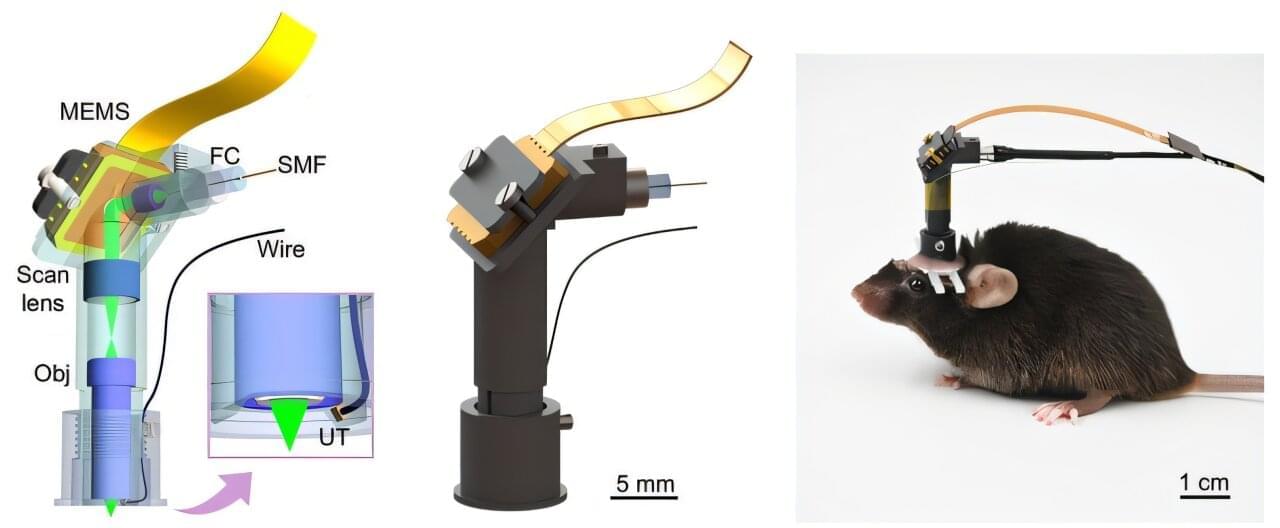
In a study published in Science Advances, a research team led by Prof. Liu Chengbo from the Shenzhen Institutes of Advanced Technology (SIAT) of the Chinese Academy of Sciences developed a 1.7-gram head-mounted microscope. This innovative device can simultaneously capture neural activity and cerebral hemodynamics in freely moving mice, providing a novel tool for exploring neurovascular coupling (NVC) in the brain and studying neurological disorders.
NVC represents the close temporal and regional relationship between neural activity and cerebral blood flow and oxygenation. When neural activity is initiated in a specific brain region, the metabolic demand within that region increases, leading to enhanced blood flow to supply greater amounts of oxygen and glucose, thus meeting the elevated metabolic needs of neurons. Conversely, if pathological changes hinder cerebral vessels’ capacity to provide sufficient oxygen and energy, the functional activity of the corresponding brain region will be significantly affected.
Conventional NVC imaging techniques face challenges in achieving simultaneous in vivo high spatiotemporal resolution of neuronal activity and cerebral blood flow. This makes it difficult to accurately capture the dynamic relationship between neural activity and local hemodynamic changes. In addition, most existing studies use head-fixed setups which do not reflect true neurovascular coupling during natural animal behaviors.