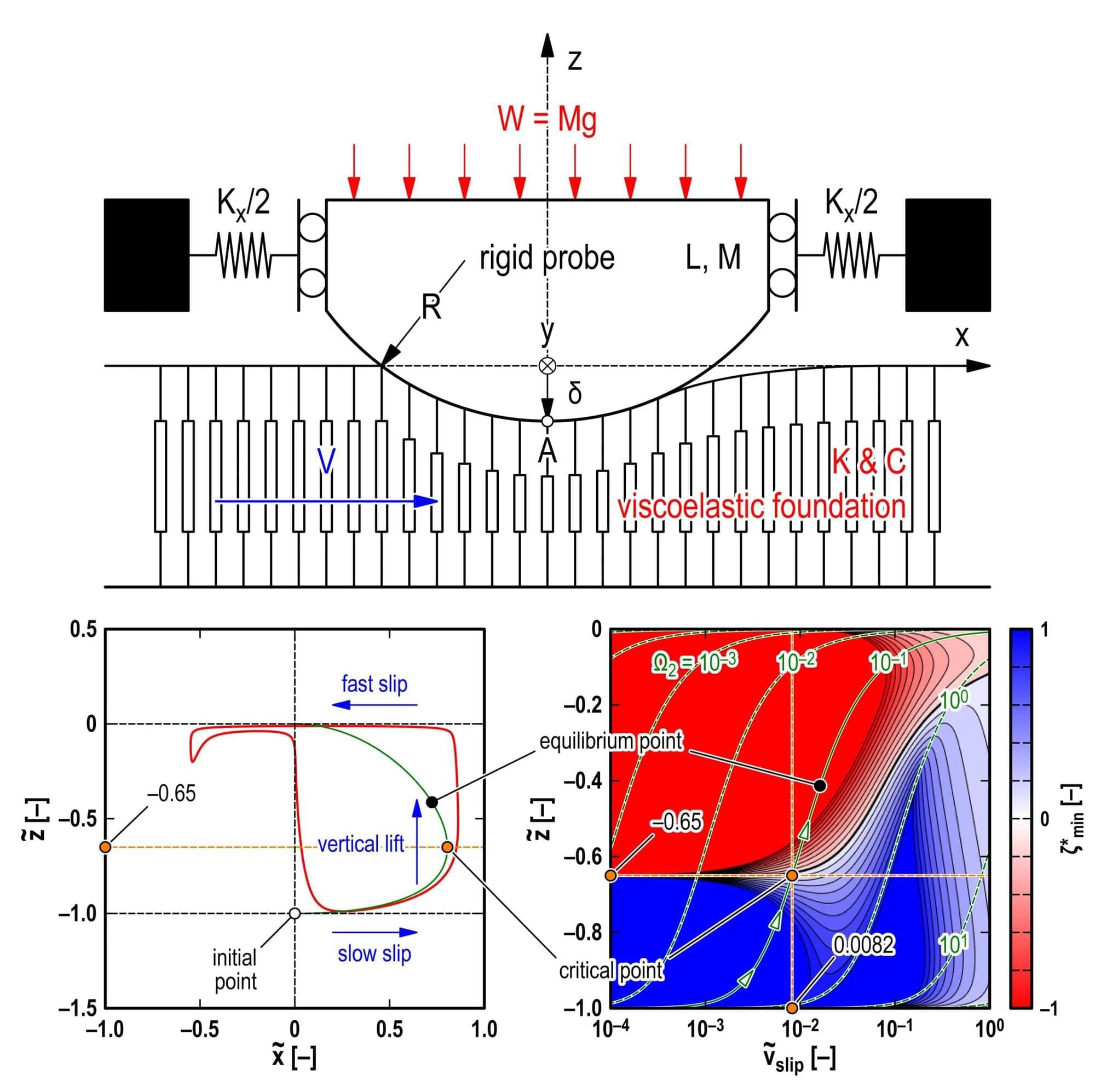
Atoms slip against one another, eventually sticking in various combinations. Tectonic plates do the same, sliding across each other until they stick in a stationary state. Everything from the tiniest particles to unfathomably large landmasses possesses this fundamental stick and slip characteristic, but only now are scientists beginning to understand the mechanics of the friction underpinning this property.
“The intermittent motion in sliding systems is termed stick-slip since the two surfaces in contact seem to repeat the stick and slip states. However, several precise measurements have found that extremely slow slip occurs in even apparently stick states before every stick-to-slip transition,” said Toshiki Watanabe, doctoral student in Yokohama National University’s Graduate School of Environmental and Information Sciences, who recently co-authored a paper describing a new model to explain the puzzling switch.
“This strange phenomenon, termed the static friction paradox, has remained an unsolved problem for decades.”