Humans like to think that being multicellular (and bigger) is a definite advantage, even though 80% of life on Earth consists of single-celled organisms—some thriving in conditions lethal to any beast.
In fact, why and how multicellular life evolved has long puzzled biologists. The first known instance of multicellularity was about 2.5 billion years ago, when marine cells (cyanobacteria) hooked up to form filamentous colonies. How this transition occurred and the benefits it accrued to the cells, though, is less than clear.
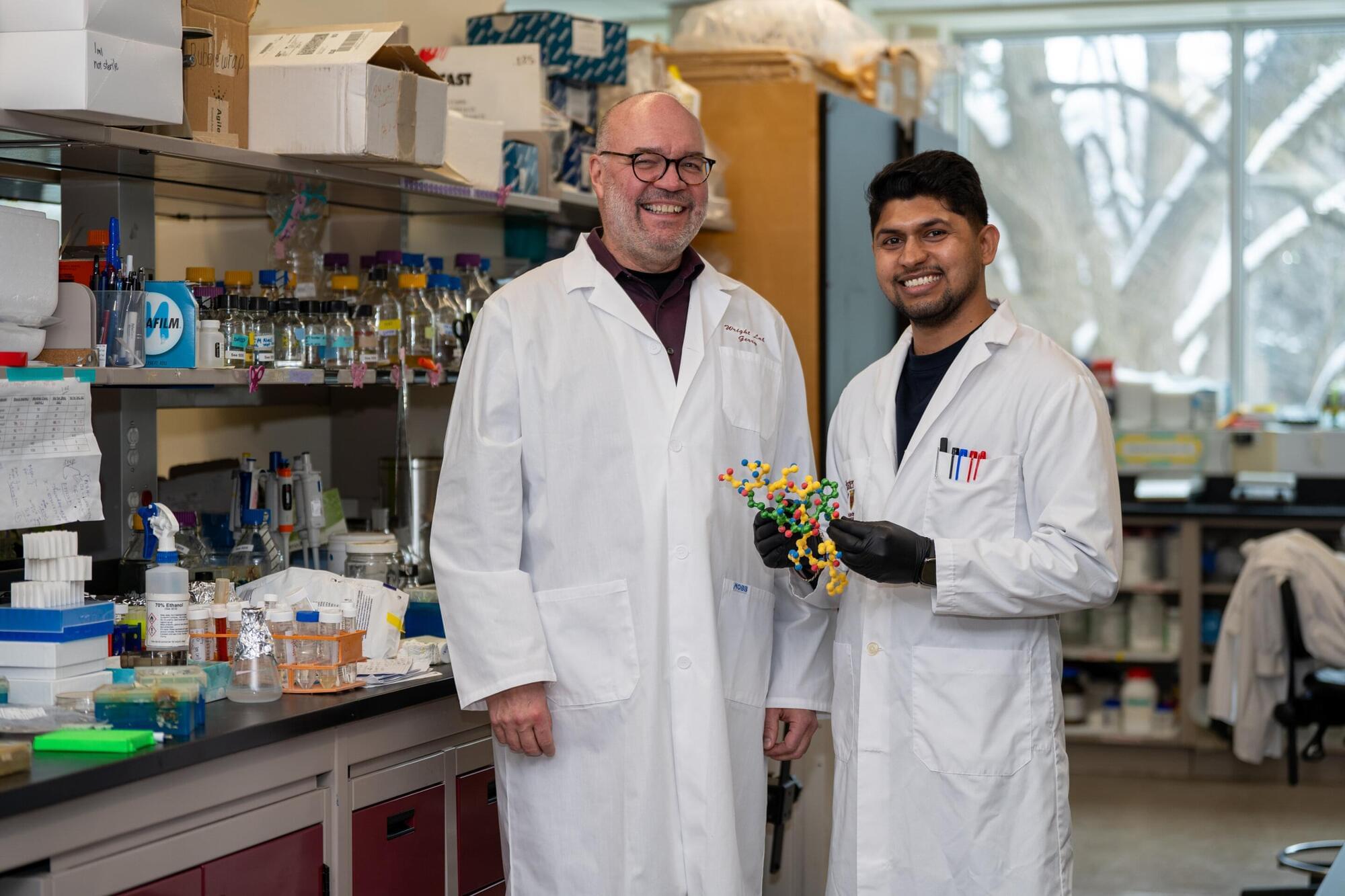
A study originating from the Marine Biological Laboratory (MBL) presents a striking example of cooperative organization among cells as a potential force in the evolution of multicellular life. Based on the fluid dynamics of cooperative feeding by Stentor, a relatively giant unicellular organism, the report is published in Nature Physics.