The needle-free injection, given for up to two years, is custom-built for people to stop their melanoma returning — which experts believe will herald a new



GPT‑4.1, GPT‑4.1 mini, and GPT‑4.1 nano are available now to all developers.
Through efficiency improvements to our inference systems, we’ve been able to offer lower prices on the GPT‑4.1 series. GPT‑4.1 is 26% less expensive than GPT‑4o for median queries, and GPT‑4.1 nano is our cheapest and fastest model ever. For queries that repeatedly pass the same context, we are increasing the prompt caching discount to 75% (up from 50% previously) for these new models. Finally, we offer long context requests at no additional cost beyond the standard per-token costs.
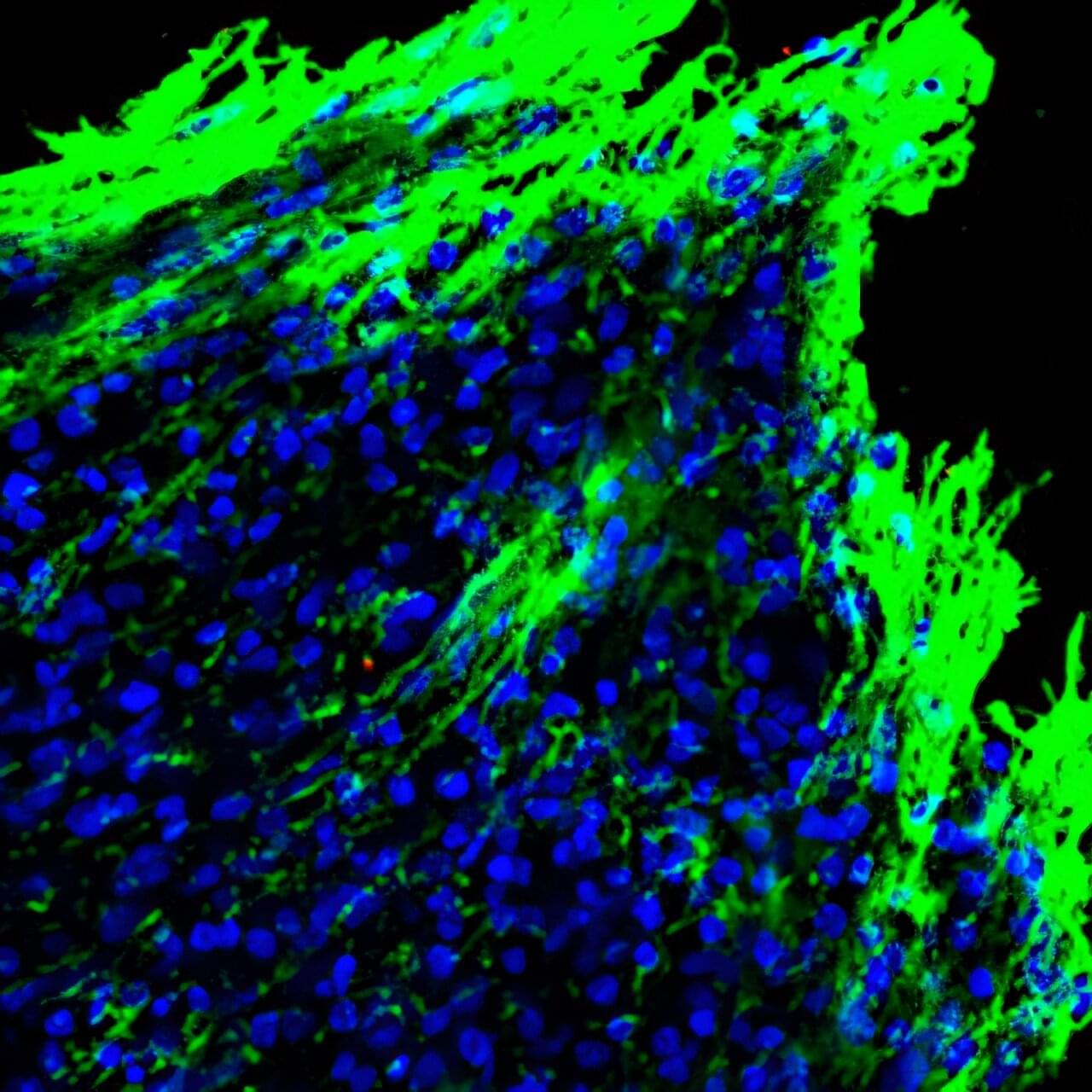
An estimated 18,000 people in the United States annually suffer from new injuries to their spinal cords. Unfortunately for those afflicted, no FDA-approved therapy is currently available. Scientists at UC San Diego are looking into the body’s healing mechanisms for clues on recovery from spinal cord injury.
A new study by researchers in the Department of Neurobiology (School of Biological Sciences) has uncovered a source of potential hope in the form of a gene that is known to be involved in key developmental processes in various tissues. Receptor tyrosine kinase, or “RYK,” has been previously associated with the regeneration of axons, the long, thin extensions of nerve cells that transmit impulses. However, RYK, the researchers found, is involved in many more functions.
Professor Yimin Zou and colleagues have published surprising results that reveal that RYK expression inhibits wound healing, offering implications for new treatments for paralysis after spinal cord injury. Their paper, “Astrocytic RYK signaling coordinates scarring and wound healing after spinal cord injury,” was published April 10, 2025 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences.
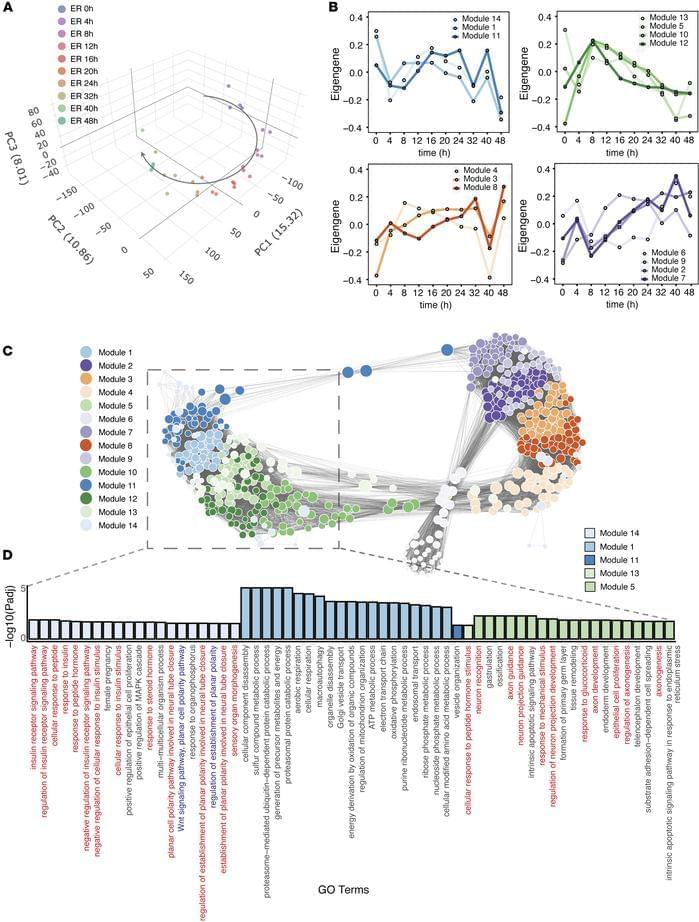
Megha Padi & team now show pyrvinium pamoate has antitumor activity through multiple pathways in pre-clinical models:
The figure shows tumor tissue from control mice or those treated with pyrvinium.
1University of Arizona Cancer Center, Tucson, Arizona, USA.
2Department of Molecular and Cellular Biology, University of Arizona, Tucson, Arizona, USA.
3Department of Pharmacology and Toxicology, The University of Arizona R. Ken Coit College of Pharmacy, Skaggs Pharmaceutical Sciences Center, Tucson, Arizona, USA.

A new multicenter study by researchers at the Icahn School of Medicine at Mount Sinai, in collaboration with the Clinical Proteomic Tumor Analysis Consortium (CPTAC) and colleagues around the world, has discovered that the genes we are born with—known as germline genetic variants—play a powerful, underappreciated role in how cancer develops and behaves.
Published in the April 14 online issue of Cell, the study, “Precision Proteogenomics Reveals Pan-Cancer Impact of Germline Variants,” is the first to detail how millions of inherited genetic differences influence the activity of thousands of proteins within tumors.
Drawing on data from more than 1,000 patients across 10 different cancer types, the research illustrates how a person’s unique genetic makeup can shape the biology of their cancer.

Researchers at Imperial College London and Lund University in Sweden found that by giving heart attack patients two drugs together – statins and ezetimibe, a cholesterol-lowering drug – their risk of another heart attack, stroke or death was reduced.
“This study shows that we could save lives and reduce further heart attacks by giving patients a combination of two low-cost drugs,” said Prof Kausik Ray, of Imperial’s School of Public Health.
But at the moment patients across the world aren’t receiving these drugs together. That is causing unnecessary and avoidable heart attacks and deaths – and also places unnecessary costs on healthcare systems.