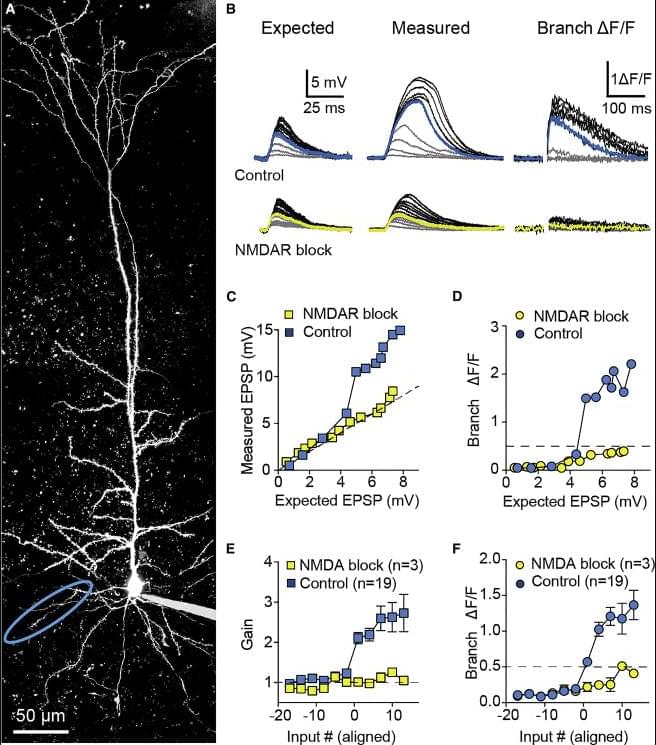
In this enlightening episode, we delve into groundbreaking research that challenges our understanding of the brain’s building blocks. Recent studies reveal that a single neuron possesses computational capabilities rivaling those of entire artificial neural networks, suggesting that each neuron may function as a complex processor in its own right.
This UPSC Podcast explores how learning in the brain is more complex than previously thought, revealing that synapses, the connections between neurons, don’t all follow the same rules. A recent study observed these tiny junctions in mice, discovering that their behavior depends on their location on a neuron’s branches called dendrites. Some synapses prioritize local connections, while others form longer circuits, indicating that different parts of a single neuron perform distinct computations, potentially explaining how the brain forms memories, including during processes like offline learning. This research offers a new perspective on how the brain encodes information and could potentially inspire more sophisticated AI methods.
Key Discussion Points:
Neuronal Complexity: Exploring how individual neurons can perform intricate computations, akin to multi-layered neural networks.
Quanta Magazine.
Dendritic Processing: Understanding the role of dendrites in enhancing a neuron’s computational power.
Quanta Magazine.
Implications for AI: Discussing how these findings could revolutionize artificial intelligence by inspiring more efficient neural network architectures.