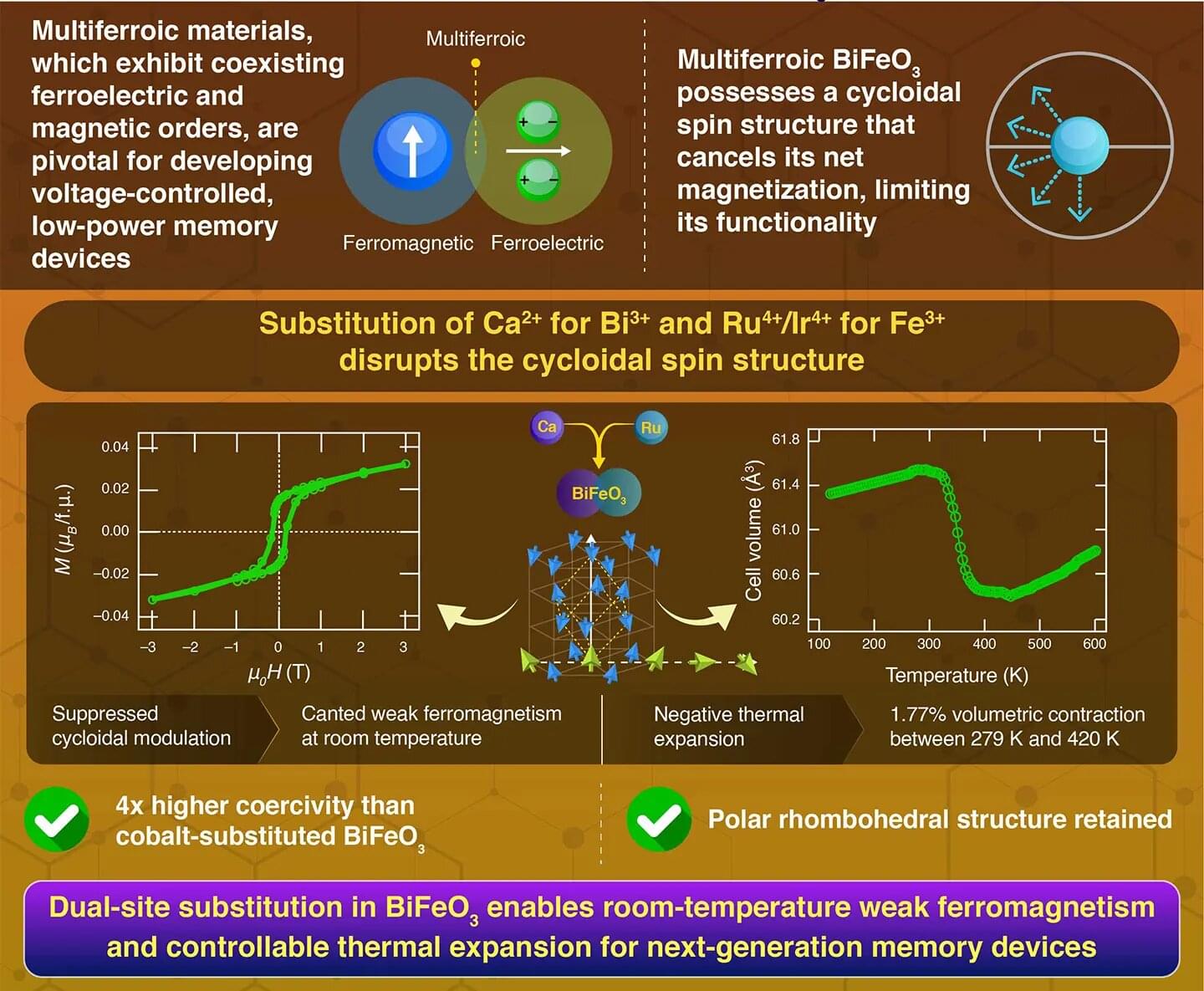
Using a dual-cation substitution approach, researchers at Science Tokyo introduced ferromagnetism into bismuth ferrite, a well-known and promising multiferroic material for next-generation memory technologies. By replacing ions at both the bismuth and iron sites with calcium ions and heavier elements, they modified the spin structure and achieved ferromagnetism at room temperature. Additionally, negative thermal expansion was observed. This ability to engineer magnetism and thermal expansion in a multiferroic material aids in realizing future memory devices.
Multiferroic materials, which show both ferroelectricity and ferromagnetism, hold strong potential for use in low-power memory devices where information can be written electrically and read magnetically. Among these materials, bismuth ferrite (BiFeO3) is one of the most widely studied because it combines ferroelectricity with antiferromagnetism at room temperature.
However, BiFeO3 naturally forms a cycloidal spin structure, which is a wave-like pattern of rotating spins. This pattern cancels out any net magnetization and makes the material difficult to use in magnetic devices.