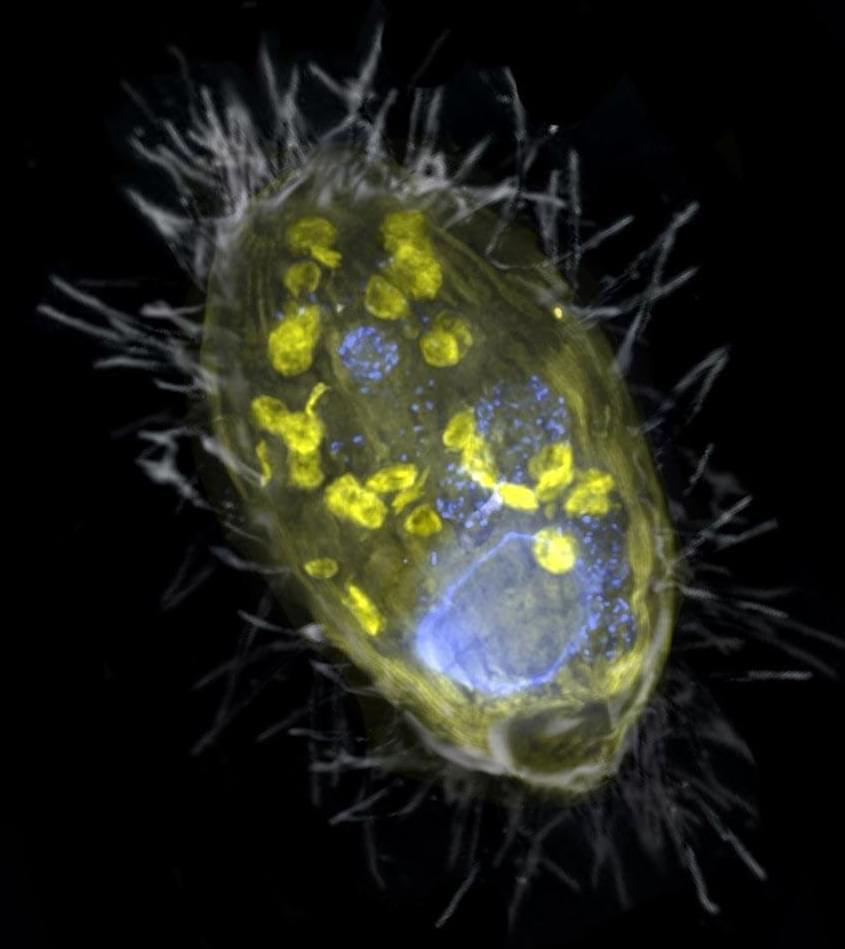
Scientists have discovered a remarkable new form of symbiosis — a bacterium that lives inside a single-celled organism (a ciliate) and provides it with energy. Unlike mitochondria, which use oxygen, this microbe powers its host by breathing nitrate.
Initially found in a freshwater lake, researchers set out to determine how widespread these microbes are. To their surprise, they uncovered them in diverse environments worldwide, from lakes and groundwater to even wastewater. This discovery challenges our understanding of microbial partnerships and reveals how these tiny organisms play a hidden yet significant role in global ecosystems.
A New Symbiotic Discovery