Many survivors of the attack by the Aum Shinrikyo doomsday cult still suffer from physical aftereffects and post-traumatic stress disorder.
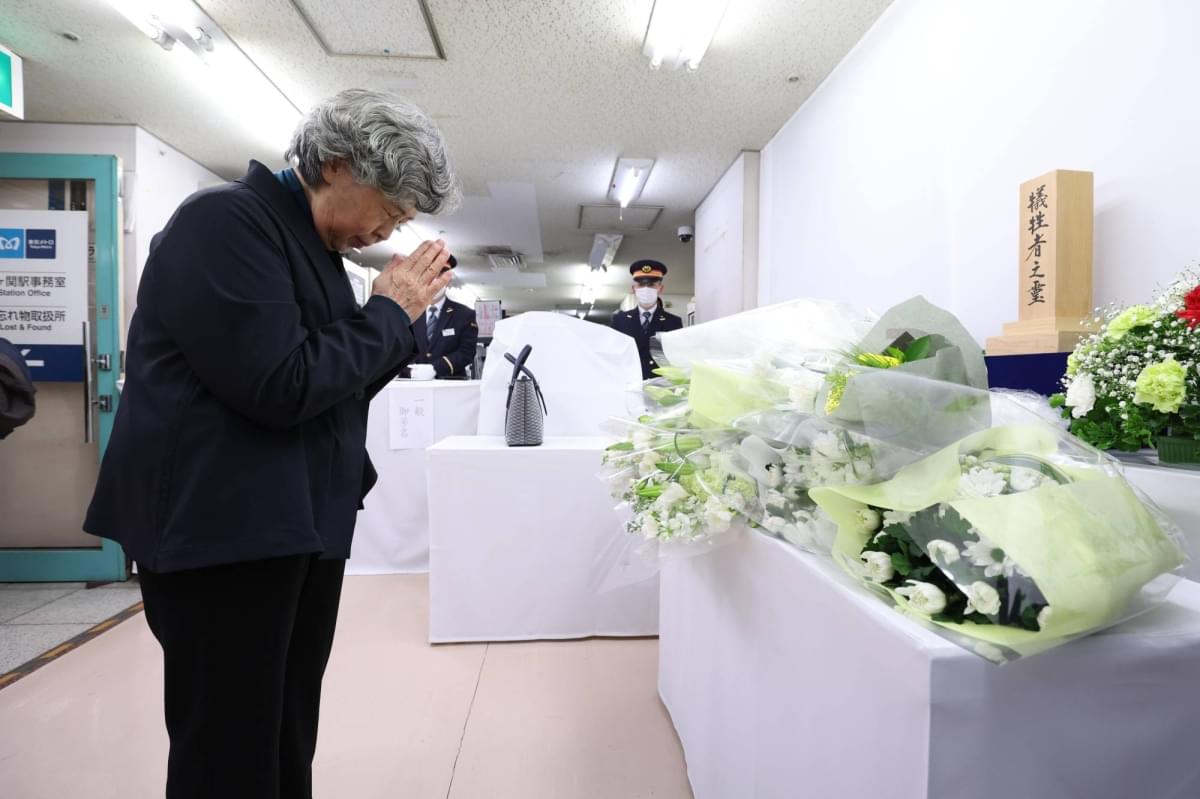



People in Japan are remembering the victims of the sarin gas attack on the Tokyo subway system on the 30th anniversary of the deadly incident on Thursday.
Members of the Aum Shinrikyo cult released highly toxic nerve gas in packed rush-hour subway cars on three lines in central Tokyo on March 20, 1995. Fourteen people died and about 6,300 others were injured.
At Kasumigaseki subway station, staff observed a moment of silence at around 8 a.m., almost the exact time of the attack.
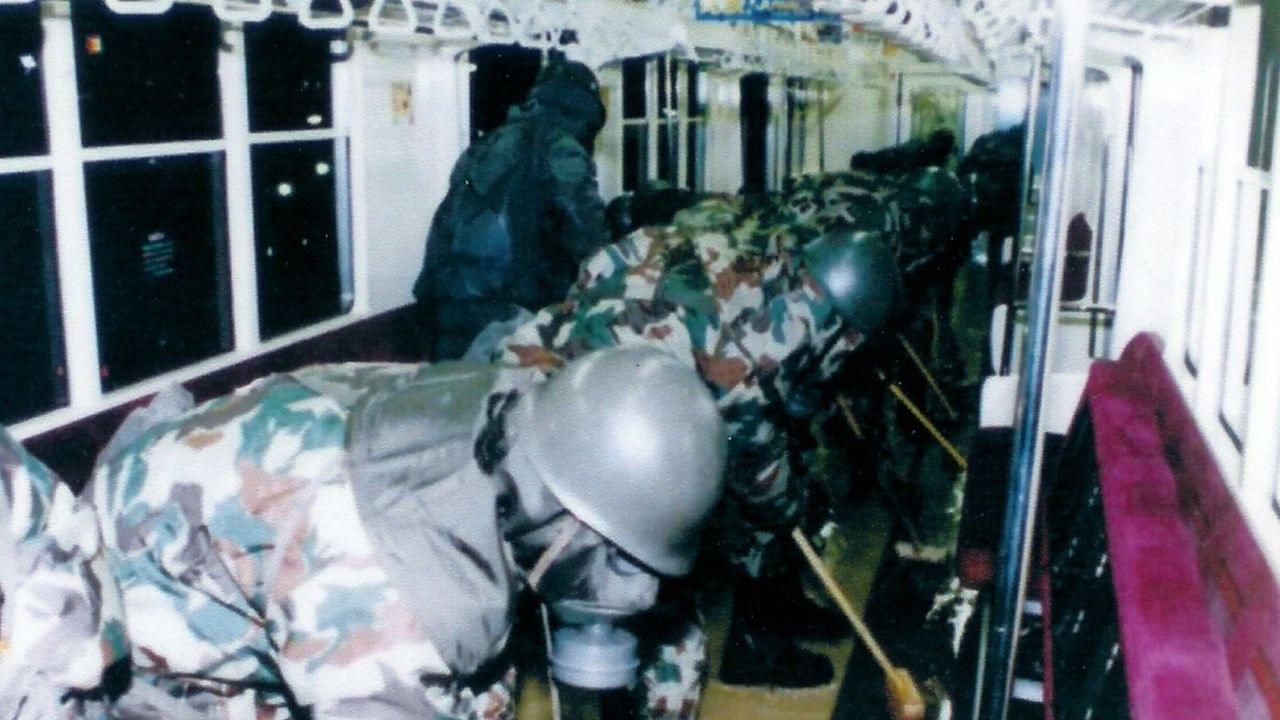



Japan on Thursday marked the 30th anniversary of the nerve gas attack on the Tokyo subway system by the AUM Shinrikyo doomsday cult, with the relatives of the victims striving to keep alive the memory of the worst terrorist attack on Japanese soil.
At Kasumigaseki Station in the Japanese capital, officials observed a moment of silence at around 8 a.m., the time when the deadly sarin nerve agent was released in train cars on March 20, 1995.
Shizue Takahashi, 78, who lost her husband, a deputy stationmaster at Kasumigaseki Station, in the attack, laid flowers at the site, and said, “It was a long 30 years. I don’t want people to forget about the incident.”
Tesla is advancing towards a sustainable future through innovations in energy solutions, autonomous vehicles, and humanoid robots, while fostering a culture of safety and continuous improvement. ## Questions to inspire discussion s Future Production and Impact ” + 🚗 Q: How many vehicles does Tesla aim to produce by 2025? A: Tesla plans to produce over 10 million vehicles in 2025, up from just 20 in 2010, enabled by their compact, high-output factories.
S vision for Optimus humanoid robots? ” +A: Tesla envisions Optimus robots creating a future of abundance for all, producing goods and services with no limit when combined with solar energy and batteries.
🚕 Q: When will autonomous Teslas become widespread? A: Tesla expects autonomous vehicles to dominate roads within 5 years, with a software update enabling 10-100x more usefulness through robotaxi services. s Service and Energy Solutions ” + s approach to customer service? ” +s service team aims to provide a loveable experience, recognizing that future sales depend on service reputation and word-of-mouth marketing. ” + 🔋 Q: How do Megapack and Powerwall 3 benefit homeowners? A: Megapack and Powerwall 3 enable off-grid living and energy assurance, with Powerwall 3 and solar making homes self-sufficient during outages.
S unique about Teslas Supercharger network allows convenient road trips across the US, Mexico, Europe, and China, with charging speeds faster than a restroom break. ” +s AI and Manufacturing Innovations ” + s role in Teslas most powerful AI training systems. ” + s AI hardware compare to others? ” +s AI4 hardware is the most powerful and efficient AI inference computer, operating at very low power in all vehicles. ” + s innovative about TeslaA: The Cybertruck line aims to produce cars in under 5 seconds, using rapid liquid metal casting and automation, resembling a high-speed electronics line. ## Future of Transportation and Energy.
S full self-driving cars? ” +s self-driving cars achieve 10x human safety, never getting tired or distracted, and free up 10–12 hours per week for drivers. ” + s batteries contribute to grid stability? ” +A: Powerwall and Megapack batteries stabilize the grid by absorbing power spikes and filling drops, acting as a virtual grid in neighborhoods.
🚖 Q: How will the role of Uber and taxi drivers change? A: In the future, Uber and taxi drivers will manage fleets of self-driving cars instead of driving individually. ## Investment and Future Technologies.

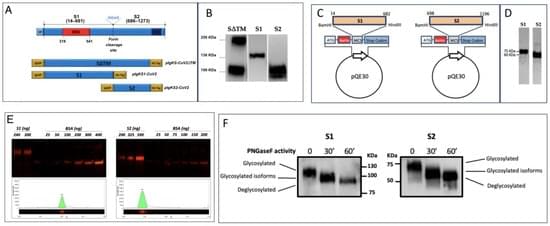
The emergence of the new pathogen SARS-CoV-2 determined a rapid need for monoclonal antibodies (mAbs) to detect the virus in biological fluids as a rapid tool to identify infected individuals to be treated or quarantined. The majority of commercially available antigenic tests for SARS-CoV-2 rely on the detection of N antigen in biologic fluid using anti-N antibodies, and their capacity to specifically identify subjects infected by SARS-CoV-2 is questionable due to several structural analogies among the N proteins of different coronaviruses. In order to produce new specific antibodies, BALB/c mice were immunized three times at 20-day intervals with a recombinant spike (S) protein. The procedure used was highly efficient, and 40 different specific mAbs were isolated, purified and characterized, with 13 ultimately being selected for their specificity and lack of cross reactivity with other human coronaviruses. The specific epitopes recognized by the selected mAbs were identified through a peptide library and/or by recombinant fragments of the S protein. In particular, the selected mAbs recognized different linear epitopes along the S1, excluding the receptor binding domain, and along the S2 subunits of the S protein of SARS-CoV-2 and its major variants of concern. We identified combinations of anti-S mAbs suitable for use in ELISA or rapid diagnostic tests, with the highest sensitivity and specificity coming from proof-of-concept tests using recombinant antigens, SARS-CoV-2 or biological fluids from infected individuals, that represent important additional tools for the diagnosis of COVID-19.