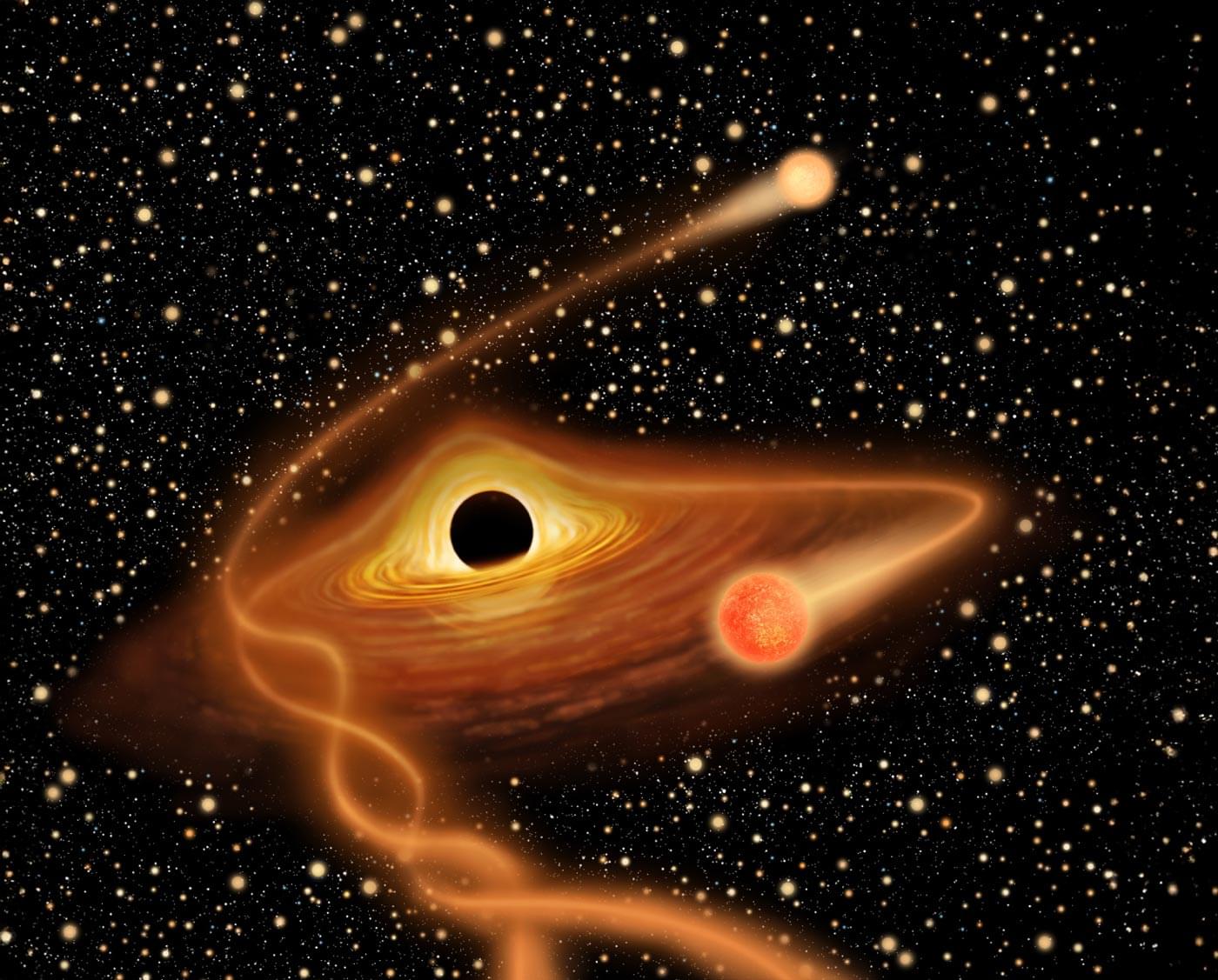
Scientists have uncovered the strongest evidence yet for the existence of elusive intermediate-mass black holes (IMBHs), long thought to be the missing link between stellar-mass and supermassive black holes. By tracking a hypervelocity star, J0731+3717, that appears to have been ejected from the