Biased agonism to treat diabetes and obesity.
Agonists of glucagon-like peptide-1 receptor (GLP-1R) and glucose-dependent insulinotropic polypeptide receptor (GIPR) have been used for diabetes and obesity treatment. Mechanism of action and signaling of these receptors are of paramount importance.
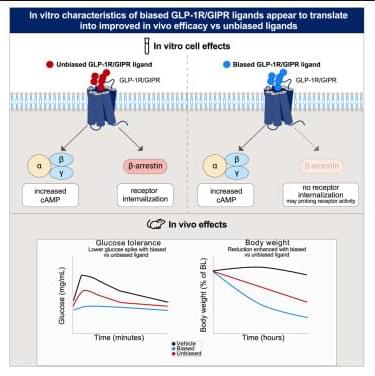
The researchers investigate the impact of biased cyclic AMP (cAMP) signaling with a dual GLP-1R/ GIPR agonist.
Biased GLP-1R and GIPR agonism with GLP-1R/GIPR agonist, CT-859 leads to better and prolonged glucose lowering, greater food intake reduction, and weight loss than unbiased agonism.
Biased GIPR agonism synergizes with GLP-1R on food intake suppression and weight loss. https://www.cell.com/cell-reports-medicine/fulltext/S2666…0229-0 https://sciencemission.com/Biased-agonism-of-GLP-1R-and-GIPR
Rodriguez et al. investigate the impact of biased signaling with a dual GLP-1R/GIPR agonist. Biased GLP-1R and GIPR agonism leads to better and prolonged glucose lowering, greater food intake reduction, and weight loss than unbiased agonism. Biased GIPR agonism synergizes with GLP-1R on food intake suppression and weight loss.