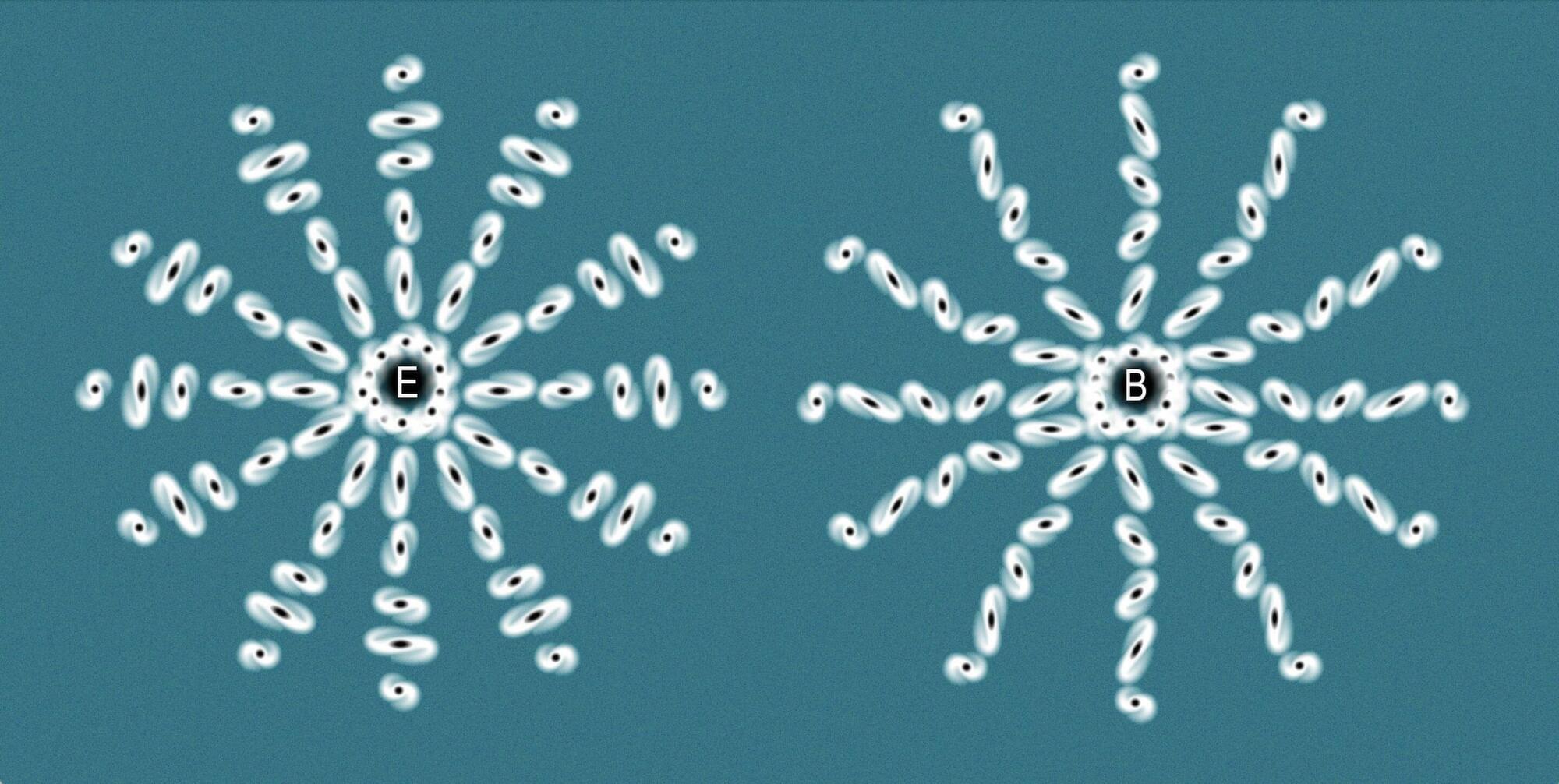
A study published in the Journal of Cosmology and Astroparticle Physics (JCAP) presents a methodology to test the assumption of cosmic homogeneity and isotropy, known as the Cosmological Principle, by leveraging weak gravitational lensing—a light distortion effect described by general relativity—in astronomical images collected by new observatories such as the Euclid Space Telescope. Finding evidence of anomalies in the Cosmological Principle could have profound implications for our current understanding of the universe.
“The Cosmological Principle is like an ultimate kind of statement of humility,” explains James Adam, astrophysicist at the University of the Western Cape, Cape Town, South Africa, and lead author of the new paper. According to the Cosmological Principle, not only are we not at the center of the universe, but a true center does not exist.
A further assumption, similar to but distinct and independent from homogeneity, is that the universe is also isotropic, meaning it has no preferred directions. These assumptions underlie the Standard Model of Cosmology, the theoretical framework used to explain the origin, evolution, and current state of the universe. It is currently the most robust and consistent model, verified by numerous scientific observations, though not yet perfect.