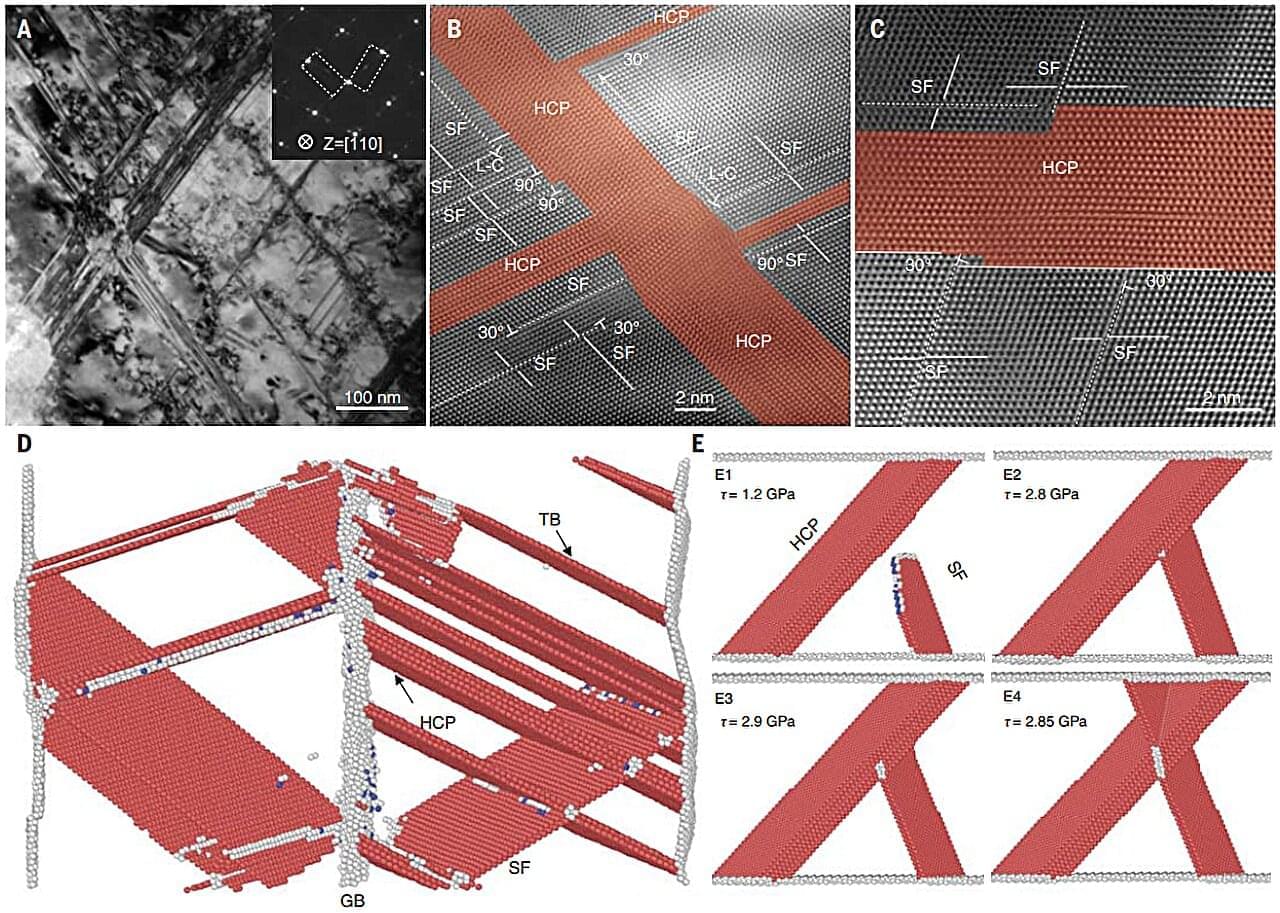
The immune system fights germs on the skin, in the tissues of the body, and in bodily fluids such as blood. It is made up of the innate (general) immune system and the adaptive (specialized) immune system. These two systems work closely together and take on different tasks.
The innate immune system is the body’s first line of defense against intruders. It responds in the same way to all germs and foreign substances, which is why it is sometimes referred to as the “non-specific” immune system. It acts very quickly – for instance, it makes sure that bacteria that have entered the skin through a small wound are detected and destroyed on the spot within a few hours. But the innate immune system can’t always stop germs from spreading.