Seven packages published on the Node Package Manager (npm) registry use the Adspect cloud-based service to separate researchers from potential victims and lead them to malicious locations.



The decades-old “finger” command is making a comeback„ with threat actors using the protocol to retrieve remote commands to execute on Windows devices.
In the past, people used the finger command to look up information about local and remote users on Unix and Linux systems via the Finger protocol, a command later added to Windows. While still supported, it’s rarely used today compared to its popularity decades ago.
When executed, the finger command returns basic information about a user, including their login name, name (if set in /etc/passwd), home directory, phone numbers, last seen, and other details.
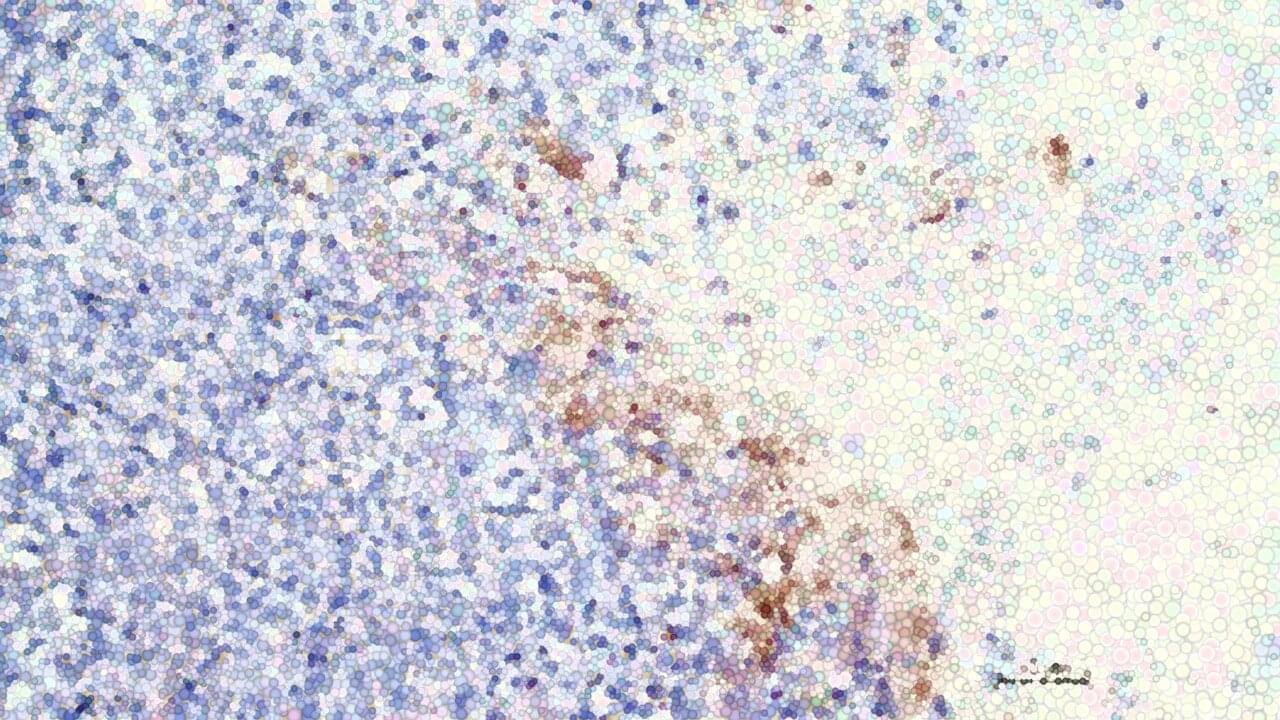
In a major step forward for cancer care, researchers at ChristianaCare’s Gene Editing Institute have shown that disabling the NRF2 gene with CRISPR technology can reverse chemotherapy resistance in lung cancer. The approach restores drug sensitivity and slows tumor growth. The findings are published in the journal Molecular Therapy Oncology.
This breakthrough stems from more than a decade of research by the Gene Editing Institute into the NRF2 gene, a known driver of treatment resistance. The results were consistent across multiple in vitro studies using human lung cancer cell lines and in vivo animal models.
“We’ve seen compelling evidence at every stage of research,” said Kelly Banas, Ph.D., lead author of the study and associate director of research at the Gene Editing Institute. “It’s a strong foundation for taking the next step toward clinical trials.”

University of Kentucky researchers have developed a new experimental model that could point the way toward more effective Alzheimer’s disease treatments by targeting one of the brain’s most important genes for risk and resilience.
The study, published in Nature Neuroscience, focuses on apolipoprotein E (APOE), a gene long known to play a major role in Alzheimer’s disease. The team created a first-of-its-kind mouse model that allows scientists to “flip a switch,” changing the high-risk version of the gene (APOE4) to the protective form (APOE2) in adult animals.

Designing quantum chips incorporates traditional microwave engineering in addition to advanced low-temperature physics. This makes a classical electromagnetic modeling tool like ARTEMIS, which was developed as part of the DOE’s Exascale Computing Project initiative, a natural choice for this type of modeling.
A large simulation for a tiny chip
Not every quantum chip simulation calls for so much computing capacity, but modeling the miniscule details of this tiny, extremely complex chip required nearly all of Perlmutter’s power. The researchers used almost all of its 7,168 NVIDIA GPUs over a period of 24 hours to capture the structure and function of a multi-layered chip measuring just 10 millimeters square and 0.3 millimeters thick, with etchings just one micron wide.