Circulating biomarkers are quickly becoming a crucial part of diagnosis and disease monitoring for physicians, researchers — and even some consumers.



MIT didn’t name the student in its statement Friday, but it did name the paper. That paper, by Aidan Toner-Rodgers, was covered by The Wall Street Journal and other media outlets.
In a press release, MIT said it “has no confidence in the provenance, reliability or validity of the data and has no confidence in the veracity of the research contained in the paper.”
The university said the author of the paper is no longer at MIT.

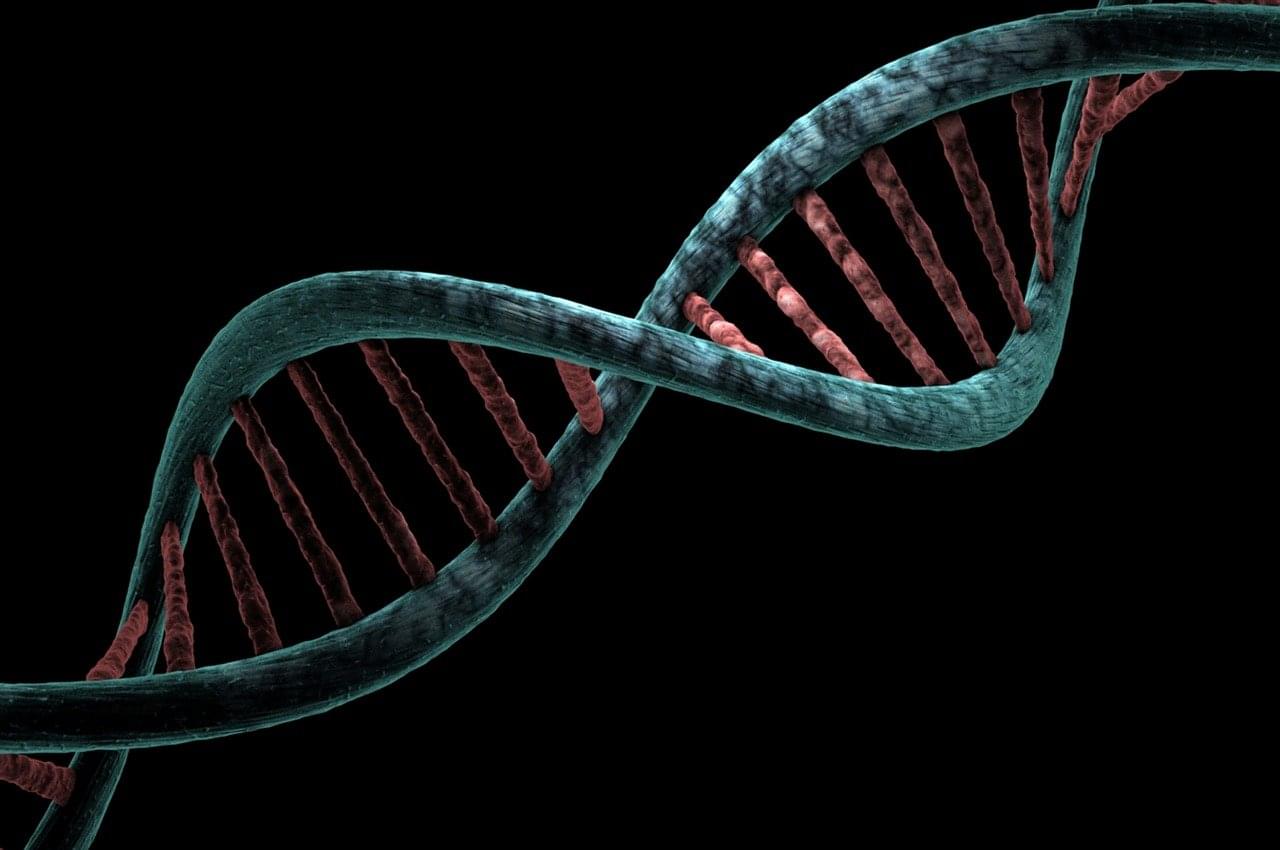
Inherited mutations in the gene BRCA2 significantly increase the risk of carriers to breast and ovarian cancers. BRCA2, a crucial player in the body’s DNA repair system, aids in repairing damaged DNA. This function is particularly intriguing as our cells constantly divide and replicate, passing on any genetic damage to newly developing cells.
Because of its significant role in maintaining genetic stability, BRCA2 belongs to a class of genes known as tumor suppressors. These genes code for proteins that control how often cells divide. However, when a tumor suppressor gene, such as BRCA2, undergoes a mutational change, the protein it codes for won’t function normally, resulting in uncontrolled cell division and, in some circumstances, cancer development.
BRCA2 predisposes carriers to cancer and research has shown that BRCA2-deficient tumors respond to therapies known as PARP inhibitors, which block the function of the poly ADP-ribose polymerase 1 (PARP1) protein. PARP1 becomes activated in tumors with BRCA2 mutations, resulting in the continued abnormal growth of damaged DNA.
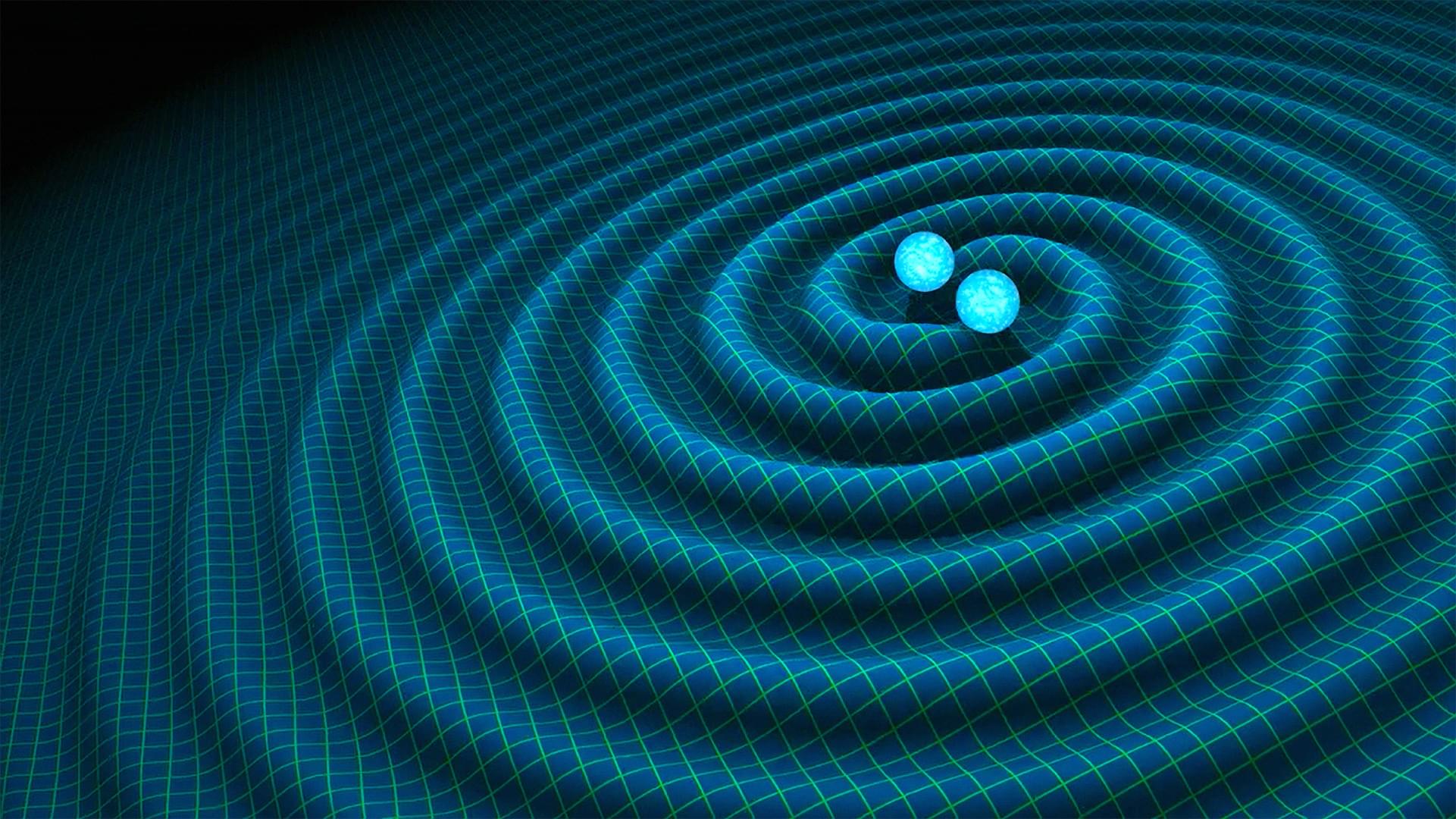
In the new study, however, these shapes appeared in calculations describing the energy radiated as gravitational waves when two black holes cruised past one another. This marks the first time they’ve appeared in a context that could, in principle, be tested through real-world experiments.
Mogull likens their emergence to switching from a magnifying glass to a microscope, revealing features and patterns previously undetectable. “The appearance of such structures sheds new light on the sorts of mathematical objects that nature is built from,” he said.
These findings are expected to significantly enhance future theoretical models that aim to predict gravitational wave signatures. Such improvements will be crucial as next-generation gravitational wave detectors — including the planned Laser Interferometer Space Antenna (LISA) and the Einstein Telescope in Europe — come online in the years ahead.
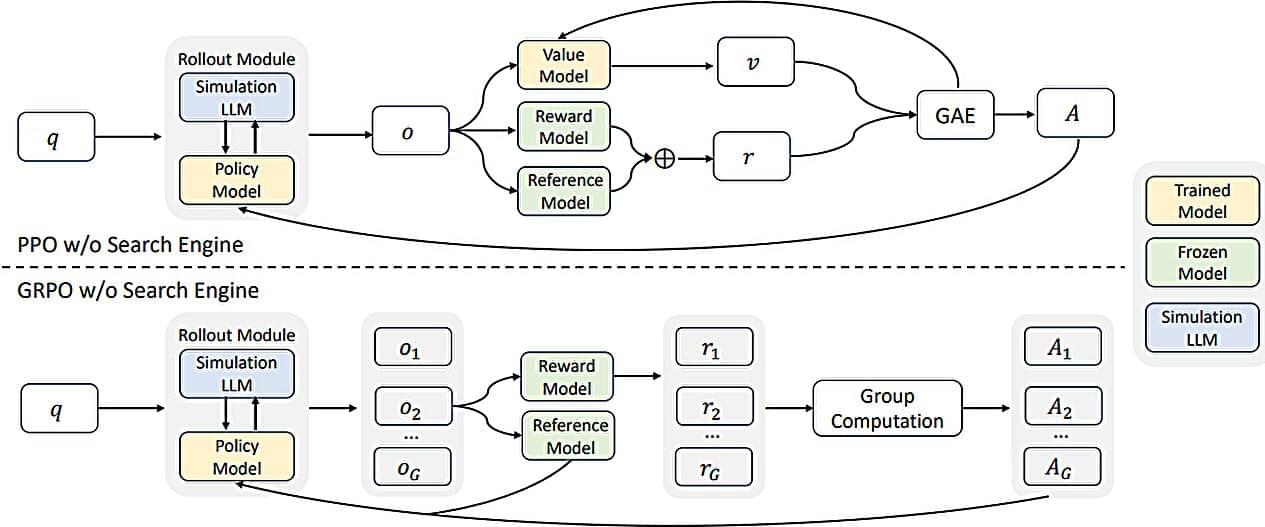
A team of AI researchers at the Alibaba Group’s Tongyi Lab, has debuted a new approach to training LLMs; one that costs much less than those now currently in use. Their paper is posted on the arXiv preprint server.
As LLMs such as ChatGPT have become mainstream, the resources and associated costs of running them have skyrocketed, forcing AI makers to look for ways to get the same or better results using other techniques. To this end, the team working at the Tongyi Lab has found a way to train LLMs in a new way that uses far fewer resources.
The idea behind ZeroSearch is to no longer use API calls to search engines to amass search results as a way to train an LLM. Their method instead uses simulated AI-generated documents to mimic the output from traditional search engines, such as Google.

White light-emitting diodes (LEDs), the semiconductor devices underpinning the functioning of countless lighting technologies on the market today, were first released to the public in 1996. Following their commercial debut, these devices have fueled significant advancements within the electronics and lighting industry, due to their remarkable energy efficiencies and extended lifespans.
Researchers at the University of Cambridge and ETH Zurich recently carried out a study aimed at re-tracing the development of white LEDs over the past three decades, as well as trends in their costs and innovations in other engineering fields that fueled their advancement. Their paper, published in Nature Energy, was part of a larger research project that investigated the factors driving innovation in the clean energy sector.
“As part of our research, we looked at three key technologies at the forefront of the ongoing energy transition: solar photovoltaics for energy generation, lithium-ion batteries for energy storage, and white LEDs for efficient energy use in lighting,” Michael P. Weinold, first author of the paper, told Tech Xplore.
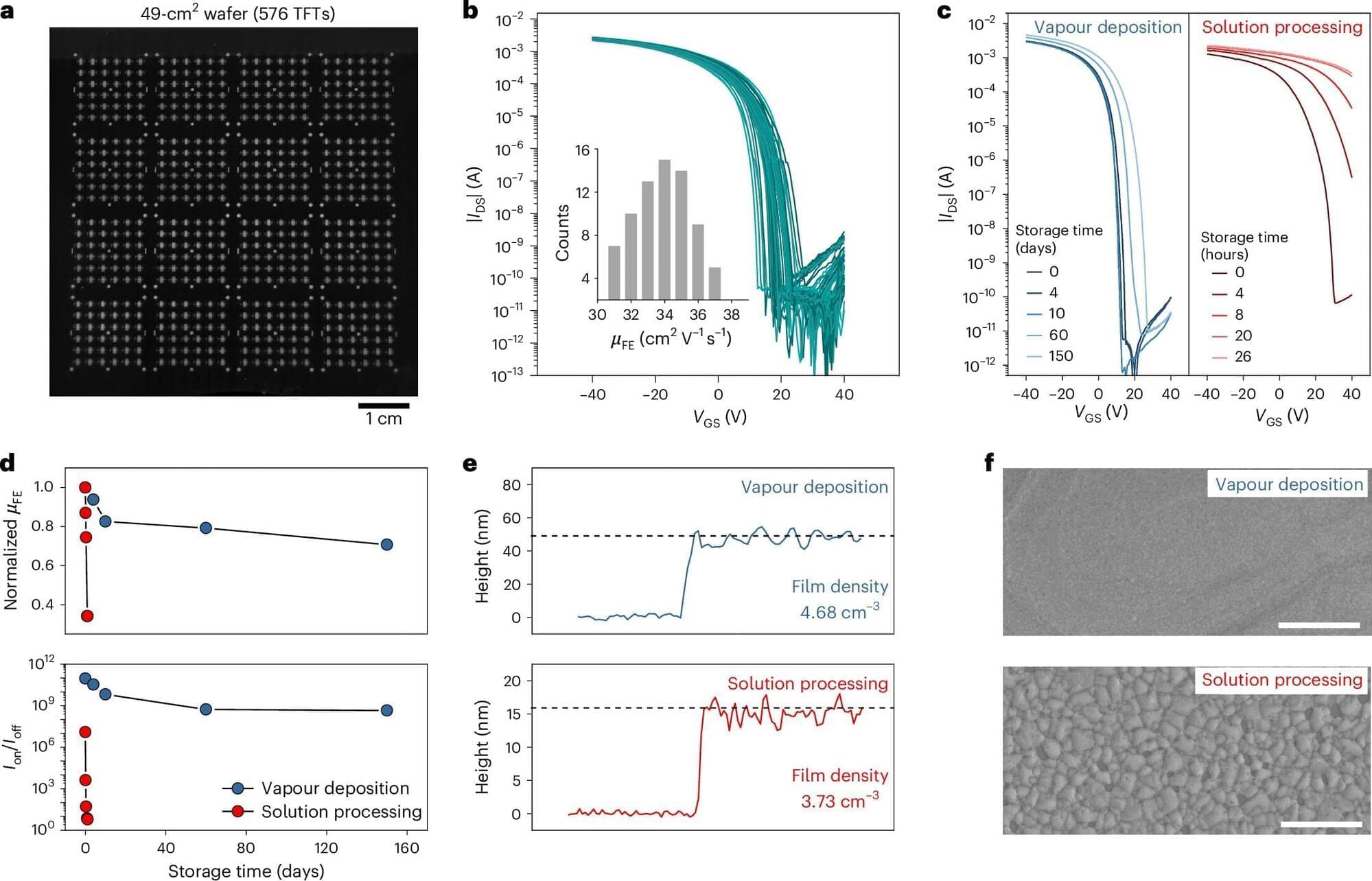
Tin-halide perovskites, a class of tin-based materials with a characteristic crystal structure that resembles that of the compound calcium titanate, could be promising alternatives to commonly used semiconductors. Past studies have explored the possibility of using these materials to fabricate p-channel thin-film transistors (TFTs), devices used to control and amplify the flow of charge carriers in electronics devices.
So far, however, the reliable fabrication and integration of thin-film perovskites into commercially available electronics has proved challenging. This is in part due to difficulties encountered when trying to produce uniform perovskite films with consistent electronic properties using scalable and industry-compatible methods.
Researchers at Pohang University of Science and Technology recently introduced a new promising strategy for the fabrication of highly performing TFTs based on tin-halide perovskites. Their approach, outlined in a paper published in Nature Electronics, relies on thermal evaporation and the use of lead chloride (PbCl2) as a reaction initiator.
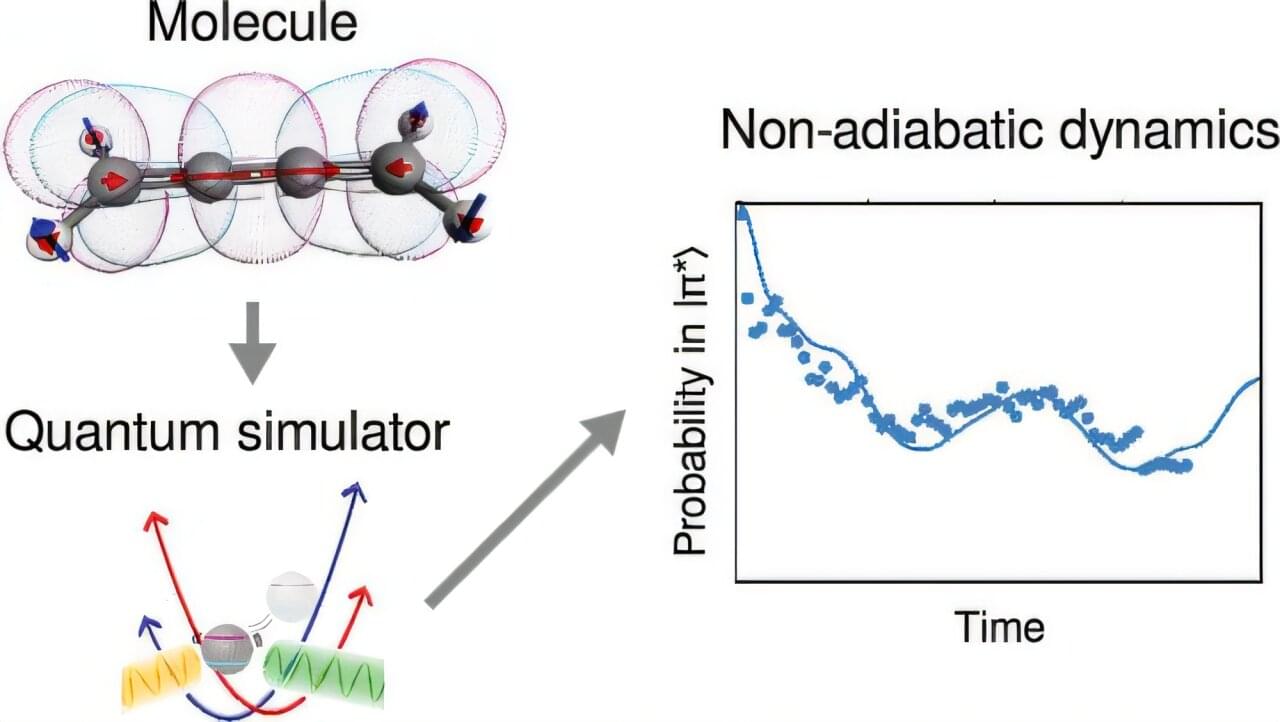
Researchers at the University of Sydney have successfully performed a quantum simulation of chemical dynamics with real molecules for the first time, marking a significant milestone in the application of quantum computing to chemistry and medicine.
Understanding in real time how atoms interact to form new compounds or interact with light has long been expected as a potential application of quantum technology. Now, quantum chemist Professor Ivan Kassal and Physics Horizon Fellow Dr. Tingrei Tan have shown it is possible using a quantum machine at the University of Sydney.
The innovative work leverages a novel, highly resource-efficient encoding scheme implemented on a trapped-ion quantum computer in the University of Sydney Nanoscience Hub, with implications that could help transform medicine, energy and materials science.