Sci. Adv. 10, eadp5805 (2024). DOI:10.1126/sciadv.adp5805
Select the format you want to export the citation of this publication.
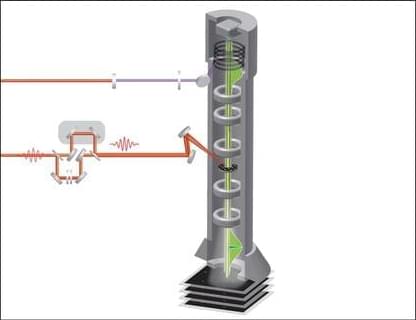
Inside every cell, inside every nucleus, your continued existence depends on an incredibly complicated dance. Proteins are constantly wrapping and unwrapping DNA, and even minor missteps can lead to cancer. A new study from the University of Chicago reveals a previously unknown part of this dance—one with significant implications for human health.
In the study, published Oct. 2 in Nature, a team of scientists led by UChicago Prof. Chuan He, in collaboration with University of Texas Health Science Center at San Antonio Prof. Mingjiang Xu, found that RNA plays a significant role in how DNA is packaged and stored in your cells, via a gene known as TET2. The paper is titled “RNA m5C oxidation by TET2 regulates chromatin state and leukaemogenesis.”
This pathway also appears to explain a long-standing puzzle about why so many cancers and other disorders involve TET2-related mutations—and suggests a set of new targets for treatments.
Unlocking the complexities of the fruit fly brain is a crucial step toward understanding the human brain. Fruit flies share many genetic similarities with humans, making them a valuable model organism for studying brain functions as well as diseases.
“An estimated 75% of human genes related to diseases have homologs in the fly genome,” Sebastian Seung, co-leader of the research team, told Interesting Engineering (IE).
“We’ve long known about the molecular similarities between fly and human brains. We have been slower to realize that there are also similarities at the circuit level, revealed by examining patterns of connectivity. We now know that fly circuits for olfaction, vision, and navigation have architectural similarities with mammalian circuits for the same functions,” Seung added.
The team says that DNA — known for its stability and density — could be an ideal candidate for MRI data storage.
Brain MRI scans provide invaluable insights into our bodies.
Interestingly, the team successfully encoded 11.28 megabytes of brain MRI data into roughly 250,000 DNA sequences. This translates to a data density of 2.39 bits per base.
The encoded oligos, which are the DNA sequences containing the MRI data, are stored in a “dry powder form.” The oligos weigh only 3 micrograms, which is incredibly small. This suggests that a vast amount of data can be stored in a tiny space.
It can “support over 300 reads under current technical standards.”
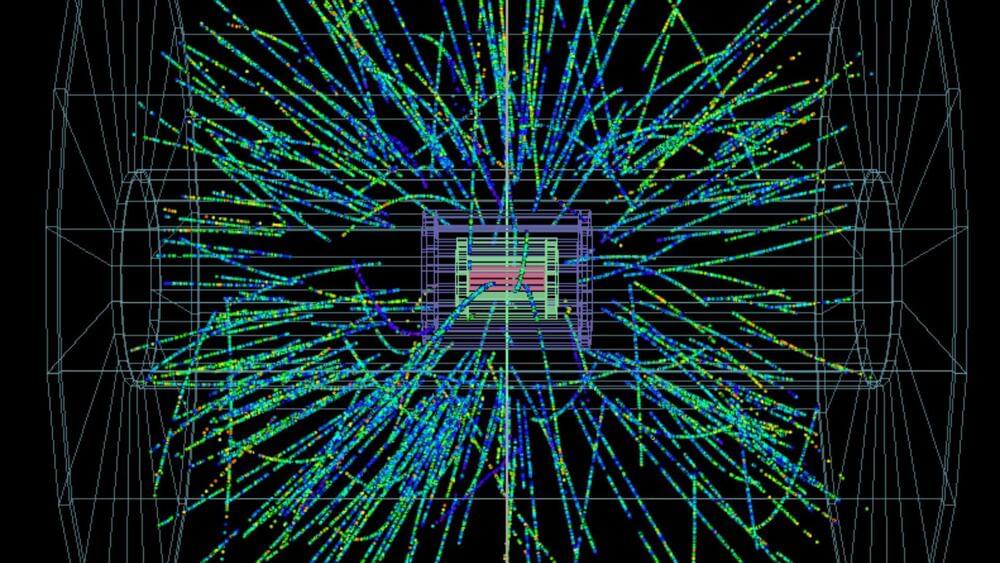
A theoretical analysis from researchers at Japan’s largest scientific research agency, RIKEN, suggests that intermediate energy heavy-ion collisions can give birth to the strongest electromagnetic fields ever observed.
Heavy ion collisions involve colliding large atomic nuclei at high velocities. Such collisions generate strong electric fields for a brief period, enabling scientists to study behaviors and phenomena that are otherwise remain hidden.

The same technique could also be applied to studies of brain damage, Ruetz said. “Neural stem cells in the subventricular zone are also in the business of repairing brain tissue damage from stroke or traumatic brain injury.”
The glucose transporter connection “is a hopeful finding,” Brunet said. For one, it suggests not only the possibility of designing pharmaceutical or genetic therapies to turn on new neuron growth in old or injured brains, but also the possibility of developing simpler behavioral interventions, such as a low carbohydrate diet that might adjust the amount of glucose taken up by old neural stem cells.
The researchers found other provocative pathways worthy of follow-up studies. Genes relating to primary cilia, parts of some brain cells that play a critical role in sensing and processing signals such as growth factors and neurotransmitters, also are associated with neural stem cell activation. This finding reassured the team that their methodology was effective, partly because unrelated previous work had already discovered associations between cilia organization and neural stem cell function. It is also exciting because the association with the new leads about glucose transmission could point toward alternative avenues of treatment that might engage both pathways, Brunet said.
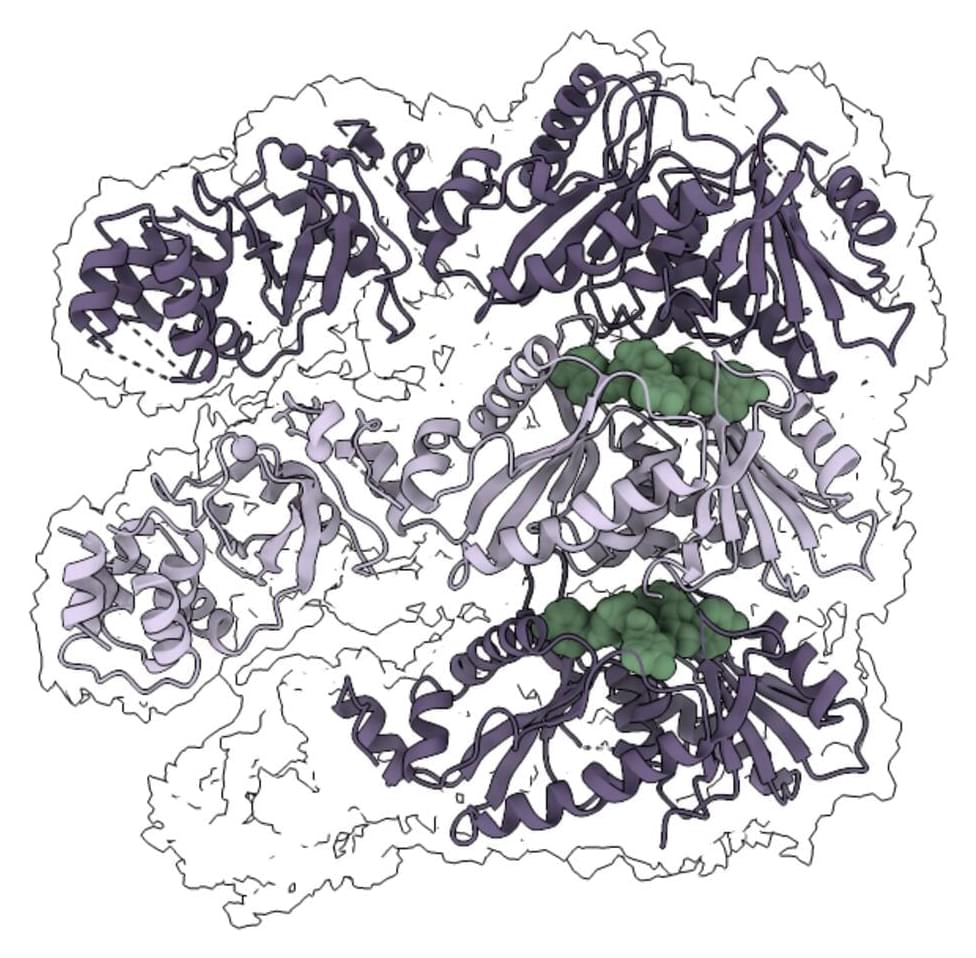
CRISPR-Cas systems help to protect bacteria from viruses. Several different types of CRISPR-Cas defense systems are found in bacteria, which differ in their composition and functions. Among them, the most studied proteins today are Cas9 and Cas12, also known as DNA or “gene scissors,” which have revolutionized the field of genome editing, enabling scientists to edit genomes and correct disease-causing mutations precisely.
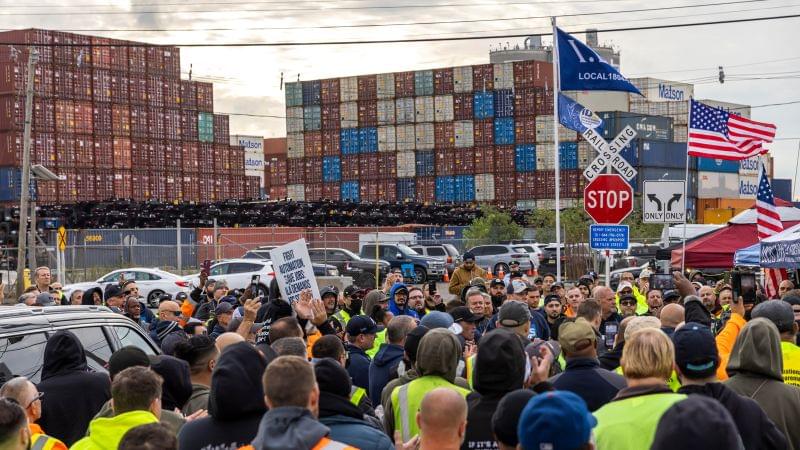

The dockworkers striking up and down the East Coast are, culturally and geographically, a world apart from the Hollywood actors and writers who staged a four-month walkout last year. But their protests share a common core principle: They don’t want bots taking their jobs.
It’s a fight you can expect to see playing out a lot more as advanced automation and AI creep into virtually every workforce.
Here’s the deal: The East Coast port strike is getting a lot of attention for its potential disruption to the economy — which is precisely the point. Longshore work can be grueling, and the people working at ports are vital to getting all of the stuff we want to buy onto store shelves. No dockworkers means no bananas (or whatever), which means no profits for the companies that produce and ship them.


In the ongoing journey to create and understand AI (artificial intelligence), a key challenge has been determining if and when a machine has achieved consciousness.
While early AI research focused on mimicking human behavior, modern advancements have revealed the limitations of traditional evaluations like the Turing Test.
As we push the boundaries of AI development, we must redefine how we measure machine intelligence, moving beyond surface-level interactions to explore deeper levels of awareness, creativity and self-consciousness.