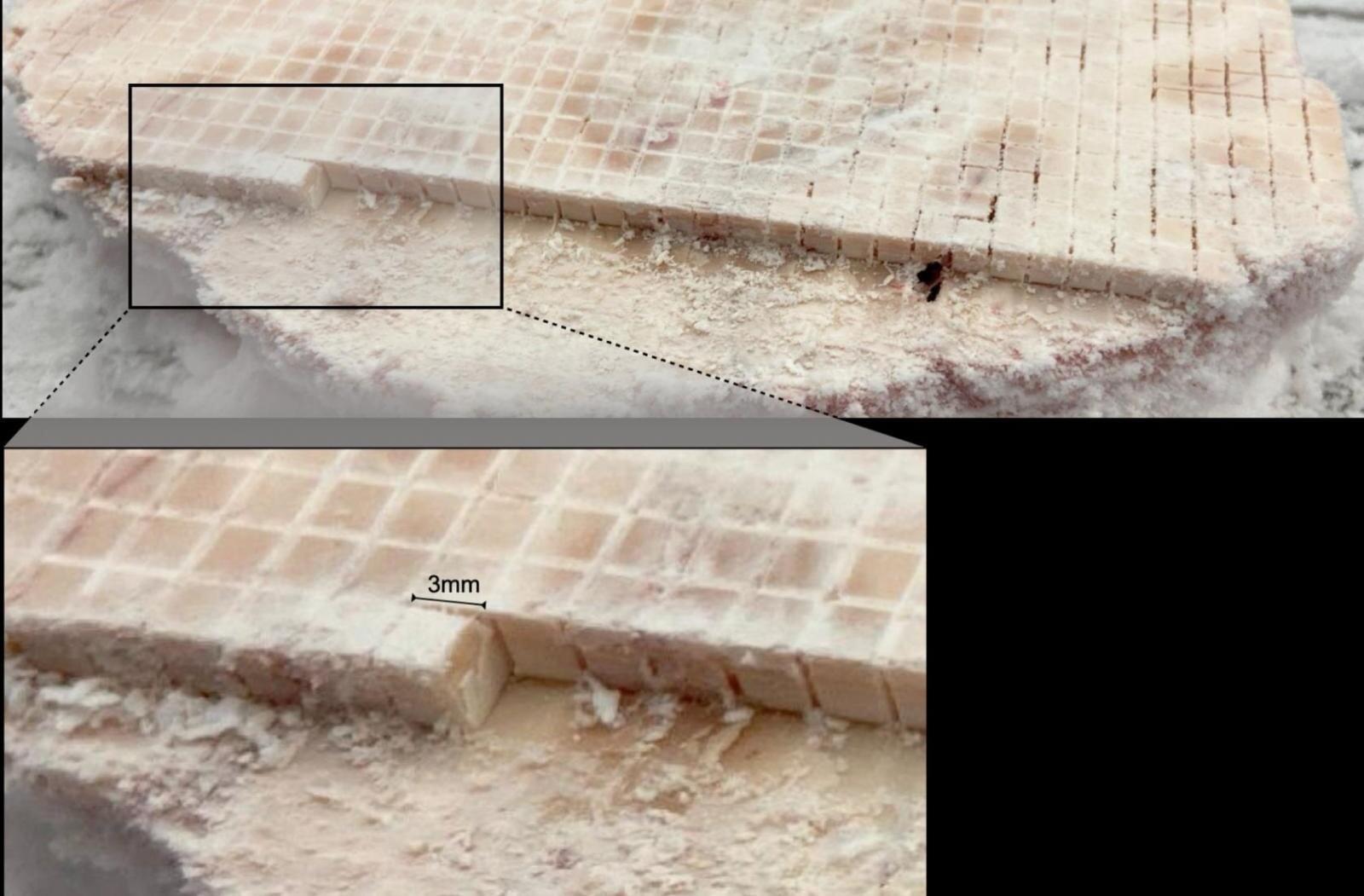
Researchers at the UAB have developed a new chemical reaction to form solid polymeric networks using light (photocuring) which will allow the preparation of solid materials with controlled shapes measuring under a thousandth of a millimeter. The research is key for the development of new, performance-enhanced lithographic and 3D printing techniques.
At present, 3D printing is an increasingly widespread and accessible technology, typically involving the formation of solid polymeric materials in a specific region, either by extruding pre-formed polymers or by generating them in situ from their corresponding monomers, the molecules that make up polymers.
However, these techniques often suffer from several drawbacks, such as long printing times or low resolution, preventing the production of printed materials with micrometric dimensions.